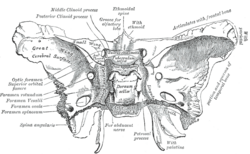
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.

The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior and middle cerebral circulation.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is about 28 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.

The middle meningeal artery is typically the third branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum to supply the dura mater and the calvaria. The middle meningeal artery is the largest of the three (paired) arteries that supply the meninges, the others being the anterior meningeal artery and the posterior meningeal artery.
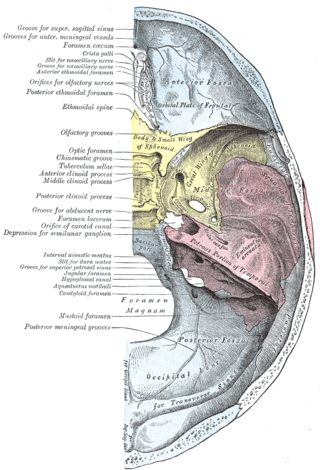
The foramen lacerum is a triangular hole in the base of skull. It is located between the sphenoid bone, the apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone, and the basilar part of the occipital bone.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.
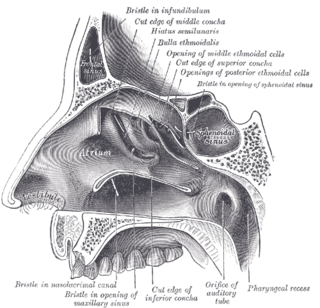
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus in the body of the sphenoid bone. It is one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The two sphenoid sinuses are separated from each other by a septum. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward.

The lesser wings of the sphenoid or orbito-sphenoids are two thin triangular plates, which arise from the upper and anterior parts of the body, and, projecting lateralward, end in sharp points [Fig. 1].

The optic foramen is the opening to the optic canal. The canal is located in the sphenoid bone; it is bounded medially by the body of the sphenoid and laterally by the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
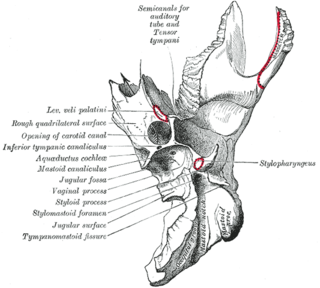
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into the cranial cavity.

The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body. In other mammals, it is a separate bone, the petrosal bone.

The basilar part of the occipital bone extends forward and upward from the foramen magnum, and presents in front an area more or less quadrilateral in outline.

The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

Along the posterior part of the lateral margin of the carotid groove of the sphenoid bone, in the angle between the body and great wing, is a ridge of bone, called the lingula.

The anterior clinoid process is a posterior projection of the sphenoid bone at the junction of the medial end of either lesser wing of sphenoid bone with the body of sphenoid bone. The bilateral processes flank the sella turcica anteriorly.

The deep temporal arteries are two arteries of the head. They ascend between the temporalis muscle and the pericranium. They anastomose with the middle temporal artery, among other vessels. They supply the temporalis muscle.

The body of the sphenoid bone, more or less cubical in shape, is hollowed out in its interior to form two large cavities, the sphenoidal sinuses, which are separated from each other by a septum.