Definition
Let X be a topological space and be the space of all continuous paths in X. Define the projection by . The topological complexity is the minimal number k such that
- there exists an open cover of ,
- for each , there exists a local section
In mathematics, topological complexity of a topological space X (also denoted by TC(X)) is a topological invariant closely connected to the motion planning problem[ further explanation needed ], introduced by Michael Farber in 2003.
Let X be a topological space and be the space of all continuous paths in X. Define the projection by . The topological complexity is the minimal number k such that
In the mathematical field of algebraic topology, the fundamental group of a topological space is the group of the equivalence classes under homotopy of the loops contained in the space. It records information about the basic shape, or holes, of the topological space. The fundamental group is the first and simplest homotopy group. The fundamental group is a homotopy invariant—topological spaces that are homotopy equivalent have isomorphic fundamental groups. The fundamental group of a topological space is denoted by .
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold is a generalization of tangent lines to curves in two-dimensional space and tangent planes to surfaces in three-dimensional space in higher dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a manifold at a point can be viewed as the space of possible velocities for a particle moving on the manifold.

In complex analysis, the residue theorem, sometimes called Cauchy's residue theorem, is a powerful tool to evaluate line integrals of analytic functions over closed curves; it can often be used to compute real integrals and infinite series as well. It generalizes the Cauchy integral theorem and Cauchy's integral formula. The residue theorem should not be confused with special cases of the generalized Stokes' theorem; however, the latter can be used as an ingredient of its proof.

In mathematics, the winding number or winding index of a closed curve in the plane around a given point is an integer representing the total number of times that the curve travels counterclockwise around the point, i.e., the curve's number of turns. For certain open plane curves, the number of turns may be a non-integer. The winding number depends on the orientation of the curve, and it is negative if the curve travels around the point clockwise.

In mathematics, a curve is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight.

A tangent bundle is the collection of all of the tangent spaces for all points on a manifold, structured in a way that it forms a new manifold itself. Formally, in differential geometry, the tangent bundle of a differentiable manifold is a manifold which assembles all the tangent vectors in . As a set, it is given by the disjoint union of the tangent spaces of . That is,

In mathematics, the beta function, also called the Euler integral of the first kind, is a special function that is closely related to the gamma function and to binomial coefficients. It is defined by the integral
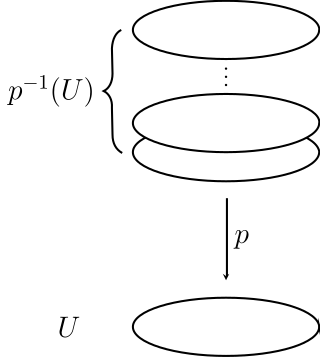
In topology, a covering or covering projection is a surjective map between topological spaces that, intuitively, locally acts like a projection of multiple copies of a space onto itself. In particular, coverings are special types of local homeomorphisms. If is a covering, is said to be a covering space or cover of , and is said to be the base of the covering, or simply the base. By abuse of terminology, and may sometimes be called covering spaces as well. Since coverings are local homeomorphisms, a covering space is a special kind of étale space.
In mathematics, a Lie algebroid is a vector bundle together with a Lie bracket on its space of sections and a vector bundle morphism , satisfying a Leibniz rule. A Lie algebroid can thus be thought of as a "many-object generalisation" of a Lie algebra.
In mathematics, a principal bundle is a mathematical object that formalizes some of the essential features of the Cartesian product of a space with a group . In the same way as with the Cartesian product, a principal bundle is equipped with
The notion of a fibration generalizes the notion of a fiber bundle and plays an important role in algebraic topology, a branch of mathematics.

In mathematics, theta functions are special functions of several complex variables. They show up in many topics, including Abelian varieties, moduli spaces, quadratic forms, and solitons. As Grassmann algebras, they appear in quantum field theory.
In mathematics and in theoretical physics, the Stone–von Neumann theorem refers to any one of a number of different formulations of the uniqueness of the canonical commutation relations between position and momentum operators. It is named after Marshall Stone and John von Neumann.
In differential geometry, a discipline within mathematics, a distribution on a manifold is an assignment of vector subspaces satisfying certain properties. In the most common situations, a distribution is asked to be a vector subbundle of the tangent bundle .
In mathematics, a local system on a topological space X is a tool from algebraic topology which interpolates between cohomology with coefficients in a fixed abelian group A, and general sheaf cohomology in which coefficients vary from point to point. Local coefficient systems were introduced by Norman Steenrod in 1943.
In mathematics, the Abel–Jacobi map is a construction of algebraic geometry which relates an algebraic curve to its Jacobian variety. In Riemannian geometry, it is a more general construction mapping a manifold to its Jacobi torus. The name derives from the theorem of Abel and Jacobi that two effective divisors are linearly equivalent if and only if they are indistinguishable under the Abel–Jacobi map.
In mathematics, Maass forms or Maass wave forms are studied in the theory of automorphic forms. Maass forms are complex-valued smooth functions of the upper half plane, which transform in a similar way under the operation of a discrete subgroup of as modular forms. They are eigenforms of the hyperbolic Laplace operator defined on and satisfy certain growth conditions at the cusps of a fundamental domain of . In contrast to modular forms, Maass forms need not be holomorphic. They were studied first by Hans Maass in 1949.
In mathematics, a unit sphere is a sphere of unit radius: the set of points at Euclidean distance 1 from some center point in three-dimensional space. More generally, the unit -sphere is an -sphere of unit radius in -dimensional Euclidean space; the unit circle is a special case, the unit -sphere in the plane. An (open) unit ball is the region inside of a unit sphere, the set of points of distance less than 1 from the center.
In mathematics, the Weil–Brezin map, named after André Weil and Jonathan Brezin, is a unitary transformation that maps a Schwartz function on the real line to a smooth function on the Heisenberg manifold. The Weil–Brezin map gives a geometric interpretation of the Fourier transform, the Plancherel theorem and the Poisson summation formula. The image of Gaussian functions under the Weil–Brezin map are nil-theta functions, which are related to theta functions. The Weil–Brezin map is sometimes referred to as the Zak transform, which is widely applied in the field of physics and signal processing; however, the Weil–Brezin Map is defined via Heisenberg group geometrically, whereas there is no direct geometric or group theoretic interpretation from the Zak transform.

In mathematics, a configuration space is a construction closely related to state spaces or phase spaces in physics. In physics, these are used to describe the state of a whole system as a single point in a high-dimensional space. In mathematics, they are used to describe assignments of a collection of points to positions in a topological space. More specifically, configuration spaces in mathematics are particular examples of configuration spaces in physics in the particular case of several non-colliding particles.