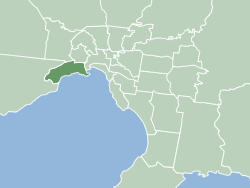
The City of Hobsons Bay is a local government area in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It comprises the south-western suburbs between 6 and 20 km from the Melbourne city centre.

The City of Wyndham is a local government area in Victoria, Australia in the outer south-western suburbs of Melbourne, within the Melbourne Metropolitan Area, between Melbourne and the regional city of Geelong. It has an area of 542 square kilometres (209 sq mi). The city had a population of 292,011 as of the 2021 census. For the year to 2018 the City of Wyndham increased its population by 14,251, the largest number of any LGA in Victoria, as well as being the second most populous and the second fastest growing at a rate of 5.9 per cent.

Altona is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 13 km (8.1 mi) south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Hobsons Bay local government area. Altona recorded a population of 11,490 at the 2021 census.

Brooklyn is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 10 km (6.2 mi) west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Cities of Brimbank and Hobsons Bay local government areas. Brooklyn recorded a population of 1,979 at the 2021 census.

Laverton established in 1886, is a suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 17 km (11 mi) south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Cities of Hobsons Bay and Wyndham local government areas. Laverton recorded a population of 4,760 at the 2021 census.

Newport is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 10 km (6.2 mi) south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Hobsons Bay local government area. Newport recorded a population of 13,658 at the 2021 census.

Williamstown is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 11 km (6.8 mi) south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Hobsons Bay local government area. Williamstown recorded a population of 14,407 at the 2021 census.
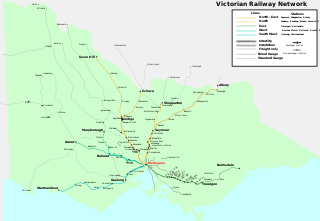
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

Altona North is a suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 10 km (6.2 mi) south-west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Hobsons Bay local government area. Altona North recorded a population of 12,962 at the 2021 census.

Yarraville is an inner-city suburb in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 6 km (3.7 mi) west of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the City of Maribyrnong local government area. Yarraville recorded a population of 15,636 at the 2021 census.

The first railway in colonial South Australia was a line from the port of Goolwa on the River Murray to an ocean harbour at Port Elliot, which first operated in December 1853, before its completion in May 1854.
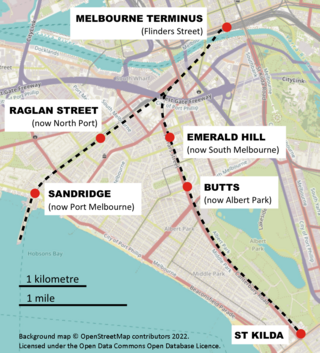
The Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. The company was incorporated on 20 January 1853 to build the line from Melbourne to the port of Sandridge, now Port Melbourne.

The National Railway Museum, Port Adelaide, South Australia is the largest railway museum in Australia. More than 100 major exhibits, mainly from the South Australian Railways (SAR) and Commonwealth Railways and their successor, Australian National, are displayed at its 3.5 hectares site. A very large archival collection of photographs of those railways and records created by them is also managed by the museum. The museum is operated with a large number of volunteers.

Point Wilson is a locality located on the northern shores of Corio Bay, Victoria. it is approximately 60 kilometres by road from Melbourne, and 25 kilometres by road from Geelong.
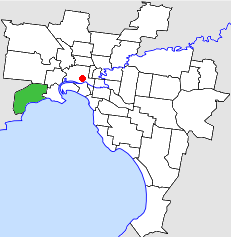
The City of Altona was a local government area about 13 kilometres (8 mi) west of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The city covered an area of 40.18 square kilometres (15.51 sq mi), and existed from 1957 until 1994.

Newington Armory is a heritage-listed former Royal Australian Navy armament depot, now used for tourism purposes, at Holker Street, Sydney Olympic Park, Cumberland Council, New South Wales, Australia. It was built from 1897 initially by the New South Wales Military Forces then by the Australian Army and later by the Royal Australian Navy. It is also known as Millennium Heritage Parklands Precinct, RAN Armament Depot Newington, Royal Australian Navy Armament Depot (RANAD), Newington Nature Reserve and Sydney Olympic Games site. The property is owned by the Sydney Olympic Park Authority. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 14 January 2011.

Cherry Lake is part of historical coastal wetlands in Altona, a suburb of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. The wetlands were converted to a lake with construction of retaining walls, levees and flow channels. The lake and surrounding reserve is an important wildlife habitat and popular recreational destination.
The Truganina Coastal Parklands are located 15 km west of Melbourne CBD, on the shores of Port Phillip Bay, stretching from Altona to Altona Meadows and adjacent to the Cheetham Wetlands and the Point Cook Coastal Park. They were formed through the 'recycling' of more than 300 hectares of parks and former industrial land and are now the largest cluster of parks on Port Phillip Bay, interlinked by cycling and walking trails and featuring a surprisingly high diversity and abundance of landscapes, natural environment and recreational areas, including beachside recreation, picnic & barbecue facilities, grassfields and wildlife conservation areas. The wetlands form part of the Cheetham and Altona Important Bird Area.

The Dry Creek explosives depot was a secure storage facility at Dry Creek, near Port Adelaide, from 1904 to 1995, serving the construction, mining and quarrying industries of South Australia and the mines of Broken Hill in New South Wales.

Chattenden and Lodge Hill Military Camps were British Army training camps in Chattenden and Hoo St Werburgh in Kent. They were built as ordnance depots and functioned as such through to the second half of the twentieth century.






































