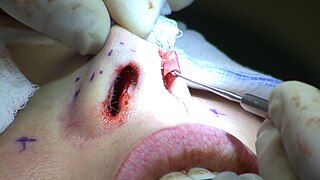
Rhinoplasty, commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery can also treat birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition. Surgery only on the septum is called a septoplasty.

The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose.

In anatomy, the axis is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests.

The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

The nasal septum separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils.

The nasalis muscle is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose. It has a transverse part and an alar part. It compresses the nasal cartilages, and can "flare" the nostrils. It can be used to test the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it.

The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.
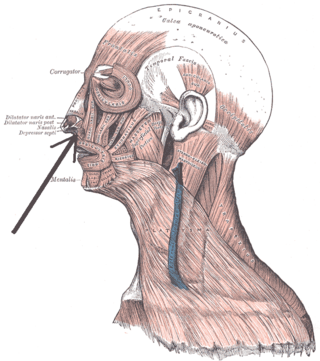
The depressor septi nasi muscle is a muscle of the face. It connects the incisive fossa of the maxilla and the orbicularis oris muscle to the nasal septum of the nose. It draws the ala of the nose downwards, reducing the size of the nostrils.

The dilator naris muscle is a part of the nasalis muscle. It has an anterior and a posterior part. It has origins from the nasal notch of the maxilla and the major alar cartilage, and a single insertion near the margin of the nostril. It controls nostril width, including changes during breathing. Its function can be tested as an analogue for the function of the facial nerve (VII), which supplies it.
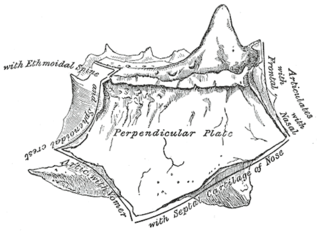
The perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone is a thin, flattened lamina, polygonal in form, which descends from the under surface of the cribriform plate, and assists in forming the septum of the nose; it is generally deflected a little to one or other side. The anterior border articulates with the spine of the frontal bone and the crest of the nasal bones.
The superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.

The external nasal nerve is the terminal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. The external nasal nerve passes inferior-ward through the lateral nasal wall. It provides sensory innervation to the area of skin of the nose between the nasal bones superiorly and the tip of the nose inferiorly.

The basilar part of the occipital bone extends forward and upward from the foramen magnum, and presents in front an area more or less quadrilateral in outline.
The piriform aperture, pyriform aperture, or anterior nasal aperture is a pear-shaped opening in the human skull. Its long axis is vertical, and narrow end upward; in the recent state it is much contracted by the lateral nasal cartilage and the greater and lesser alar cartilages of the nose.
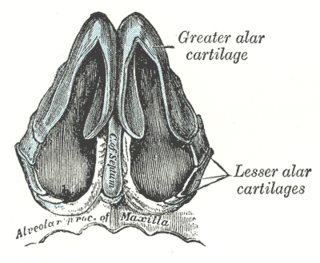
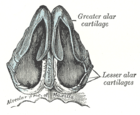
The major alar cartilage is a thin, flexible plate, situated immediately below the lateral nasal cartilage, and bent upon itself in such a manner as to form the medial wall and lateral wall of the nostril of its own side.

The septal nasal cartilage is composed of hyaline cartilage. It is somewhat quadrilateral in form, thicker at its margins than at its center, and completes the separation between the nasal cavities in front.

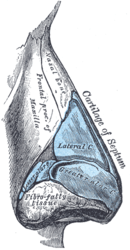
The lateral nasal cartilage is situated below the inferior margin of the nasal bone, and is flattened, and triangular in shape.

The nasal cartilages are structures within the nose that provide form and support to the nasal cavity. The nasal cartilages are made up of a flexible material called hyaline cartilage in the distal portion of the nose. There are five individual cartilages that make up the nasal cavity: septal nasal cartilage, lateral nasal cartilage, major alar cartilage, minor alar cartilage, and vomeronasal cartilage.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

A plate in animal anatomy may refer to several things: