
Chiari malformation (CM) is a structural defect in the cerebellum, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum.

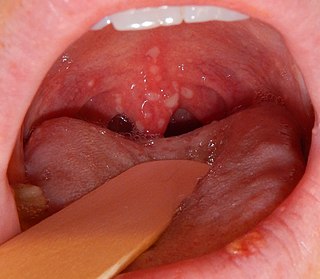
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates and severe swelling.

Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure in which both palatine tonsils are fully removed from the back of the throat. The procedure is mainly performed for recurrent tonsillitis, throat infections and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those with frequent throat infections, surgery results in 0.6 fewer sore throats in the following year, but there is no evidence of long term benefits. In children with OSA, it results in improved quality of life.

In anatomy, the pharyngeal tonsil, also known as the nasopharyngeal tonsil or adenoid, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphatic tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. In children, it normally forms a soft mound in the roof and back wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula.

Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can be acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis typically has a rapid onset. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and enlarged lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess (Quinsy).
Herpangina, also called mouth blisters, is a painful mouth infection caused by coxsackieviruses. Usually, herpangina is produced by one particular strain of coxsackie virus A, but it can also be caused by coxsackievirus B or echoviruses. Most cases of herpangina occur in the summer, affecting mostly children. However, it occasionally occurs in adolescents and adults. It was first characterized in 1920.

Tonsil stones, also known as tonsilloliths, are mineralizations of debris within the crevices of the tonsils. When not mineralized, the presence of debris is known as chronic caseous tonsillitis (CCT). Symptoms may include bad breath, foreign body sensation, sore throat, pain or discomfort with swallowing, and cough. Generally there is no pain, though there may be the feeling of something present. The presence of tonsil stones may be otherwise undetectable, however some people have reported seeing white material in the rear of their throat.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.
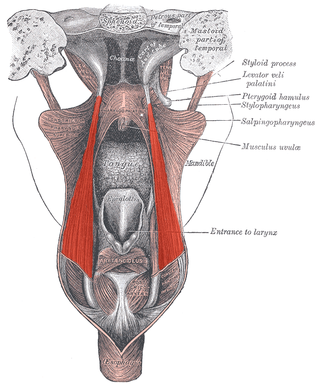
The salpingopharyngeus muscle is a muscle of the pharynx. It arises from the lower part of the cartilage of the Eustachian tube, and inserts into the palatopharyngeus muscle by blending with its posterior fasciculus. It is innervated by vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus. It raises the pharynx and larynx during deglutition (swallowing) and laterally draws the pharyngeal walls up. It opens the pharyngeal orifice of the Eustachian tube during swallowing to allow for the equalization of pressure between it and the pharynx.

Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz was a German anatomist, known for summarizing neuron theory and for naming the chromosome. He is also remembered by anatomical structures of the human body which were named after him: Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and Waldeyer's glands.

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.

The ascending palatine artery is an artery is a branch of the facial artery which ascends along the neck before splitting into two terminal branches; one branch supplies the soft palate, and the other supplies the palatine tonsil and pharyngotympanic tube.

The torus tubarius is an elevation of the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx formed by the underlying base of the cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube. The torus tubarius is situated behind the pharyngeal orifice of the auditory tube.
This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.
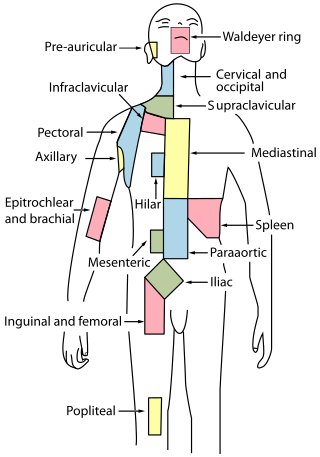
Waldeyer's tonsillar ring is a ringed arrangement of lymphoid organs in the pharynx. Waldeyer's ring surrounds the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate.

The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system.

The fauces, isthmus of fauces, or the oropharyngeal isthmus is the opening at the back of the mouth into the throat. It is a narrow passage between the velum and the base of the tongue.

The pharynx is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea. It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx.

The human palatine tonsils (PT) are covered by stratified squamous epithelium that extends into deep and partly branched tonsillar crypts, of which there are about 10 to 30. The crypts greatly increase the contact surface between environmental influences and lymphoid tissue. In an average adult palatine tonsil the estimated epithelial surface area of the crypts is 295 cm2, in addition to the 45 cm2 of epithelium covering the oropharyngeal surface.

The tonsillar artery is (usually) a branch of the facial artery that represents the main source of arterial blood supply for the palatine tonsil.



















