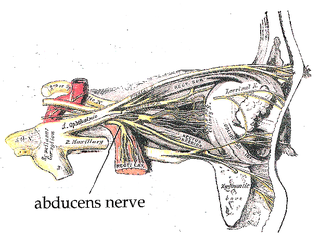
The abducens nerve is the sixth cranial nerve (CNVI), in humans, that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, responsible for outward gaze. It is a somatic efferent nerve.

The trochlear nerve, also called the fourth cranial nerve or CN IV, is a motor nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pulley-like trochlea.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, check ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
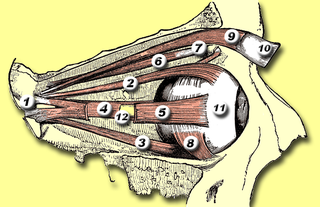
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular muscle innervated by the trochlear nerve.

Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes, helping in acquiring, fixating and tracking visual stimuli. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep.

In anatomy, a process is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage, or to fit, with another vertebra. The word is used even at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as apophysis, tubercle, or protuberance.

The superior orbital fissure is a foramen in the skull, although strictly it is more of a cleft, lying between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone.
The orbital or horizontal part of the frontal bone consists of two thin triangular plates, the orbital plates, which form the vaults of the orbits, and are separated from one another by a median gap, the ethmoidal notch.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The ophthalmic nerve (V1) is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). It has three branches that provide sensory innervation to the eye, skin of the upper face and anterior scalp.

The lesser wings of the sphenoid or orbito-sphenoids are two thin triangular plates, which arise from the upper and anterior parts of the body, and, projecting lateralward, end in sharp points [Fig. 1].
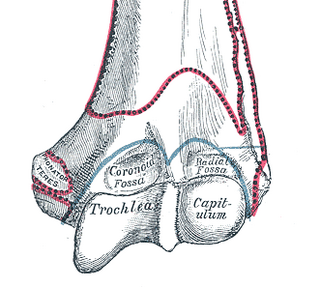
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm.

The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.
The trochlear notch, also known as semilunar notch and greater sigmoid cavity, is a large depression in the upper extremity of the ulna that fits the trochlea of the humerus as part of the elbow joint. It is formed by the olecranon and the coronoid process.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It branches from the ophthalmic artery near the trochlea of the superior oblique muscle in the orbit.
The Orbital Fascia forms the periosteum of the orbit.
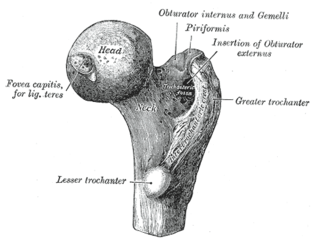
The femoral head is the highest part of the thigh bone (femur). It is supported by the femoral neck.

The humeroulnar joint, is part of the elbow-joint. It is composed of two bones, the humerus and ulna, and is the junction between the trochlear notch of ulna and the trochlea of humerus. It is classified as a simple hinge-joint, which allows for movements of flexion, extension and circumduction. Owing to the obliquity of the trochlea of the humerus, this movement does not take place in the antero-posterior plane of the body of the humerus.

The intercondylar fossa of femur is a deep notch between the rear surfaces of the medial and lateral epicondyle of the femur, two protrusions on the distal end of the femur that joins the knee. On the front of the femur, the condyles are but much less prominent and are separated from one another by a smooth shallow articular depression called the patellar surface because it articulates with the posterior surface of the patella (kneecap).
Fovea is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.

















