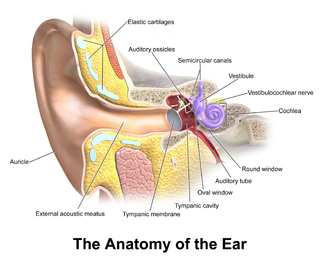
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:

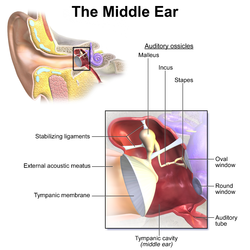
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea.
The ossicles are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" and may refer to any small bone throughout the body, it typically refers specifically to the malleus, incus and stapes of the middle ear.
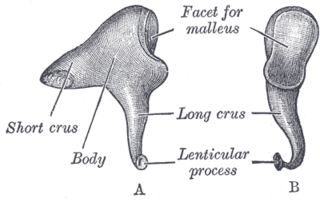
The incus or anvil in the ear is one of three small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The incus receives vibrations from the malleus, to which it is connected laterally, and transmits these to the stapes medially. The incus is named for its resemblance to an anvil.

The stapes or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other tetrapods which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the footplate to transmit sound energy through the oval window into the inner ear. The stapes is the smallest and lightest bone in the human body, and is so-called because of its resemblance to a stirrup.
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit changes in pressure of sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and thence to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. The ear thereby converts and amplifies vibration in the air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles.

The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea.

The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs and the auditory parts of the sensory system.

In vertebrates, an ear is the organ that enables hearing and body balance using the vestibular system. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the auricle and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear, the word "ear" often refers to the external part (auricle) alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ear canal is cleaned via earwax, which naturally migrates to the auricle.

The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or stirrup bone of the middle ear.

The tensor tympani is a muscle within the middle ear, located in the bony canal above the bony part of the auditory tube, and connects to the malleus bone. Its role is to dampen loud sounds, such as those produced from chewing, shouting, or thunder. Because its reaction time is not fast enough, the muscle cannot protect against hearing damage caused by sudden loud sounds, like explosions or gunshots, however some individuals have voluntary control over the muscle, and may tense it pre-emptively.

The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.

The round window is one of the two openings from the middle ear into the inner ear. It is sealed by the secondary tympanic membrane, which vibrates with opposite phase to vibrations entering the inner ear through the oval window. It allows fluid in the cochlea to move, which in turn ensures that hair cells of the basilar membrane will be stimulated and that audition will occur.

The vestibule is the central part of the bony labyrinth in the inner ear, and is situated medial to the eardrum, behind the cochlea, and in front of the three semicircular canals.

The tympanum is an external hearing structure in animals such as mammals, birds, some reptiles, some amphibians and some insects.

The evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles was an evolutionary process that resulted in the formation of the mammalian middle ear, where the three middle ear bones or ossicles, namely the incus, malleus and stapes, are a defining characteristic of mammals. The event is well-documented and important academically as a demonstration of transitional forms and exaptation, the re-purposing of existing structures during evolution.

Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
Electrocochleography is a technique of recording electrical potentials generated in the inner ear and auditory nerve in response to sound stimulation, using an electrode placed in the ear canal or tympanic membrane. The test is performed by an otologist or audiologist with specialized training, and is used for detection of elevated inner ear pressure or for the testing and monitoring of inner ear and auditory nerve function during surgery.
In the auditory system, the columella contributes to hearing in amphibians, reptiles and birds. The columella form thin, bony structures in the interior of the skull and serve the purpose of transmitting sounds from the eardrum. It is an evolutionary homolog of the stapes, one of the auditory ossicles in mammals.
A middle ear implant is a hearing device that is surgically implanted into the middle ear. They help people with conductive, sensorineural or mixed hearing loss to hear.