The stylomastoid foramen is a foramen between the styloid and mastoid processes of the temporal bone of the skull. It is the termination of the facial canal, and transmits the facial nerve, and stylomastoid artery. Facial nerve inflammation in the stylomastoid foramen may cause Bell's palsy.

The jugular fossa is a deep depression in the inferior part of the temporal bone at the base of the skull. It lodges the bulb of the internal jugular vein.

The internal auditory meatus is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear.

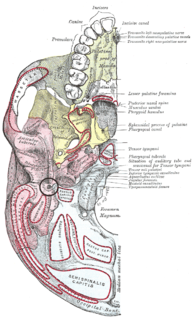
The inferior orbital fissure is formed by the sphenoid bone and the maxilla. It is located posteriorly along the boundary of the floor and lateral wall of the orbit. It transmits a number of structures, including:
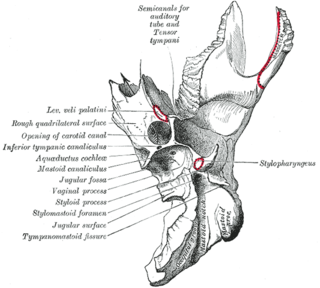
In the lateral part of the jugular fossa of the temporal bone is the mastoid canaliculus for the entrance of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve.
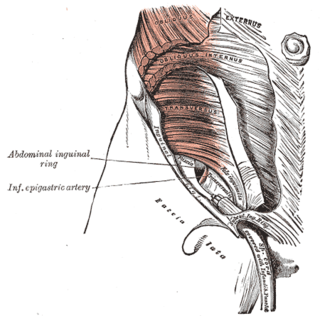
The transversalis fascia is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.

The zygomaticofrontal suture is the cranial suture between the zygomatic bone and the frontal bone. The suture can be palpated just lateral to the eye.

The occipitomastoid suture or occipitotemporal suture is the cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.

Along the posterior part of the lateral margin of the carotid groove of the sphenoid bone, in the angle between the body and great wing, is a ridge of bone, called the lingula.
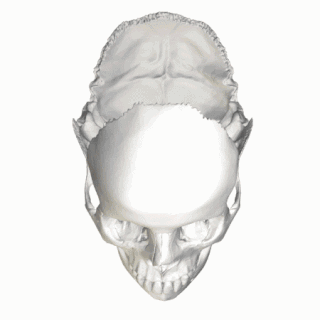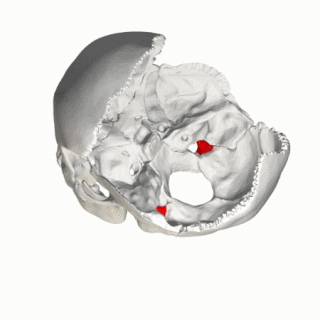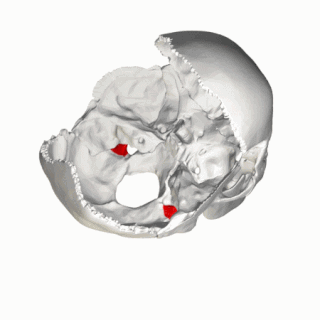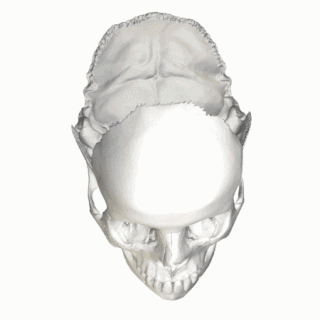
The jugular process is a quadrilateral or triangular bony plate projecting lateralward from the posterior half of the occipital condyle; it is a part of the lateral part of the occipital bone.

The tuberculum sellae is a part of the sphenoid bone that is an elevation behind the chiasmatic groove. A variable slight to prominent median elevation forming the posterior boundary of the chiasmatic groove and the anterior boundary of the hypophysial fossa.

The carotid groove is an anatomical groove in the sphenoid bone located above the attachment of each great wing of the sphenoid bone. The groove is curved like the italic letter f, and lodges the internal carotid artery and the cavernous sinus.

The inner surface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus; in it may be seen the opening of the mastoid foramen.

Along the internal surface of the occipital bone, at the point of intersection of the four divisions of the cruciform eminence, is the internal occipital protuberance. Running transversely on either side is a groove for the transverse sinus.

The anterior nasal spine, or anterior nasal spine of maxilla, is a bony projection in the skull that serves as a cephalometric landmark. The anterior nasal spine is the projection formed by the fusion of the two maxillary bones at the intermaxillary suture. It is placed at the level of the nostrils, at the uppermost part of the philtrum and rarely fractures.

The sphenoidal spine is a downwardly directed process at the apex of the great wings of the sphenoid bone that serves as the origin of the sphenomandibular ligament.

The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.

The lesser tubercle of the humerus, although smaller, is more prominent than the greater tubercle: it is situated in front, and is directed medially and anteriorly.

Just before each crus of the penis meets its fellow, it presents a slight enlargement, which Georg Ludwig Kobelt named the bulb of the corpus cavernosum penis. The bulb of penis is also known as the urethral bulb.
The incisive papilla is a projection on the palate near the incisors.
















