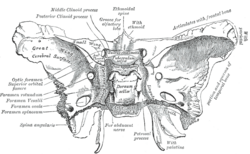
The foramen ovale is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.

In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is a unpaired bone which consists of two portions. These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word frons.

The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone.
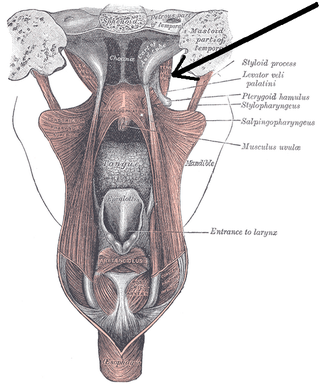
The tensor veli palatini muscle is a thin, triangular muscle of the head that tenses the soft palate and opens the Eustachian tube to equalise pressure in the middle ear.

The foramen spinosum is a small open hole in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone that gives passage to the middle meningeal artery and vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.
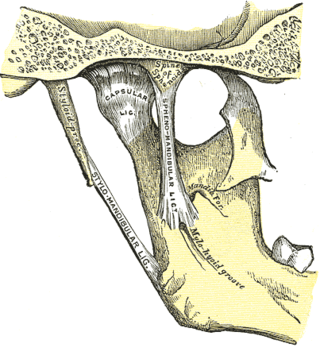
The sphenomandibular ligament is one of the three ligaments of the temporomandibular joint. It is situated medially to - and generally separate from - the articular capsule of the joint. Superiorly, it is attached to the spine of the sphenoid bone; inferiorly, it is attached to the lingula of mandible. The SML acts to limit inferior-ward movement of the mandible.
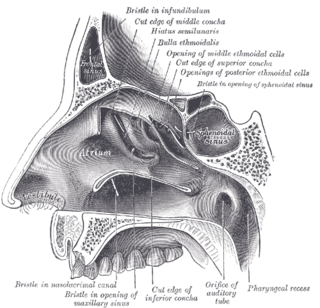
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid, one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The lesser wings of the sphenoid or orbito-sphenoids are two thin triangular plates, which arise from the upper and anterior parts of the body, and, projecting lateralward, end in sharp points [Fig. 1].

The optic foramen is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
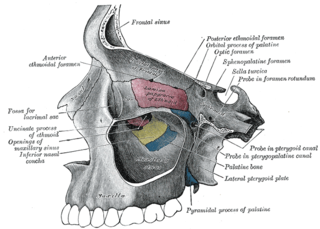
The sphenopalatine foramen is a foramen of the skull that connects the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa. It gives passage to the sphenopalatine artery, nasopalatine nerve, and the superior nasal nerve.

The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove. The lesser wings of the sphenoid separate the anterior and middle fossae.

The dorsum sellae is part of the sphenoid bone in the skull. Together with the basilar part of the occipital bone it forms the clivus.

The carotid groove is an anatomical groove in the sphenoid bone located above the attachment of each great wing of the sphenoid bone. The groove is curved like the italic letter f, and lodges the internal carotid artery and the cavernous sinus.

The pterion is the region where the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones join. It is located on the side of the skull, just behind the temple. It is also considered to be the weakest part of the skull, which makes it clinically significant, as if there is a fracture around the pterion it could be accompanied by an epidural hematoma.

The petrotympanic fissure is a fissure in the temporal bone that runs from the temporomandibular joint to the tympanic cavity.

The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone presents in front a prominent spine, the ethmoidal spine, for articulation with the cribriform plate of the ethmoid; behind this is a smooth surface slightly raised in the middle line, and grooved on either side for the olfactory lobes of the brain.

The irregular bones are bones which, from their peculiar form, cannot be grouped as long, short, flat or sesamoid bones. Irregular bones serve various purposes in the body, such as protection of nervous tissue, affording multiple anchor points for skeletal muscle attachment, and maintaining pharynx and trachea support, and tongue attachment. They consist of cancellous tissue enclosed within a thin layer of compact bone. Irregular bones can also be used for joining all parts of the spinal column together. The spine is the place in the human body where the most irregular bones can be found. There are, in all, 33 irregular bones found here.

The clivus or Blumenbach clivus is a part of the occipital bone at the base of the skull. It is a shallow depression behind the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. It slopes gradually to the anterior part of the basilar occipital bone at its junction with the sphenoid bone. It extends to the foramen magnum. It is related to the pons and the abducens nerve.