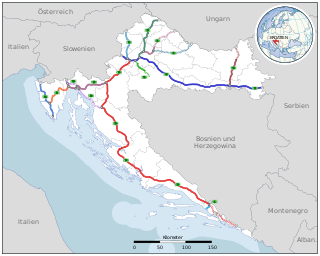
Transport in Croatia relies on several main modes, including transport by car, train, ship and plane. Road transport incorporates a comprehensive network of state, county and local routes augmented by a network of highways for long-distance travelling. Water transport can be divided into sea, based on the ports of Rijeka, Ploče, Split and Zadar, and river transport, based on Sava, Danube and, to a lesser extent, Drava. Croatia has 9 international airports and several airlines, of which the most notable are Croatia Airlines and Trade Air. Rail network is fairly developed but regarding inter-city transport, bus tends to be far more common than the rail.

Light rail transit (LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit characterized by a combination of tram and rapid transit features. While its rolling stock is similar to a traditional tram, it operates at a higher capacity and speed, and often on an exclusive right-of-way. In many cities, light rail transit systems more closely resemble, and are therefore indistinguishable from, traditional underground or at-grade subways and heavy-rail metros.

The West Midlands Metro is a light-rail/tram system in the county of West Midlands, England. The network has 31 stops with a total of 14 miles (23 km) track; it currently consists of a single route, Line 1, which operates between the cities of Birmingham and Wolverhampton via the towns of Bilston, West Bromwich and Wednesbury, on a mixture of former railway lines and urban on-street running. The system is owned by the public body Transport for West Midlands, and operated through Midland Metro Ltd, a company wholly owned by the West Midlands Combined Authority.

Rijeka is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a population of 108,622 inhabitants. Historically, because of its strategic position and its excellent deep-water port, the city was fiercely contested, especially between the Holy Roman Empire, Italy and Croatia, changing rulers and demographics many times over centuries. According to the 2011 census data, the majority of its citizens are Croats, along with small numbers of Serbs, Bosniaks and Italians.

The Berlin tramway is the main tram system in Berlin, Germany. It is one of the oldest tram networks in the world having its origins in 1865 and is operated by Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe (BVG), which was founded in 1929. It is notable for being the third-largest tram system in the world, after Melbourne and St. Petersburg. Berlin's tram system is made up of 22 lines that operate across a standard gauge network, with almost 800 stops and measuring almost 190 kilometres (120 mi) in route length and 430 kilometres (270 mi) in line length. Nine of the lines, called Metrotram, operate 24 hours a day and are identified with the letter "M" before their number; the other thirteen lines are regular city tram lines and are identified by just a line number.

The Brussels tramway network is a tram system serving a large part of the Brussels-Capital Region of Belgium. It is the 16th largest tram system in the world by route length, in 2017 providing 149.1 million journeys over routes 140.6 km (87.4 mi) in length. In 2018, it consisted of 18 tram lines. Brussels trams are operated by STIB/MIVB, the local public transport company.

The Helsinki tram network forms part of the Helsinki public transport system organised by Helsinki Regional Transport Authority and operated by Metropolitan Area Transport Ltd in the Finnish capital city of Helsinki. The trams are the main means of transport in the city centre. 56.7 million trips were made in 2013. The Helsinki system is one of the oldest electrified tram networks in the world.

Europe has an extensive number of tramway networks. Some of these networks have been upgraded to light rail standards, called Stadtbahn in Germany, premetros in Belgium, sneltram in the Netherlands, elétrico in Portugal and fast trams in some other countries.

The Gråkallen Line is an 8.8-kilometre (5.5 mi) suburban tram line located in Trondheim, Norway. As the only remaining part of the Trondheim Tramway, it runs from the city centre at St. Olav's Gate, via the suburban area Byåsen to Lian. It is designated Line 9, and is served by six Class 8 articulated trams. After the closure of the Arkhangelsk tramway in 2004, it became the world's northernmost tramway system.

Doncaster Corporation Tramways was an electric tramway network serving the town of Doncaster, England. It was authorised in 1899, and the first route to Bentley opened in 1902. This remained separated from the rest of the system until North Bridge was built to carry traffic over the Great Northern Railway main line to Edinburgh. Soon afterwards, deep mining of coal began in the area, and several extensions to the system were made between 1913 and 1916 to serve new communities which developed around the pit heads. The Racecourse route was unusual, in that it had balloon loops at both ends to enable almost continuous running on race days, a feature that was not common in England, and only found favour in Europe in the 1950s and 1960s.

The Kingston upon Hull tramway network was a network of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge tram lines following the five main roads radially out of the city centre of Kingston upon Hull, East Riding of Yorkshire, England. Two of these lines went west, and two east. The fifth went to the north, and branched to include extra lines serving suburban areas. Additionally a short line linked the city centre to the Corporation Pier where a ferry crossed the Humber Estuary to New Holland, Lincolnshire.

The Turku tramway network was the first—and until the 2021 opening of Tampere Light Rail, second to last—tram system to be operated in Finland. It was operated as horse tramway from 1890 until 1892, and as an electrified tramway from 1908 until 1972. Prior to 1919 the tram system was owned by private interests, and from that year onwards by the City of Turku until closure of the system.

The Frankfurt am Main tramway network is a network of tramways forming a major part of the public transport system in Frankfurt am Main, a city in the federal state of Hesse, Germany.

Between 1901 and 1949 Manchester Corporation Tramways was the municipal operator of electric tram services in Manchester, England. At its peak in 1928, the organisation carried 328 million passengers on 953 trams, via 46 routes, along 292 miles (470 km) of track.

The Belgrade tram system is a 1000 mm gauge network that in 2021 had 12 routes running on 43.5 kilometres (27.0 mi) of track in the city of Belgrade, Serbia. It is operated with 231 trams, including ČKD Tatra KT4, CAF Urbos, and Duewag Be 4/6 trams. The first tram line was introduced on 14 October 1892. In the late 2000s, complete reconstruction of the system commenced.

Trams no longer operate in Hobart, the capital of the Australian state of Tasmania, but the city once had an extensive and popular system that reached the majority of its suburbs. It was the first complete electric tram system in the Southern Hemisphere, and the only one in Australia to operate double-decker trams.

Public transport is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typically managed on a schedule, operated on established routes, and that charge a posted fee for each trip. There is no rigid definition of which kinds of transport are included, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams and passenger trains, rapid transit and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world.

The Bern tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Bern, the capital city of Switzerland. In operation since 1890, it presently has five lines, one of which incorporates the Bern–Worb Dorf railway.

The Karlsruhe tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Karlsruhe, a city in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany.

Autonomous Rail Rapid Transit (ART) is a lidar guided articulated bus system for urban passenger transport. Developed by CRRC Zhuzhou Institute Co Ltd, it was unveiled in Zhuzhou in the Hunan province on June 2, 2017. ART has been described as a combination between a bus and a tram - often called a "trackless tram". Its exterior is composed of individual fixed sections joined by articulated gangways, resembling a rubber-tyred tram.



























