History
Middle Bronze
Turukkum was regarded by the Kingdom of Upper Mesopotamia as a constant threat, during the reign of Amorite Shamshi-Adad I (1813-1782 BCE) and his son and successor Ishme-Dagan (1781-1750 BCE). The Turukkaeans were allied to the Land of Ahazum, and they gathered at the town of Ikkallum to face the army of Ishme-Dagan, as Shamshi-Adad wrote in a letter to his other son Yasmah-Adad. Ishme-Dagan destroyed the army reporting "Not one man escaped". [1] Turukkum seems to have been made up of a collection of kingdoms with mixed populations, possibly mostly Hurrian but also heavily Semitic. [2]
The Turukkaeans were reported to have sacked the city of Mardaman, apparently under Hurrian rule, around the year 1769/68 BCE. [3] Babylon's defeat of Turukku was celebrated in the 37th year of Hammurabi's reign (c. 1773 BCE).
A significant early reference to them is an inscription by the Babylonian king Hammurabi, (r. circa 1792 – c. 1752 BCE) that mentions a kingdom named Tukriš(UET I l. 46, iii–iv, 1–4), alongside Gutium, Subartu and another name that is usually reconstructed as Elam. Other texts from the same period refer to the kingdom as Tukru.
Iron Age
By the early part of the 1st millennium BCE, names such as Turukkum, Turukku and ti-ru-ki-i are being used for the same region. In a broader sense, names such as Turukkaean been used in a generic sense to mean "mountain people" or "highlanders".
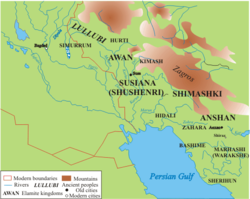
Tukru or Turukkum was said to have spanned the north-east edge of Mesopotamia and an adjoining part of the Zagros Mountains. In particular, they were associated with the Lake Urmia basin and the valleys of the north-east Zagros. They were therefore located north of ancient Lullubi, and at least one Neo-Assyrian (9th to 7th centuries BCE) text refers to the whole area and its peoples as "Lullubi-Turukki" (VAT 8006).