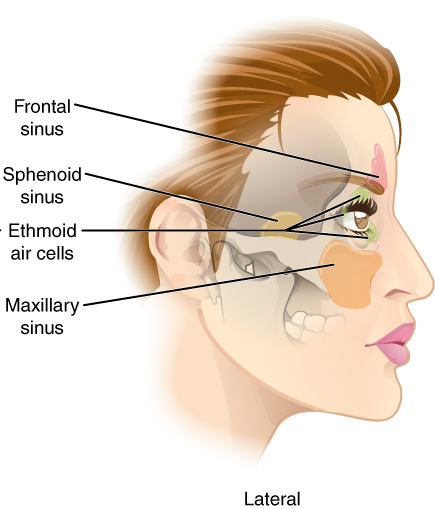
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located.

The ethmoid bone is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye.
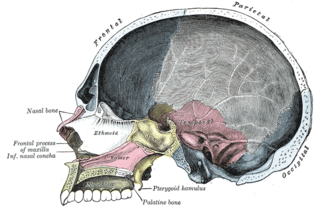
The palatine bones are two irregular bones of the facial skeleton in many animal species. Together with the maxillae they comprise the hard palate.

The internal carotid artery is a major paired artery, one on each side of the head and neck, in human anatomy. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries at cervical vertebral level 3 or 4; the internal carotid artery supplies the brain, while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as face, scalp, skull, and meninges.

The sella turcica is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, orangutans, and gorillas. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa.

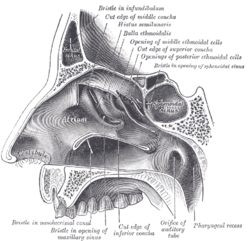
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose.

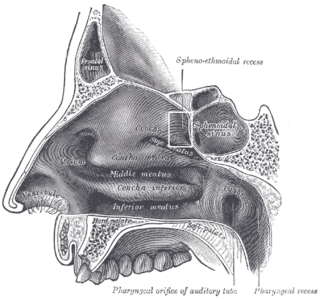
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoidal air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The cells are variable in both size and number in the lateral mass of each of the ethmoid bones and cannot be palpated during an extraoral examination. They are divided into anterior and posterior groups. The ethmoidal air cells are numerous thin-walled cavities situated in the ethmoidal labyrinth and completed by the frontal, maxilla, lacrimal, sphenoidal, and palatine bones. They lie between the upper parts of the nasal cavities and the orbits, and are separated from these cavities by thin bony lamellae.

The maxillary nerve (CN V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxillary, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The sphenoidal conchae are two thin, curved plates, situated at the anterior and lower part of the body of the sphenoid. An aperture of variable size exists in the anterior wall of each, and through this the sphenoidal sinus opens into the nasal cavity.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone; there is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.
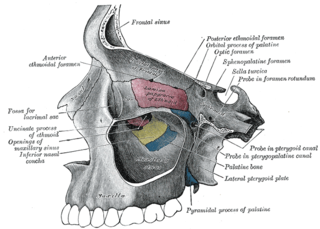
The sphenopalatine foramen is a foramen in the skull that connects the nasal cavity with the pterygopalatine fossa.

The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove. The lesser wings of the sphenoid separate the anterior and middle fossae.

The perpendicular plate of palatine bone is the vertical part of the palatine bone, and is thin, of an oblong form, and presents two surfaces and four borders.

The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is a minimally invasive technique used mainly in neurosurgery and otolaryngology. A neurosurgeon or an otolaryngologist, using an endoscope that is entered through the nose, fixes or removes brain defects or tumors in the anterior skull base. Normally an otolaryngologist performs the initial stage of surgery through the nasal cavity and sphenoid bone; a neurosurgeon performs the rest of the surgery involving drilling into any cavities containing a neural organ such as the pituitary gland.