The ossicles are three bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sound vibrations sent from the ear drum to the fluid-filled labyrinth (cochlea). The absence of the auditory ossicles would constitute a moderate-to-severe hearing loss. The term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone". Though the term may refer to any small bone throughout the body, it typically refers to the malleus, incus, and stapes of the middle ear.
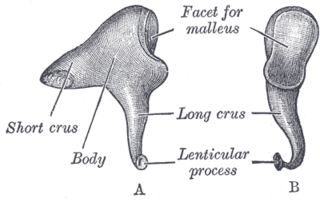
The incus or anvil in the ear is one of three small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The incus receives vibrations from the malleus, to which it is connected laterally, and transmits these to the stapes medially. The incus is named for its resemblance to an anvil.

The stapes or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other tetrapods which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the footplate to transmit sound energy through the oval window into the inner ear. The stapes is the smallest and lightest bone in the human body, and is so-called because of its resemblance to a stirrup.

Derek Bailey was an English avant-garde guitarist and an important figure in the free improvisation movement. Bailey abandoned conventional performance techniques found in jazz, exploring atonality, noise, and whatever unusual sounds he could produce with the guitar. Much of his work was released on his own label Incus Records. In addition to solo work, Bailey collaborated frequently with other musicians and recorded with collectives such as Spontaneous Music Ensemble and Company.
Incus Records is a British record company and label founded by Derek Bailey, Tony Oxley, Evan Parker and Michael Walters that specializes in free jazz and improvised music.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

Evan Shaw Parker is a British tenor and soprano saxophone player who plays free improvisation.
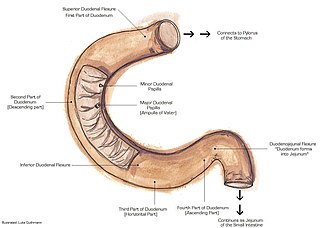
The suspensory muscle of duodenum is a thin muscle connecting the junction between the duodenum and jejunum, as well as the duodenojejunal flexure to connective tissue surrounding the superior mesenteric and coeliac arteries. The suspensory muscle most often connects to both the third and fourth parts of the duodenum, as well as the duodenojejunal flexure, although the attachment is quite variable.

The acromioclavicular joint, or AC joint, is a joint at the top of the shoulder. It is the junction between the acromion and the clavicle. It is a plane synovial joint.

The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are transient structures seen in the embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches support the gills and are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.

In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body.

In humans, the cartilaginous bar of the mandibular arch is formed by what are known as Meckel's cartilages also known as Meckelian cartilages; above this the incus and malleus are developed. Meckel's cartilage arises from the first pharyngeal arch.

The cruciate ligament of the atlas is a cross-shaped ligament in the neck forming part of the atlanto-axial joint. It consists of the transverse ligament of atlas, a superior longitudinal band, and an inferior longitudinal band.
The posterior ligament of the incus is a fibrous band that connects the tip of the short crus of the incus to the fossa incudis, running to the mastoid. The posterior incudal ligament plays an important role in the vibration of the middle ear bones: together with the anterior ligament of the malleus, it forms a pivotal axis around which the ossicles rotate. This rotation conveys vibrations from the tympanum to the oval window on the bony labyrinth.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
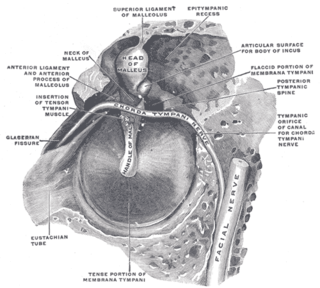
The ligaments of malleus are three ligaments that attach the malleus in the middle ear. They are the anterior, lateral and superior ligaments.
Ligament of incus may refer to:

The malleus, or hammer, is a hammer-shaped small bone or ossicle of the middle ear. It connects with the incus, and is attached to the inner surface of the eardrum. The word is Latin for 'hammer' or 'mallet'. It transmits the sound vibrations from the eardrum to the incus (anvil).














