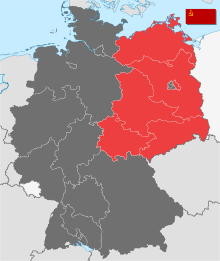
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic, was a country in Central Europe that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. Until 1989, it was generally viewed as a communist state, and it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state". Before its establishment, the country's territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces with the autonomy of the native communists following the Berlin Declaration abolishing German sovereignty in World War II; when the Potsdam Agreement established the Soviet-occupied zone, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The GDR was dominated by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), a communist party from 1949 to 1989, before being democratized and liberalized under the impact of the Revolutions of 1989 against the communist states, helping East Germany be united with the West. Unlike West Germany, SED did not see its state as the successor of the German Reich (1871–1945) and abolished the goal of unification in the constitution (1974). Under the SED rule, GDR was often judged as a Soviet satellite state; most scholars and academics described it as a totalitarian regime.

The Potsdam Conference was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. The participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. They were represented respectively by General Secretary Joseph Stalin, Prime Ministers Winston Churchill and Clement Attlee, and President Harry S. Truman. They gathered to decide how to administer Germany, which had agreed to an unconditional surrender nine weeks earlier. The goals of the conference also included establishing the postwar order, solving issues on the peace treaty, and countering the effects of the war.

The Potsdam Agreement was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe on 1 August 1945 and it was published the next day. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned the military occupation and reconstruction of Germany, its border, and the entire European Theatre of War territory. It also addressed Germany's demilitarisation, reparations, the prosecution of war criminals and the mass expulsion of ethnic Germans from various parts of Europe. France was not invited to the conference but formally remained one of the powers occupying Germany.

The Yalta Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union to discuss the postwar reorganization of Germany and Europe. The three states were represented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, Prime Minister Winston Churchill, and General Secretary Joseph Stalin. The conference was held near Yalta in Crimea, Soviet Union, within the Livadia, Yusupov, and Vorontsov palaces.

Otto Emil Franz Grotewohl was a German politician who served as the first prime minister of the German Democratic Republic from its foundation in October 1949 until his death in September 1964.
The Soviet Military Administration in Germany was the Soviet military government, headquartered in Berlin-Karlshorst, that directly ruled the Soviet occupation zone of Germany from the German surrender in May 1945 until after the establishment of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in October 1949.
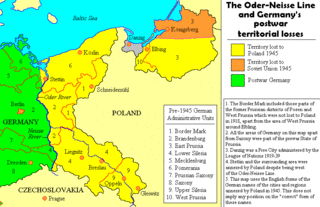
The "former eastern territories of Germany" refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e., the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union after World War II in Europe. In many of these territories, Germans used to be the dominant or sole ethnicity. In contrast to the lands awarded to the restored Polish state by the Treaty of Versailles after World War I, the German territories lost with the Potsdam Agreement after World War II in Europe on 2 August 1945 were either almost exclusively inhabited by Germans before 1945, mixed German-Polish with a German majority, or mixed German-Czech with a German majority (Glatz). Virtually the entire German population of the territories that did not flee voluntarily in the face of the Red Army advance of 1945, was expelled to Germany, with their possessions being expropriated.

The Bizone or Bizonia was the combination of the American and the British occupation zones on 1 January 1947 during the occupation of Germany after World War II. With the addition of the French occupation zone on 1 August 1948 the entity became the Trizone. Later, on 23 May 1949, the Trizone became the Federal Republic of Germany, commonly known as West Germany.

The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and former state: after Nazi Germany surrendered on 8 May 1945, four countries representing the Allies asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC) under the Berlin Declaration of 5 June 1945 that led to the fall of the German Reich. At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria; the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the Soviet Union all regions of Germany east of the Oder–Neisse line and divided the remaining "Germany as a whole" into four occupation zones, each administered by one of the Allies.

The German Democratic Republic (GDR), German: Deutsche Demokratische Republik (DDR), often known in English as East Germany, existed from 1949 to 1990. It covered the area of the present-day German states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt, and Thüringen. This area was occupied by the Soviet Union at the end of World War II excluding the former eastern lands annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union, with the remaining German territory to the west occupied by the British, American, and French armies. Following the economic and political unification of the three western occupation zones under a single administration and the establishment of the Federal Republic of Germany in May 1949, the German Democratic Republic was founded on 7 October 1949 as a sovereign nation.
The administrative divisions of the German Democratic Republic were constituted in two different forms during the country's history. The GDR first retained the traditional German division into federated states called Länder, but in 1952 they were replaced with districts called Bezirke. Immediately before German reunification in 1990, the Länder were restored, but they were not effectively reconstituted until after reunification had completed.
The territorial evolution of Germany in this article include all changes in the modern territory of Germany from its unification making it a country on 1 January 1871 to the present although the history of "Germany" as a territorial polity concept and the history of the ethnic Germans are much longer and much more complex. Modern Germany was formed when the Kingdom of Prussia unified most of the German states, with the exception of multi-ethnic Austria, into the German Empire. After the First World War, on 10 January 1920, Germany lost about 10% of its territory to its neighbours, and the Weimar Republic was formed two days before this war was over. This republic included territories to the east of today's German borders.

The flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland was the largest of a series of flights and expulsions of Germans in Europe during and after World War II. The German population fled or was expelled from all regions which are currently within the territorial boundaries of Poland: including the former eastern territories of Germany annexed by Poland after the war and parts of pre-war Poland; despite acquiring territories from Germany, the Poles themselves were also expelled from the former eastern territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union. West German government figures of those evacuated, migrated, or expelled by 1950 totaled 8,030,000. Research by the West German government put the figure of Germans emigrating from Poland from 1951 to 1982 at 894,000; they are also considered expellees under German Federal Expellee Law.

NKVD special camps were NKVD-run late and post-World War II internment camps in the Soviet-occupied parts of Germany from May 1945 to January 6, 1950. They were set up by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (SMAD) and run by the Soviet Ministry of Internal Affairs MVD. On 8 August 1948, the camps were made subordinate to the Gulag. Because the camp inmates were permitted no contact with the outside world, the special camps were also known as silence camps.

The Oder–Neisse line is an unofficial term for the modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion of Polish territory does fall west of the line, including the cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście.

The Democratic Bloc was an association of political parties and organizations in the German Democratic Republic.
The German People's Congress were a series of congresses held in Germany. They consisted of members of the Socialist Unity Party, the SED, and other political parties and mass organizations. Delegates from all over Germany gathered for the first time on 6 December 1947. Their main demand was the establishment of a German government.

The Soviet Control Commission was a monitoring and management committee established by the Soviet Union in order to oversee the leadership of the German Democratic Republic. It was active from 10 October 1949 and 20 September 1955 and it was legitimated by the Potsdam Agreement between the Allies.

The State of Saxony-Anhalt was a subdivision of the Soviet occupation zone and state of East Germany which corresponds widely to the present-day German state Saxony-Anhalt. After the retreat of the US troops from the Western parts - following the agreements of the Yalta Conference - it was formed as administrative division called Province of Saxony by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (SMAD) in July 1945. The province was a re-establishment of the Province of Saxony which existed in Prussia from 1816 to 1944. On 1 July 1944, the Province of Saxony was divided along the lines of its three government districts of Halle-Merseburg, Magdeburg and Erfurt. The two provinces became part of the new state including small parts of Thuringia (Allstedt) and Soviet-occupied parts of Anhalt (Dessau) and Brunswick. Following the first election for the Landtag in October 1946, the state was renamed to Province of Saxony-Anhalt on the same day. With the abolition of Prussia in February 1947, it was named State of Saxony-Anhalt. Compared to the administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, it comprised the Gaue Magdeburg-Anhalt, Halle-Merseburg and small parts of Southern Hanover-Brunswick and Thuringia.

The State of Brandenburg was a subdivision of the Soviet occupation zone and state of East Germany which corresponds widely to the present-day German state Brandenburg. The state was originally formed as administrative division Province of March Brandenburg by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (SMAD) in July 1945, a re-establishment of the Prussian Province of Brandenburg, excluding the Eastern parts behind the Oder–Neisse line to Poland. With the abolition of Prussia in February 1947, it was named State of March Brandenburg but in June 1947 the SMAD forced to change the name to State of Brandenburg. In August 1945, a transfer of territory was ruled out between Allied-occupied Berlin. Compared to the administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, it comprised the Western part of the Gau March Brandenburg and small parts of Berlin.