| Torus tubarius | |
|---|---|
 Auditory tube, laid open by a cut in its long axis (torus tubarius not labeled) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Torus tubarius |
| TA | A05.3.01.012 |
| FMA | 54993 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
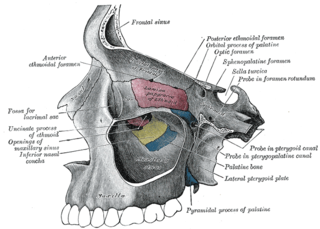
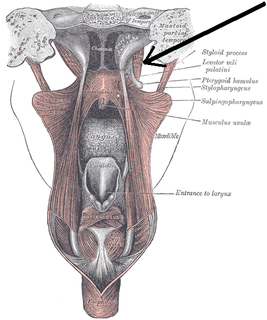
The base of the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube (eustachian tube, pharyngotympanic tube) lies directly under the mucous membrane of the nasal part of the pharynx, where it forms an elevation, the torus tubarius, the torus of the auditory tube, or cushion, behind the pharyngeal orifice of the tube. The torus tubarius is very close to the tubal tonsil, [1] which is sometimes also called the tonsil of (the) torus tubarius. [2] Equating the torus with its tonsil however might be seen as incorrect or imprecise.

Cartilage is a resilient and smooth elastic tissue, a rubber-like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints, and is a structural component of the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the bronchial tubes, the intervertebral discs, and many other body components. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans,collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin.

A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at various body openings such as the eyes, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lip, vagina, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.

The tubal tonsil is one of the four main tonsil groups comprising Waldeyer's tonsillar ring, which also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils, and the pharyngeal tonsils.
Two folds run posteriorly and anteriorly:
- posteriorly, the vertical fold of mucous membrane, the salpingopharyngeal fold, stretches from the lower part of the torus tubarius; it contains the Salpingopharyngeus muscle which originates from the superior border of the medial lamina of the cartilage of the auditory tube, [3] and passes downward and blends with the posterior fasciculus of the palatopharyngeus muscle.
- anteriorly, the second and smaller fold, the salpingopalatine fold, smaller than the salpingopharyngeal fold, contains some fibers of muscle, called salpingopalatine muscle by Simkins (1943), [3] it stretches from the superior border of lateral lamina of the cartilage, anteroinferiorly, to the back of the hard palate. The tensor veli palatini does not contribute to the fold, since the origin is deep to the cartilaginous opening.

The salpingopharyngeus muscle arises from the superior border of the medial cartilage of the pharyngotympanic tube, in the nasal cavity, making the posterior welt of the torus tubarius; it passes downward and blends with the posterior fasciculus of the palatopharyngeus muscle.

The palatopharyngeusmuscle is a small muscle in the roof of the mouth.