
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.

Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.

The MultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens, MMC is based on a surface-contact low pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack substrate assembly, and is therefore much smaller than earlier systems based on high pin-count parallel interfaces using traditional surface-mount assembly such as CompactFlash. Both products were initially introduced using SanDisk NOR-based flash technology. MMC is about the size of a postage stamp: 32 mm × 24 mm × 1.4 mm. MMC originally used a 1-bit serial interface, but newer versions of the specification allow transfers of 4 or 8 bits at a time. MMC can be used in many devices that can use Secure Digital (SD) cards.

A USB flash drive is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface. It is typically removable, rewritable and much smaller than an optical disc. Most weigh less than 30 g (1 oz). Since first appearing on the market in late 2000, as with virtually all other computer memory devices, storage capacities have risen while prices have dropped. As of March 2016, flash drives with anywhere from 8 to 256 gigabytes (GB) were frequently sold, while 512 GB and 1 terabyte (TB) units were less frequent. As of 2018, 2 TB flash drives were the largest available in terms of storage capacity. Some allow up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the exact type of memory chip used, and are thought to physically last between 10 and 100 years under normal circumstances.
Large-file support (LFS) is the term frequently applied to the ability to create files larger than either 2 or 4 GiB on 32-bit filesystems.

In computing, a file system or filesystem is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one large body of data with no way to tell where one piece of data stopped and the next began, or where any piece of data was located when it was time to retrieve it. By separating the data into pieces and giving each piece a name, the data are easily isolated and identified. Taking its name from the way a paper-based data management system is named, each group of data is called a "file". The structure and logic rules used to manage the groups of data and their names is called a "file system."

The USB mass storage device class is a set of computing communications protocols, specifically a USB Device Class, defined by the USB Implementers Forum that makes a USB device accessible to a host computing device and enables file transfers between the host and the USB device. To a host, the USB device acts as an external hard drive; the protocol set interfaces with a number of storage devices.

Das U-Boot is an open-source, primary boot loader used in embedded devices to package the instructions to boot the device's operating system kernel. It is available for a number of computer architectures, including 68k, ARM, Blackfin, MicroBlaze, MIPS, Nios, SuperH, PPC, RISC-V and x86.
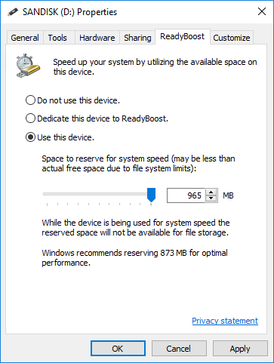
ReadyBoost is a disk caching software component developed by Microsoft for Windows Vista and included in later versions of Windows. ReadyBoost enables NAND memory mass storage CompactFlash, SD card, and USB flash drive devices to be used as a cache between the hard drive and random access memory in an effort to increase computing performance. ReadyBoost relies on the SuperFetch and also adjusts its cache based on user activity. ReadyDrive for hybrid drives is implemented in a manner similar to ReadyBoost.

A live USB is a portable USB-attached external data storage device containing a full operating system that can be booted from. The term is reminiscent of USB flash drives but may encompass an external hard disk drive or solid-state drive, though they may be referred to as "live HDD" and "live SSD" respectively. They are the evolutionary next step after live CDs, but with the added benefit of writable storage, allowing customizations to the booted operating system. Live USBs can be used in embedded systems for system administration, data recovery, or test driving, and can persistently save settings and install software packages on the USB device.

A memory card reader is a device for accessing the data on a memory card such as a CompactFlash (CF), Secure Digital (SD) or MultiMediaCard (MMC). Most card readers also offer write capability, and together with the card, this can function as a pen drive.
exFAT is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specification. Microsoft owns patents on several elements of its design.

NTFS-3G is an open-source cross-platform implementation of the Microsoft Windows NTFS file system with read/write support. NTFS-3G often uses the FUSE file system interface, so it can run unmodified on many different operating systems. It is runnable on Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenSolaris, illumos, BeOS, QNX, WinCE, Nucleus, VxWorks, Haiku, MorphOS, Minix, macOS and OpenBSD. It is licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is a partial fork of ntfsprogs and is under active maintenance and development.

Eye-Fi was a company based in Mountain View, California, that produced SD memory cards with Wi-Fi capabilities. Using an Eye-Fi card inside a digital camera, one could wirelessly and automatically upload digital photos to a local computer or a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet computer. The company ceased business in 2016.

Paragon Software Group is a German software company that develops hard drive management software, low-level file system drivers and storage technologies. The Smart Handheld Device Division (SHDD) offers multilingual dictionaries, multilingual handwriting recognition, weather information, and two-way data synchronization with desktop devices.

Datalight was a privately held software company specializing in power failsafe and high performance software for preserving data integrity in embedded systems. The company was founded in 1983 by Roy Sherrill, and is headquartered in Bothell, Washington. As of 2019 the company is a subsidiary of Tuxera under the name of Tuxera US Inc.














