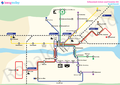
| Arnhem trolleybus | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Overview | |
| Locale | Arnhem, Netherlands |
| Transit type | Trolleybus |
| Number of lines | 8 |
| Operation | |
| Began operation | 5 September 1949 |
| Operator(s) | Hermes (under the brands Breng and RRReis) |
The Arnhem trolleybus system is the trolleybus system in the city of Arnhem. It is unique in the Netherlands as the only trolleybus system still operating in that country. It opened on 5 September 1949. [1]