Related Research Articles

East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a country in Central Europe that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state, and it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces with the autonomy of the native communists following the Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II; when the Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The GDR was dominated by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), a communist party from 1949 to 1989, before being democratized and liberalized under the impact of the Revolutions of 1989 against the communist states, helping East Germany be united with the West. Unlike West Germany, SED did not see its state as the successor of the German Reich (1871–1945) and abolished the goal of unification in the constitution (1974). Under the SED rule, GDR was often judged as a Soviet satellite state; most scholars and academics described it as a totalitarian regime.

The Warsaw Pact (WP), formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance (TFCMA), was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republics of Central and Eastern Europe in May 1955, during the Cold War. The term "Warsaw Pact" commonly refers to both the treaty itself and its resultant defensive alliance, the Warsaw Treaty Organization (WTO). The Warsaw Pact was the military and economic complement to the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon), the regional economic organization for the Eastern Bloc states of Central and Eastern Europe.

The Hallstein Doctrine, named after Walter Hallstein, was a key principle in the foreign policy of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1955 to 1970. As usually presented, it prescribed that the Federal Republic would not establish or maintain diplomatic relations with any state that recognized the German Democratic Republic. In fact it was more nuanced. There was no public official text of the "doctrine", but its main architect, Wilhelm Grewe, explained it publicly in a radio interview. Konrad Adenauer, who served as Chancellor of Germany from 1949 to 1963, explained the outlines of the policy in a statement to the German parliament on 22 September 1955. It meant that the Federal German government would regard it as an unfriendly act if third countries were to recognize the "German Democratic Republic" or to maintain diplomatic relations with it – with the exception of the Soviet Union. The West German response to such could mean breaking off diplomatic relations, though this was not stated as an automatic response under the policy and in fact remained the ultima ratio.

Neue Ostpolitik, or Ostpolitik for short, was the normalization of relations between the Federal Republic of Germany and Eastern Europe, particularly the German Democratic Republic beginning in 1969. Influenced by Egon Bahr, who proposed "change through rapprochement" in a 1963 speech at the Evangelische Akademie Tutzing, the policies were implemented beginning with Willy Brandt, fourth Chancellor of the FRG from 1969 to 1974, and winner of the 1971 Nobel Prize for Peace for his efforts to place this policy at the acme of the FRG.

German reunification was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single full sovereign state, which took place between 9 November 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the "Unification Treaty" entered into force dissolving the German Democratic Republic and integrating its recently re-established constituent federated states into the Federal Republic of Germany to form present-day Germany, has been chosen as the customary German Unity Day and has thereafter been celebrated each year as a national holiday in Germany since 1991. As part of the reunification, East and West Berlin of the two countries were also de facto united into a single city, which later eventually became the capital of this country.

The history of Germany from 1945–1990 spans the period following World War II, from the Berlin Declaration marking the abolition of the German Reich and Allied-occupied period in Germany on 5 June 1945 to German reunification on 3 October 1990.

The National People's Army were the armed forces of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from 1956 to 1990.

The Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany , or the Two Plus Four Agreement , is an international agreement that allowed the reunification of Germany in the early 1990s. It was negotiated in 1990 between the 'two', the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, in addition to the Four Powers which had occupied Germany at the end of World War II in Europe: France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The treaty supplanted the 1945 Potsdam Agreement: in it, the Four Powers renounced all rights they had held with regard to Germany, allowing for its reunification as a fully sovereign state the following year. Additionally, the two German states agreed to reconfirm the existing border with Poland, accepting that German territory post-reunification would consist only of what was presently administered by West and East Germany—renouncing explicitly any possible claims to the former eastern territories of Germany including East Prussia, most of Silesia, as well as the eastern parts of Brandenburg and Pomerania.

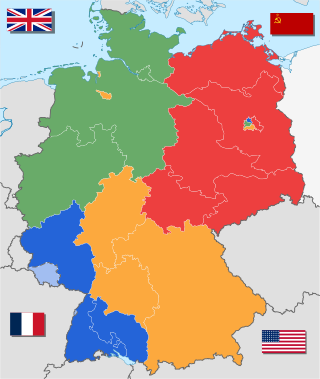
The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Nazi Germany surrendered on 8 May 1945, four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC) under the Berlin Declaration of 5 June 1945 that led to the fall of the German Reich. At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria; the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.
The Stalin Note, also known as the March Note, was a document delivered to the representatives of the Western Allies from the Soviet Union in separated Germany including the two countries in West and East on 10 March 1952. Soviet general secretary and premier Joseph Stalin put forth a proposal for a German reunification and neutralisation with no conditions on economic policies and with guarantees for "the rights of man and basic freedoms, including freedom of speech, press, religious persuasion, political conviction, and assembly" and free activity of democratic parties and organizations.

Republikflucht was the colloquial term in the German Democratic Republic for illegal emigration to West Germany, West Berlin, and non-Warsaw Pact countries; the official term was Ungesetzlicher Grenzübertritt. Republikflucht applied to both the 3.5 million Germans who migrated legally from the Soviet occupation zone and East Germany before the Berlin Wall was built on 13 August 1961, and the thousands who migrated illegally across the Iron Curtain until 23 December 1989. It has been estimated that 30,000 people left the GDR per year between 1984 and 1988, and up to 300,000 per year before the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961.

The Third World War and The Third World War: The Untold Story are war novels by Sir John Hackett, published in 1978 and 1982, by Macmillan in New York and Sidgwick & Jackson in London, respectively. The novels detail a hypothetical World War III waged between NATO and the Warsaw Pact in 1985, written in the style of a non-fiction historical retrospective interspersed with accounts of the conflict from the perspectives of various people.

The German Democratic Republic (GDR), German: Deutsche Demokratische Republik (DDR), often known in English as East Germany, existed from 1949 to 1990. It covered the area of the present-day German states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt, and Thüringen. This area was occupied by the Soviet Union at the end of World War II excluding the former eastern lands annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union, with the remaining German territory to the west occupied by the British, American, and French armies. Following the economic and political unification of the three western occupation zones under a single administration and the establishment of the Federal Republic of Germany in May 1949, the German Democratic Republic was founded on 7 October 1949 as a sovereign nation.

The remilitarization of the Rhineland began on 7 March 1936, when German military forces entered the Rhineland, which directly contravened the Treaty of Versailles and the Locarno Treaties. Neither France nor Britain was prepared for a military response, so they did not act. After 1939 commentators often said that a strong military move in 1936 might have ruined Hitler's expansionist plans. However, recent historiography agrees that both public and elite opinion in Britain and France strongly opposed a military intervention, and neither had an army prepared to move in.
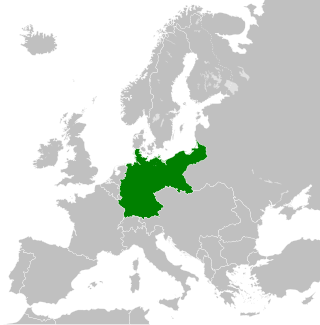
The territorial evolution of Germany in this article include all changes in the modern territory of Germany from its unification making it a country on 1 January 1871 to the present although the history of "Germany" as a territorial polity concept and the history of the ethnic Germans are much longer and much more complex. Modern Germany was formed when the Kingdom of Prussia unified most of the German states, with the exception of multi-ethnic Austria, into the German Empire. After the First World War, on 10 January 1920, Germany lost about 10% of its territory to its neighbours, and the Weimar Republic was formed two days before this war was over. This republic included territories to the east of today's German borders.

The Border Troops of the German Democratic Republic was the border guard of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from 1946 to 1990.

During World War II, the Soviet Union occupied and annexed several countries effectively handed over by Nazi Germany in the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of 1939. These included the eastern regions of Poland, as well as Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania, part of eastern Finland and eastern Romania. Apart from the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and post-war division of Germany, the USSR also occupied and annexed Carpathian Ruthenia from Czechoslovakia in 1945.
The legal status of Germany concerns the question of the extinction, or otherwise continuation, of the German nation-state following the rise and downfall of Nazi Germany, and constitutional hiatus of the military occupation of Germany by the four Allied powers from 1945 to 1949. It became current once again when the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany in 1990.

The London and Paris Conferences were two related conferences held in London and Paris during September–October 1954 to determine the status of West Germany. The talks concluded with the signing of the Paris Agreements, which granted West Germany some sovereignty, ended the occupation, and allowed its admittance to NATO. Furthermore, both West Germany and Italy joined the Brussels Treaty on 23 October 1954. The Agreements went into force on 5 May 1955. The participating powers included France, the United Kingdom, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, West Germany, Italy, Canada, the United States, and remaining NATO members.
The development of the inner German border took place in a number of stages between 1945 and the mid-1980s. After its establishment in 1945 as the dividing line between the Western and Soviet occupation zones of Germany, in 1949 the inner German border became the frontier between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic. The border remained relatively easy to cross until it was abruptly closed by the GDR in 1952 in response to the large-scale emigration of East Germans to the West. Barbed-wire fences and minefields were installed and draconian restrictions were placed on East German citizens living near the border. Thousands were expelled from their homes, with several thousand more fleeing to the West. From the late 1960s, the border fortifications were greatly strengthened through the installation of new fences, detectors, watchtowers and booby-traps designed to prevent attempts to escape from East Germany. The improved border defences succeeded in reducing the scale of unauthorised emigration to a trickle.
References
- ↑ "Division of Germany after WWII". 24 February 1993.
- ↑ "Constitution of the German Democratic Republic (1949) - Wikisource, the free online library".
- ↑ "Text of the Warsaw Security Pact (see preamble)". Avalon Project. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ "Soviet-German Agreements".
- ↑ "Soviet-German Agreements".
- ↑ MacLean, Rory (2014). Berlin: Imagine a City. ISBN 978-0297868835.
- ↑ Sundhaussen, Ulf (2008). "Voting for Reunification: East Germany's Four Elections in 1990". Australian Journal of Politics & History. 37 (2): 200–235. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8497.1991.tb00030.x.