| Tupiniquins Ecological Station | |
|---|---|
| Estação Ecológica dos Tupiniquins | |
IUCN category Ia (strict nature reserve) | |
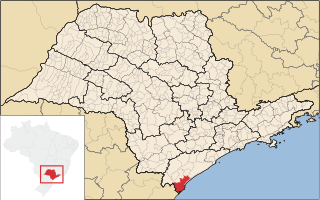
| Nearest city | Iguape, São Paulo |
| Coordinates | 25°04′44″S47°13′01″W / 25.079°S 47.217°W Coordinates: 25°04′44″S47°13′01″W / 25.079°S 47.217°W |
| Area | 1,728 hectares (4,270 acres) |
| Designation | Ecological station |
| Created | 21 July 1986 |
Tupiniquins Ecological Station (Portuguese : Estação Ecológica dos Tupiniquins) is a coastal marine ecological station on the coast of São Paulo State, Brazil.
Portuguese is a Western Romance language originating in the Iberian Peninsula. It is the sole official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Angola, and São Tomé and Príncipe. It also has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau in China. As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese and Portuguese creole speakers are also found in Goa, Daman and Diu in India; in Batticaloa on the east coast of Sri Lanka; in the Indonesian island of Flores; in the Malacca state of Malaysia; and the ABC islands in the Caribbean where Papiamento is spoken, while Cape Verdean Creole is the most widely spoken Portuguese-based Creole. Reintegrationists maintain that Galician is not a separate language, but a dialect of Portuguese. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone" (Lusófono).

An ecological station in Brazil is a type of protected area of Brazil as defined by the National System of Conservation Units (SNUC). The purpose is to preserve untouched representative samples of the different biomes in Brazil.

São Paulo is one of the 26 states of the Federative Republic of Brazil and is named after Saint Paul of Tarsus. As the richest Brazilian state and a major industrial complex, often dubbed the "locomotive of Brazil", the state is responsible for 33.9% of the Brazilian GDP. São Paulo also has the second highest Human Development Index (HDI) and GDP per capita, the fourth lowest infant mortality rate, the third highest life expectancy, and the third lowest rate of illiteracy among the federative units of Brazil, being by far, the safest state in the country. The homicide rate is 3.8 per 100 thousand as of 2018, almost 1/4 of the Brazilian rate. São Paulo alone is richer than Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay and Bolivia combined. If São Paulo were an independent country, its nominal GDP would be ranked among the top 20 in the world. The economy of São Paulo State is the most developed in Brazil.