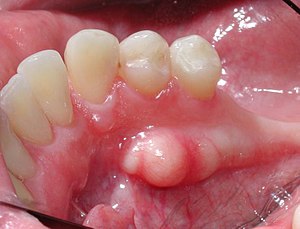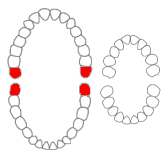
The third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is the most posterior of the three molars in each quadrant of the human dentition. The age at which wisdom teeth come through (erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, one in each of the four quadrants, but it is possible to have none, fewer, or more, in which case the extras are called supernumerary teeth. Wisdom teeth may become stuck (impacted) against other teeth if there is not enough space for them to come through normally. Impacted wisdom teeth are still sometimes removed for orthodontic treatment, believing that they move the other teeth and cause crowding, though this is not held anymore as true.

Alveolar osteitis, also known as dry socket, is inflammation of the alveolar bone. Classically, this occurs as a postoperative complication of tooth extraction.

Prognathism, also called Habsburg chin, Habsburg's chin, Habsburg jaw or Habsburg's jaw primarily in the context of its prevalence amongst members of the House of Habsburg, is a positional relationship of the mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull. In general dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and orthodontics, this is assessed clinically or radiographically (cephalometrics). The word prognathism derives from Greek πρό and γνάθος. One or more types of prognathism can result in the common condition of malocclusion, in which an individual's top teeth and lower teeth do not align properly.

Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply, jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, and other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be treated easily with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries, and malproportions where correction may be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self-esteem.

In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from occlusion, and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.

A dental extraction is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed. In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.
Mandibular means "related to the mandible ". Terms containing "mandibular" include:
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor/dentist has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders and facial pain, taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth".

In human anatomy, the mandibular canal is a canal within the mandible that contains the inferior alveolar nerve, inferior alveolar artery, and inferior alveolar vein. It runs obliquely downward and forward in the ramus, and then horizontally forward in the body, where it is placed under the alveoli and communicates with them by small openings.
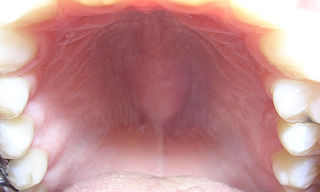
A torus palatinus, or palatal torus, is a bony protrusion on the palate. Palatal tori are usually present on the midline of the hard palate. Most palatal tori are less than 2 cm in diameter, but their size can change throughout life.

A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the reduced enamel epithelium and encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth at the cemento-enamel junction. Fluid is accumulated between reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth.

A buccal exostosis is an exostosis on the buccal surface of the alveolar ridge of the maxilla or mandible. More commonly seen in the maxilla than the mandible, buccal exostoses are considered to be site specific. Existing as asymptomatic bony nodules, buccal exostoses don’t usually present until adult life, and some consider buccal exostoses to be a variation of normal anatomy rather than disease. Bone is thought to become hyperplastic, consisting of mature cortical and trabecular bone with a smooth outer surface. They are less common when compared with mandibular tori.

The Stafne defect is a depression of the mandible, most commonly located on the lingual surface. The Stafne defect is thought to be a normal anatomical variant, as the depression is created by ectopic salivary gland tissue associated with the submandibular gland and does not represent a pathologic lesion as such. This cavity is commonly observed on panoramic radiograph.

Cementoma is an odontogenic tumor of cementum. It is usually observed as a benign spherical mass of hard tissue fused to the root of a tooth. It is found most commonly in the mandible in the region of the lower molar teeth, occurring between the ages of 8 and 30 in both sexes with equal frequency. It causes distortion of surrounding areas but is usually a painless growth, at least initially. Considerable thickening of the cementum can often be observed. A periapical form is also recognized. Cementoma is not exclusive to the mandible as it can infrequently occur in the maxilla and other parts of the body such as the long bones.
Oral and maxillofacial pathology refers to the diseases of the mouth, jaws and related structures such as salivary glands, temporomandibular joints, facial muscles and perioral skin. The mouth is an important organ with many different functions. It is also prone to a variety of medical and dental disorders.
A jaw abnormality is a disorder in the formation, shape and/or size of the jaw. In general abnormalities arise within the jaw when there is a disturbance or fault in the fusion of the mandibular processes. The mandible in particular has the most differential typical growth anomalies than any other bone in the human skeleton. This is due to variants in the complex symmetrical growth pattern which formulates the mandible.
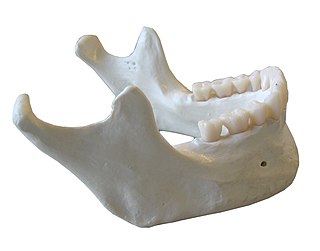
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the bottom skeleton that makes up the lower half of the mouth in jawed vertebrates. In arthropods, the largest pair of appendages of their mouthparts are also named mandibles.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.

Pulp stones are nodular, calcified masses appearing in either or both the coronal and root portion of the pulp organ in teeth. Pulp stones are not painful unless they impinge on nerves.

An oral torus is a lesion made of compact bone and occurs along the palate or the mandible inside the mouth. The palatal torus or torus palatinus occurs along the palate, close to the midline, whereas the mandibular torus or torus mandibularis occur along the lingual side of the mandible.