Related Research Articles
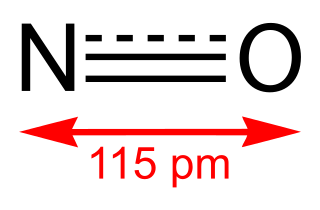
Nitric oxide is a colorless gas with the formula NO. It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical, i.e., it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula. Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a historic class that drew researches which spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding.

Arginase (EC 3.5.3.1, arginine amidinase, canavanase, L-arginase, arginine transamidinase) is a manganese-containing enzyme. The reaction catalyzed by this enzyme is: arginine + H2O → ornithine + urea. It is the final enzyme of the urea cycle. It is ubiquitous to all domains of life.

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.
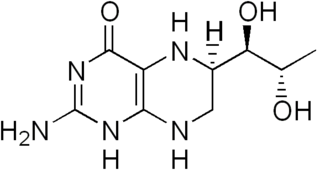
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4, THB), also known as sapropterin (INN), is a cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and is a cofactor for the production of nitric oxide (NO) by the nitric oxide syntheses. Chemically, its structure is that of a (dihydropteridine reductase) reduced pteridine derivative (Quinonoid dihydrobiopterin).

Spermidine is a polyamine compound found in ribosomes and living tissues, and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen.
Argininosuccinate synthase or synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of argininosuccinate from citrulline and aspartate. In humans, argininosuccinate synthase is encoded by the ASS gene located on chromosome 9.

Nicorandil is a vasodilatory drug used to treat angina.

Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS3 gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte adhesion, and platelet aggregation. Therefore, a functional eNOS is essential for a healthy cardiovascular system.
Nitric oxide synthase, inducible is an enzyme which is encoded by the NOS2 gene in humans and mice.
Nitric oxide synthase 1 (neuronal), also known as NOS1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NOS1 gene.

Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1), also known as prostaglandin G/H synthase 1, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 or prostaglandin H2 synthase 1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGS1 gene. In humans it is one of two cyclooxygenases.
Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DYNLL1 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Nitric oxide synthase 1 adaptor protein (NOS1AP) also known as carboxyl-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein (CAPON) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NOS1AP gene.

Guanylate cyclase soluble subunit beta-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCY1B3 gene.

S-Nitrosothiols, also known as thionitrites, are organic compounds or functional groups containing a nitroso group attached to the sulfur atom of a thiol. S-Nitrosothiols have the general formula RSNO, where R denotes an organic group. Originally suggested by Ignarro to serve as intermediates in the action of organic nitrates, endogenous S-nitrosothiols were discovered by Stamler and colleagues and shown to represent a main source of NO bioactivity in vivo. More recently, S-nitrosothiols have been implicated as primary mediators of protein S-nitrosylation, the oxidative modification of Cys thiol that provides ubiquitous regulation of protein function.
Nitric oxide is a molecule and chemical compound with chemical formula of NO. In mammals including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule involved in many physiological and pathological processes. It is a powerful vasodilator with a half-life of a few seconds in the blood. Standard pharmaceuticals such as nitroglycerine and amyl nitrite are precursors to nitric oxide. Low levels of nitric oxide production are typically due to ischemic damage in the liver.
Claudius cells are considered as supporting cells within the organ of Corti in the cochlea. These cells extend from Hensen's cells to the spiral prominence epithelium, forming the outer sulcus. They are in direct contact with the endolymph of the cochlear duct. These cells are sealed via tight junctions that prevent flow of endolymph between them. Boettcher cells are located immediately under Claudius cells in the lower turn of the cochlea.
Arginase, type II is an arginase protein that in humans is encoded by the ARG2 gene.
Gaseous signaling molecules are gaseous molecules that are either synthesised internally (endogenously) in the organism, tissue or cell or are received by the organism, tissue or cell from outside and that are used to transmit chemical signals which induce certain physiological or biochemical changes in the organism, tissue or cell. The term is applied to, for example, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, methane, hydrogen, ethylene, etc.
References
- ↑ Kanazawa, A.; Sunami, K.; Takayama, M.; Nishiura, H.; Tokuhara, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Iguchi, H.; Yamane, H. (Oct 2004). "Probable function of Boettcher cells based on results of morphological study: localization of nitric oxide synthase". Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 124 (554): 12–6. doi:10.1080/03655230410018444. PMID 15513504. S2CID 39636271.
- ↑ Wang XH, Streeter M, Liu YP, Zhao HB (January 2009). "Identification and characterization of pannexin expression in the mammalian cochlea". J. Comp. Neurol. 512 (3): 336–46. doi:10.1002/cne.21898. PMC 2630187 . PMID 19009624.