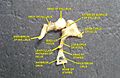
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The Eustachian tube, also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi.

The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.

The mastoid antrum is an air space in the petrous portion of the temporal bone, communicating posteriorly with the mastoid cells and anteriorly with the epitympanic recess of the middle ear via the aditus to mastoid antrum. These air spaces function as sound receptors, provide voice resonance, act as acoustic insulation and dissipation, provide protection from physical damage and reduce the mass of the cranium. The roof is formed by the tegmen antri which is a continuation of the tegmen tympani and separates it from the middle cranial fossa. The lateral wall of the antrum is formed by a plate of bone which is an average of 1.5 cm in adults. The mastoid air cell system is a major contributor to middle ear inflammatory diseases.
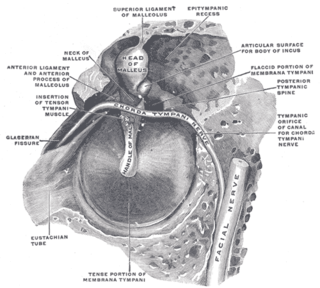
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory (taste) sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic (secretomotor) innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands.

The internal auditory meatus is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear.

The squamous part of temporal bone, or temporal squama, forms the front and upper part of the temporal bone, and is scale-like, thin, and translucent.
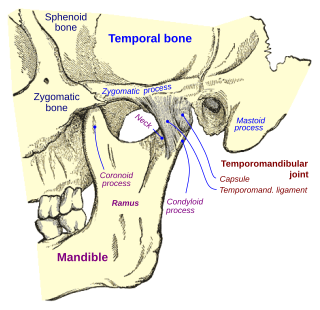
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones.

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone.

The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.

The facial canal is a Z-shaped canal in the temporal bone of the skull. It extends between the internal acoustic meatus and stylomastoid foramen. It transmits the facial nerve.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The anterior tympanic artery is a branch of the maxillary artery. It passes through the petrotympanic fissure to entre the middle ear where it contributes to the formation of the circular anastomosis around the tympanic membrane. It provides arterial supply to part of the lining of the middle ear. It is accompanied by the chorda tympani nerve.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The petrotympanic fissure is a fissure in the temporal bone that runs from the temporomandibular joint to the tympanic cavity.

The mastoid cells are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells is called mastoiditis.
Pierre Charles Huguier was a French surgeon and gynecologist born in Sézanne.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy: