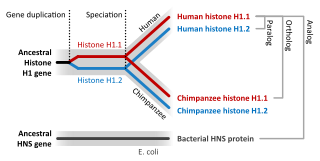
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).

In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids or proteins across species, or within a genome, or between donor and receptor taxa. Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection.

Pfam is a database of protein families that includes their annotations and multiple sequence alignments generated using hidden Markov models. The most recent version, Pfam 35.0, was released in November 2021 and contains 19,632 families.
Inparanoid is an algorithm that finds orthologous genes and paralogous genes that arose—most likely by duplication—after some speciation event. Such protein-coding genes are called in-paralogs, as opposed to out-paralogs.

Richard Michael Durbin is a British computational biologist and Al-Kindi Professor of Genetics at the University of Cambridge. He also serves as an associate faculty member at the Wellcome Sanger Institute where he was previously a senior group leader.

OrthoDB presents a catalog of orthologous protein-coding genes across vertebrates, arthropods, fungi, plants, and bacteria. Orthology refers to the last common ancestor of the species under consideration, and thus OrthoDB explicitly delineates orthologs at each major radiation along the species phylogeny. The database of orthologs presents available protein descriptors, together with Gene Ontology and InterPro attributes, which serve to provide general descriptive annotations of the orthologous groups, and facilitate comprehensive orthology database querying. OrthoDB also provides computed evolutionary traits of orthologs, such as gene duplicability and loss profiles, divergence rates, sibling groups, and gene intron-exon architectures.
PhylomeDB is a public biological database for complete catalogs of gene phylogenies (phylomes). It allows users to interactively explore the evolutionary history of genes through the visualization of phylogenetic trees and multiple sequence alignments. Moreover, phylomeDB provides genome-wide orthology and paralogy predictions which are based on the analysis of the phylogenetic trees. The automated pipeline used to reconstruct trees aims at providing a high-quality phylogenetic analysis of different genomes, including Maximum Likelihood tree inference, alignment trimming and evolutionary model testing.
The human gene Chromosome 3 open reading frame 14 is a gene of uncertain function located at 3p14.2 near fragile site FRBA3—which falls between this gene and the centromere. Its protein is expected to localize to the nucleus and bind DNA. Orthologs have been identified in all of the major animal groups, minus amphibians and insects, tracing as far back as the sea anemone; indicating an origin of over 1000 mya, highlighting its importance in the animal genome.
Heng Li is a Chinese bioinformatics scientist. He is an associate professor at the department of Biomedical Informatics of Harvard Medical School and the department of Data Science of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. He was previously a research scientist working at the Broad Institute in Cambridge, Massachusetts with David Reich and David Altshuler. Li's work has made several important contributions in the field of next generation sequencing.

UPF0172 protein FAM158A, also known as c14orf122 or CGI112, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM158A gene located on chromosome 14q11.2.

Protein FAM214A, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 214, A (FAM214A) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the FAM214A gene. FAM214A is a gene with unknown function found at the q21.2-q21.3 locus on Chromosome 15 (human). The protein product of this gene has two conserved domains, one of unknown function (DUF4210) and another one called Chromosome_Seg. Although the function of the FAM214A protein is uncharacterized, both DUF4210 and Chromosome_Seg have been predicted to play a role in chromosome segregation during meiosis.
In bioinformatics, the PANTHER classification system is a large curated biological database of gene/protein families and their functionally related subfamilies that can be used to classify and identify the function of gene products. PANTHER is part of the Gene Ontology Reference Genome Project designed to classify proteins and their genes for high-throughput analysis.

Family with sequence similarity 167, member A is a protein in humans that is encoded by the FAM167A gene located on chromosome 8. FAM167A and its paralogs are protein encoding genes containing the conserved domain DUF3259, a protein of unknown function. FAM167A has many orthologs in which the domain of unknown function is highly conserved.
Model organism databases (MODs) are biological databases, or knowledgebases, dedicated to the provision of in-depth biological data for intensively studied model organisms. MODs allow researchers to easily find background information on large sets of genes, plan experiments efficiently, combine their data with existing knowledge, and construct novel hypotheses. They allow users to analyse results and interpret datasets, and the data they generate are increasingly used to describe less well studied species. Where possible, MODs share common approaches to collect and represent biological information. For example, all MODs use the Gene Ontology (GO) to describe functions, processes and cellular locations of specific gene products. Projects also exist to enable software sharing for curation, visualization and querying between different MODs. Organismal diversity and varying user requirements however mean that MODs are often required to customize capture, display, and provision of data.

FAM163A, also known as cebelin and neuroblastoma-derived secretory protein (NDSP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM163A gene. This protein has been implicated in promoting proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of neuroblastoma cancer cells. In addition, this protein has been found to be up-regulated in the lung tissue of chronic smokers. FAM163A is found on human chromosome 1q25.2; its protein product is 167 amino acids long. FAM163A contains a very highly conserved signal peptide sequence, coded for by the first ~37 amino acids in its sequence; albeit only conserved in eukaryotes, the most distant of which being the Japanese Rice Fish.
In molecular phylogenetics, relationships among individuals are determined using character traits, such as DNA, RNA or protein, which may be obtained using a variety of sequencing technologies. High-throughput next-generation sequencing has become a popular technique in transcriptomics, which represent a snapshot of gene expression. In eukaryotes, making phylogenetic inferences using RNA is complicated by alternative splicing, which produces multiple transcripts from a single gene. As such, a variety of approaches may be used to improve phylogenetic inference using transcriptomic data obtained from RNA-Seq and processed using computational phylogenetics.

SHLD1 or shieldin complex subunit 1 is a gene on chromosome 20. The C20orf196 gene encodes an mRNA that is 1,763 base pairs long, and a protein that is 205 amino acids long.

Family with sequence 98, member C or FAM98C is a gene that encodes for FAM98C has two aliases FLJ44669 and hypothetical protein LOC147965. FAM98C has two paralogs in humans FAM98A and FAM98B. FAM98C can be characterized for being a Leucine-rich protein. The function of FAM98C is still not defined. FAM98C has orthologs in mammals, reptiles, and amphibians and has a distant orhtologs in Rhinatrema bivittatum and Nanorana parkeri.
Genome mining describes the exploitation of genomic information for the discovery of biosynthetic pathways of natural products and their possible interactions. It depends on computational technology and bioinformatics tools. The mining process relies on a huge amount of data accessible in genomic databases. By applying data mining algorithms, the data can be used to generate new knowledge in several areas of medicinal chemistry, such as discovering novel natural products.

UBALD1 is a protein encoded by the UBALD1 gene, located on chromosome 16 in humans. UBALD1 has high ubiquitous tissue expression and localizes in the nucleus and cytoplasm. UBALD1 is conserved in animals, including invertebrates. An alias for UBALD1 is FAM100A.












