
Smart growth is an urban planning and transportation theory that concentrates growth in compact walkable urban centers to avoid sprawl. It also advocates compact, transit-oriented, walkable, bicycle-friendly land use, including neighborhood schools, complete streets, and mixed-use development with a range of housing choices. The term "smart growth" is particularly used in North America. In Europe and particularly the UK, the terms "compact city", "urban densification" or "urban intensification" have often been used to describe similar concepts, which have influenced government planning policies in the UK, the Netherlands and several other European countries.

New Urbanism is an urban design movement that promotes environmentally friendly habits by creating walkable neighbourhoods containing a wide range of housing and job types. It arose in the United States in the early 1980s, and has gradually influenced many aspects of real estate development, urban planning, and municipal land-use strategies. New Urbanism attempts to address the ills associated with urban sprawl and post-Second World War suburban development.
Urban studies is the diverse range of disciplines and approaches to the study of all aspects of cities, their suburbs, and other urban areas. This includes among others: urban economics, urban planning, urban ecology, urban transportation systems, urban politics, sociology and urban social relations. This can be contrasted with the study of rural areas and rural lifestyles.

Urban sprawl is defined as "the spreading of urban developments on undeveloped land near a more or less densely populated city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growth in many urban areas of housing, commercial development, and roads over large expanses of land, with little concern for very dense urban planning. Sometimes the urban areas described as the most "sprawling" are the most densely populated. In addition to describing a special form of urbanization, the term also relates to the social and environmental consequences associated with this development. In modern times some suburban areas described as "sprawl" have less detached housing and higher density than the nearby core city. Medieval suburbs suffered from the loss of protection of city walls, before the advent of industrial warfare. Modern disadvantages and costs include increased travel time, transport costs, pollution, and destruction of the countryside. The revenue for building and maintaining urban infrastructure in these areas are gained mostly through property and sales taxes. As most jobs in the US are now located in suburbs generating much of the revenue, although a lack of growth will require higher tax rates.

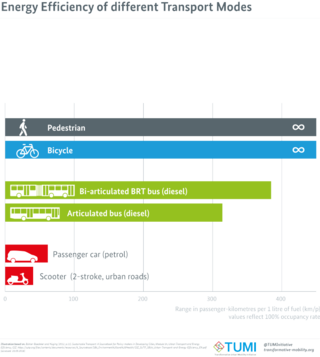
Sustainable transport refers to ways of transportation that are sustainable in terms of their social and environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used for road, water or air transport; the source of energy; and the infrastructure used to accommodate the transport. Transport operations and logistics as well as transit-oriented development are also involved in evaluation. Transportation sustainability is largely being measured by transportation system effectiveness and efficiency as well as the environmental and climate impacts of the system. Transport systems have significant impacts on the environment, accounting for between 20% and 25% of world energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. The majority of the emissions, almost 97%, came from direct burning of fossil fuels. In 2019, about 95% of the fuel came from fossil sources. The main source of greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union is transportation. In 2019 it contributes to about 31% of global emissions and 24% of emissions in the EU. In addition, up to the COVID-19 pandemic, emissions have only increased in this one sector. Greenhouse gas emissions from transport are increasing at a faster rate than any other energy using sector. Road transport is also a major contributor to local air pollution and smog.

In urban planning, transit-oriented development (TOD) is a type of urban development that maximizes the amount of residential, business and leisure space within walking distance of public transport. It promotes a symbiotic relationship between dense, compact urban form and public transport use. In doing so, TOD aims to increase public transport ridership by reducing the use of private cars and by promoting sustainable urban growth.
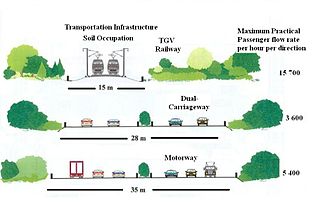
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.

In urban planning and design, an urban village is an urban development typically characterized by medium-density housing, mixed use zoning, good public transit and an emphasis on pedestrianization and public space. Contemporary urban village ideas are closely related to New Urbanism and smart growth ideas initiated in the United States.

Mixed use is a type of urban development, urban design, urban planning and/or a zoning classification that blends multiple uses, such as residential, commercial, cultural, institutional, or entertainment, into one space, where those functions are to some degree physically and functionally integrated, and that provides pedestrian connections. Mixed-use development may be applied to a single building, a block or neighborhood, or in zoning policy across an entire city or other administrative unit. These projects may be completed by a private developer, (quasi-) governmental agency, or a combination thereof. A mixed-use development may be a new construction, reuse of an existing building or brownfield site, or a combination.

A sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus will also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register, a visual artist, first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.

A transit village is a pedestrian-friendly mixed-use district or neighborhood oriented around the station of a high-quality transit system, such as rail or B.R.T. Often a civic square of public space abuts the train station, functioning as the hub or centerpiece of the surrounding community and encouraging social interaction. While mainly residential in nature, many transit villages offer convenience retail and services to residents heading to and from train stations.

Car dependency is the concept that some city layouts cause cars to be favoured over alternate forms of transportation, such as bicycles, public transit, and walking.

In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities by foot. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel.

The Finger Plan is an urban plan from 1947 which provides a strategy for the development of the Copenhagen metropolitan area, Denmark. According to the plan, Copenhagen is to develop along five 'fingers', centred on S-train commuter rail lines, which extend from the 'palm', that is the dense urban fabric of central Copenhagen. In between the fingers, green "wedges" are intended to provide land for agriculture and recreational purposes.

Peter Calthorpe is a San Francisco–based architect, urban designer and urban planner. He is a founding member of the Congress for New Urbanism, a Chicago-based advocacy group formed in 1992 that promotes sustainable building practices. For his works on redefining the models of urban and suburban growth in America Calthorpe has been named one of twenty-five ‘innovators on the cutting edge’ by Newsweek magazine.

Green urbanism has been defined as the practice of creating communities beneficial to humans and the environment. According to Timothy Beatley, it is an attempt to shape more sustainable places, communities and lifestyles, and consume less of the world's resources. Urban areas are able to lay the groundwork of how environmentally integrated and sustainable city planning can both provide and improve environmental benefits on the local, national, and international levels. Green urbanism is interdisciplinary, combining the collaboration of landscape architects, engineers, urban planners, ecologists, transport planners, physicists, psychologists, sociologists, economists and other specialists in addition to architects and urban designers.
Sustainable urbanism is both the study of cities and the practices to build them (urbanism), that focuses on promoting their long term viability by reducing consumption, waste and harmful impacts on people and place while enhancing the overall well-being of both people and place. Well-being includes the physical, ecological, economic, social, health and equity factors, among others, that comprise cities and their populations. In the context of contemporary urbanism, the term cities refers to several scales of human settlements from towns to cities, metropolises and mega-city regions that includes their peripheries / suburbs / exurbs. Sustainability is a key component to professional practice in urban planning and urban design along with its related disciplines landscape architecture, architecture, and civil and environmental engineering. Green urbanism and ecological urbanism are other common terms that are similar to sustainable urbanism, however they can be construed as focusing more on the natural environment and ecosystems and less on economic and social aspects. Also related to sustainable urbanism are the practices of land development called Sustainable development, which is the process of physically constructing sustainable buildings, as well as the practices of urban planning called smart growth or growth management, which denote the processes of planning, designing, and building urban settlements that are more sustainable than if they were not planned according to sustainability criteria and principles.
Fairview–Pointe-Claire is a Réseau express métropolitain (REM) station under construction in Pointe-Claire, Quebec, Canada. It will be operated by CDPQ Infra and serves as a station of the Anse-à-l'Orme branch of the REM, with an expected opening in the fourth quarter of 2024.

Robert Cervero is an author, consultant, and educator in sustainable transportation policy and planning. During his years as a faculty member in city and regional planning at the University of California, Berkeley, he gained recognition for his work in the sphere of urban transportation and land-use planning. His research has spanned the topics of induced demand, transit-oriented development (TOD), transit villages, paratransit, car sharing, and suburban growth.
A walking city is a type of city that is created to avoid internal transportation, and therefore be small enough that a person can use walking to navigate the city. It is characterized by narrow, often winding streets. Its transport system is inherently egalitarian, with no one being disadvantaged by a lack of transport, unlike modern automotive cities. Walkability within areas positively impacts equity, sustainability, health, social benefits, less demand on other modes, economic development, and enjoyment.


















