
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes. Unlike a standard acoustic guitar, it uses one or more pickups to convert the vibration of its strings into electrical signals, which ultimately are reproduced as sound by loudspeakers. The sound is sometimes shaped or electronically altered to achieve different timbres or tonal qualities from that of an acoustic guitar via amplifier settings or knobs on the guitar. Often, this is done through the use of effects such as reverb, distortion and "overdrive"; the latter is considered to be a key element of electric blues guitar music and jazz, rock and heavy-metal guitar-playing. Designs also exist combining attributes of the electric and acoustic guitars: the semi-acoustic and acoustic-electric guitars.

The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted and typically has six or twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A guitar pick may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant hollow chamber on the guitar, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.
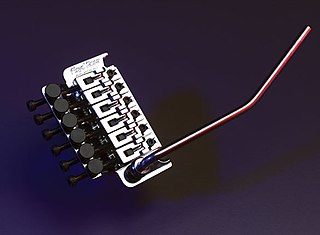
The Floyd Rose Locking Tremolo, or simply Floyd Rose, is a type of locking vibrato arm for a guitar. Floyd D. Rose invented the locking vibrato in 1976, the first of its kind, and it is now manufactured by a company of the same name. The Floyd Rose gained popularity in the 1980s through guitarists like Eddie Van Halen, Neal Schon, Brad Gillis, Joe Satriani, Steve Vai, and Alex Lifeson, who used its ability to stay in tune even with extreme changes in pitch. Its tuning stability comes through the double-locking design that has been widely regarded as revolutionary; the design has been listed on Guitar World's "10 Most Earth Shaking Guitar Innovations" and Guitar Player's "101 Greatest Moments in Guitar History 1979–1983."

The Chapman Stick is an electric musical instrument devised by Emmett Chapman in the early 1970s. A member of the guitar family, the Chapman Stick usually has ten or twelve individually tuned strings and is used to play bass lines, melody lines, chords, or textures. Designed as a fully polyphonic chordal instrument, it can also cover several of these musical parts simultaneously.
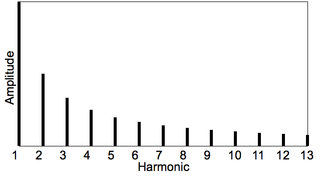
In music, inharmonicity is the degree to which the frequencies of overtones depart from whole multiples of the fundamental frequency.

Michael Alden Hedges was an American acoustic guitarist and songwriter. He was known as a virtuoso who used unorthodox playing techniques, and much of his output was classified as new age music. Hedges died in an auto accident, and won a posthumous Grammy Award for his album Oracle.
The Fender Stratocaster, colloquially known as the Strat, is a model of electric guitar designed between 1952 and 1954 by Leo Fender, Bill Carson, George Fullerton, and Freddie Tavares. The Fender Musical Instruments Corporation has continuously manufactured the Stratocaster since 1954. It is a double-cutaway guitar, with an extended top "horn" shape for balance. "Stratocaster" and "Strat" are trademark terms belonging to Fender. Guitars that duplicate the Stratocaster by other manufacturers are sometimes called S-Type or ST-type guitars. Many prominent rock musicians have been associated with the Stratocaster for use in studio recording and live performances, most notably Eric Clapton, Buddy Holly, David Gilmour, Mark Knopfler, Jimi Hendrix, Stevie Ray Vaughan, John Frusciante, Jeff Beck and George Harrison.

A machine head is a geared apparatus for tuning stringed musical instruments by adjusting string tension. Machine heads are used on mandolins, guitars, double basses and others, and are usually located on the instrument's headstock. Other names for guitar tuners include pegs, gears, machines, cranks, knobs, tensioners and tighteners.
A vibrato system on a guitar is a mechanical device used to temporarily change the pitch of the strings. It adds vibrato to the sound by changing the tension of the strings, typically at the bridge or tailpiece of an electric guitar using a controlling lever, which is alternately referred to as a whammy bar, vibrato bar, or tremolo arm. The lever enables the player to quickly and temporarily vary the tension and sometimes length of the strings, changing the pitch to create a vibrato, portamento, or pitch bend effect. Instruments without a vibrato have other bridge and tailpiece systems.

EMG, Inc. is the current legal name of an American company based in Santa Rosa, California that manufactures guitar pickups and EQ accessories. Among guitar and bass accessories, the company sells active humbucker pickups, such as the EMG 81, the EMG 85, the EMG 60, and the EMG 89. They also produce passive pickups such as the EMG-HZ series, which include SRO-OC1's and SC Sets. There is also a series geared towards a more traditional and passive sound known as the X series.
Steinberger is a series of distinctive electric guitars and bass guitars, designed and originally manufactured by Ned Steinberger. The name "Steinberger" can be used to refer to either the instruments themselves or the company that originally produced them. Although the name has been applied to a variety of instruments, it is primarily associated with a minimalist "headless" design of electric basses and guitars.

Floyd Rose SpeedLoader is a floating guitar bridge based on the Floyd Rose Original. In development since 1991, it was introduced to the public in 2003. This tremolo was developed in San Diego CA at AJ manufacturing by tool makers Jerry Morhman, Richard J Price, Steve Lamms, and Kerry L Stottlemyer under the direct guidance of Floyd Rose himself. With Richard J Price doing the majority of the design work and machining of the prototypes. Over 3000 hours and $150,000 were spent in developing this new ground breaking tremolo system and the first working unit on a guitar body. It inherited the locking floating bridge principle from the original version, but improved usability and diminished most of disadvantages that the Floyd Rose Original was criticized for, while adding the inconvenience of needing special-purpose strings. The Floyd Rose SpeedLoader is available in Tremolo, Fixed Bridge, and Convergent Tuning forms. However, the issues with strings became more apparent, as the specially made strings for the Speedloader were discontinued due to quality control issues. With no strings currently being manufactured, there is no way to properly string and set up any guitar with the Floyd Rose Speedloader. Customers have voiced their discontent with Floyd Rose for a lack of development of any parts that could remedy the situation.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to guitars:
Finger vibrato is vibrato produced on a string instrument by cyclic hand movements. Despite the name, normally the entire hand moves, and sometimes the entire upper arm. It can also refer to vibrato on some woodwind instruments, achieved by lowering one or more fingers over one of the uncovered holes in a trill-like manner. This flattens the note periodically creating the vibrato.
The Jackson Rhoads is a model of electric guitar, originally commissioned by guitarist Randy Rhoads and produced by Jackson Guitars.
The Epiphone Sheraton is a thinline semi-hollow body electric guitar. Though the Sheraton and all its variations were introduced under the ownership of the Gibson Guitar Corporation, Epiphone is the exclusive manufacturer.

Each bass guitar tuning assigns pitches to the strings of an electric bass. Because pitches are associated with notes, bass-guitar tunings assign open notes to open strings. There are several techniques for accurately tuning the strings of an electric bass. Bass method or lesson books introduce one or more tuning techniques, such as:

A bridge is a device that supports the strings on a stringed musical instrument and transmits the vibration of those strings to another structural component of the instrument—typically a soundboard, such as the top of a guitar or violin—which transfers the sound to the surrounding air. Depending on the instrument, the bridge may be made of carved wood, metal or other materials. The bridge supports the strings and holds them over the body of the instrument under tension.

The Peavey EVH Wolfgang guitar series is a collaboration between guitarist Eddie Van Halen and Hartley Peavey's company, Peavey Electronics. The EVH stands for "Eddie Van Halen" while Wolfgang is the name of Eddie Van Halen's son.

The EVH Wolfgang is an electric guitar manufactured by Eddie Van Halen's company, EVH, which is owned by Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. The Wolfgang is named after Van Halen's son Wolfgang Van Halen, as well as classical composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.













