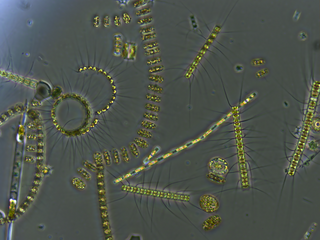
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community, having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequently, they drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers.
The dinoflagellates are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey.

The Noctilucales are an order of marine dinoflagellates. They differ from most others in that the mature cell is diploid and its nucleus does not show a dinokaryotic organization. They show gametic meiosis.
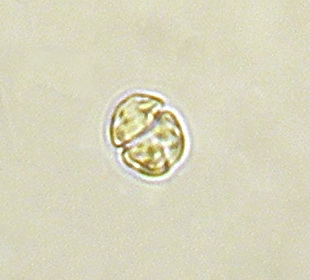
Gymnodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates, a type of marine and freshwater plankton. It is one of the few naked dinoflagellates, or species lacking armor known as cellulosic plates. Since 2000, the species which had been considered to be part of Gymnodinium have been divided into several genera, based on the nature of the apical groove and partial LSU rDNA sequence data. Amphidinium was redefined later. Gymnodinium belong to red dinoflagellates that, in concentration, can cause red tides. The red tides produced by some Gymnodinium, such as Gymnodinium catenatum, are toxic and pose risks to marine and human life, including paralytic shellfish poisoning.
Dinocysts or dinoflagellate cysts are typically 15 to 100 µm in diameter and produced by around 15–20% of living dinoflagellates as a dormant, zygotic stage of their lifecycle, which can accumulate in the sediments as microfossils. Organic-walled dinocysts are often resistant and made out of dinosporin. There are also calcareous dinoflagellate cysts and siliceous dinoflagellate cysts.

Symbiodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known and have photosymbiotic relationships with many species. These unicellular microalgae commonly reside in the endoderm of tropical cnidarians such as corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish, where the products of their photosynthetic processing are exchanged in the host for inorganic molecules. They are also harbored by various species of demosponges, flatworms, mollusks such as the giant clams, foraminifera (soritids), and some ciliates. Generally, these dinoflagellates enter the host cell through phagocytosis, persist as intracellular symbionts, reproduce, and disperse to the environment. The exception is in most mollusks, where these symbionts are intercellular. Cnidarians that are associated with Symbiodinium occur mostly in warm oligotrophic (nutrient-poor), marine environments where they are often the dominant constituents of benthic communities. These dinoflagellates are therefore among the most abundant eukaryotic microbes found in coral reef ecosystems.

The genus Ceratium is restricted to a small number of freshwater dinoflagellate species. Previously the genus contained also a large number of marine dinoflagellate species. However, these marine species have now been assigned to a new genus called Tripos. Ceratium dinoflagellates are characterized by their armored plates, two flagella, and horns. They are found worldwide and are of concern due to their blooms.

Oxyrrhis is a genus of heterotrophic dinoflagellate, the only genus in the family Oxyrrhinaceae. It inhabits a range of marine environments worldwide and is important in the food web dynamics of these ecosystems. It has the potential to be considered a model organism for the study of other protists. Oxyrrhis is an early-branching lineage and has long been described in literature as a monospecific genus, containing only Oxyrrhis marina. Some recent molecular phylogenetic studies argue that Oxyrrhis comprises O. marina and O. maritima as distinct species, while other publications state that the two are genetically diverse lineages of the same species. The genus has previously been suggested to contain O. parasitica as a separate species, however the current consensus appears to exclude this, with Oxyrrhis being monospecific and containing O. marina and O. maritima as separate lineages of the type species. The genus is characterised by its elongated body which is anteriorly prolonged to a point, its complex flagellar apparatuses which attach to the ventral side of the cell, and the unique features of its nucleus.
Syndinium is a cosmopolitan genus of parasitic dinoflagellates that infest and kill marine planktonic species of copepods and radiolarians. Syndinium belongs to order Syndiniales, a candidate for the uncultured group I and II marine alveolates. The lifecycle of Syndinium is not well understood beyond the parasitic and zoospore stages.
Amoebophyra is a genus of dinoflagellates. Amoebophyra is a syndinian parasite that infects free-living dinoflagellates that are attributed to a single species by using several host-specific parasites. It acts as "biological control agents for red tides and in defining species of Amoebophrya." Researchers have found a correlation between a large amount of host specify and the impact host parasites may have on other organisms. Due to the host specificity found in each strain of Amoebophrya's physical makeup, further studies need to be tested to determine whether the Amoebophrya can act as a control against harmful algal blooms.

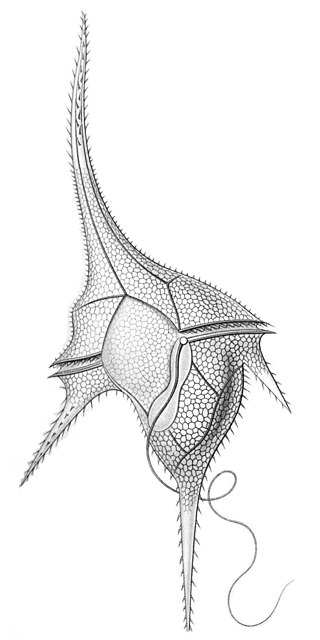
Ornithocercus is a genus of planktonic dinoflagellate that is known for its complex morphology that features considerable lists growing from its thecal plates, giving an attractive appearance. Discovered in 1883, this genus has a small number of species currently categorized but is widespread in tropical and sub-tropical oceans. The genus is marked by exosymbiotic bacteria gardens under its lists, the inter-organismal dynamics of which are a current field of research. As they reside only in warm water, the genus has been used as a proxy for climate change and has potential to be an indicator species for environmental change if found in novel environments.

Gonyaulacales is an order of dinoflagellates found in marine environments.

Parvilucifera is a genus of marine alveolates that behave as endoparasites of dinoflagellates. It was described in 1999 by biologists Fredrik Norén and Øjvind Moestrup, who identified the genus among collections of Dinophysis dinoflagellates off the coast of Sweden. Initially mistaken for products of sexual reproduction, the round bodies found within these collections were eventually recognized as sporangia, spherical structures that generate zoospores of a parasitic protist. This organism was later identified as P. infectans, the type species. The examination of this organism and its close genetic relationship to Perkinsus led to the creation of the Perkinsozoa phylum within the Alveolata group.
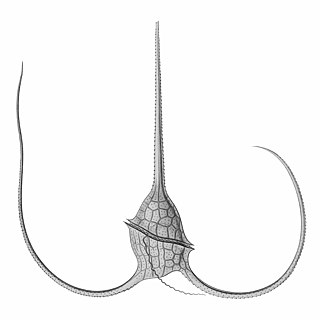
Tripos muelleri is a species of dinoflagellates of the genus Tripos.

Tripos is a genus of marine dinoflagellates in the family Ceratiaceae. It was formerly part of Ceratium, then separated out as Neoceratium, a name subsequently determined to be invalid.
Cymbodinium elegans is a species of marine dinoflagellates in the order Noctilucales. It is the only species in its genus.
Oxytoxum elegans is a species of dinoflagellates in the order Peridiniales. It is found in the Gulf of Mexico, the Lebanese Exclusive Economic Zone waters and the North Atlantic Ocean.
Corythodinium elegans is a species of dinoflagellates in the family Oxytoxaceae. It is found Worldwide. The type locality is the Mediterranean. It is also found in Australian and New Zealand waters.

Balanophyllia elegans, the orange coral or orange cup coral, is a species of solitary cup coral, a stony coral in the family Dendrophylliidae. It is native to the eastern Pacific Ocean. As an azooxanthellate species, it does not contain symbiotic dinoflagellates in its tissues in the way that most corals do.












