The Mali Empire was an empire in West Africa from c. 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws, and customs.
Sundiata Keita was a prince and founder of the Mali Empire. He was also the great-uncle of the Malian ruler Mansa Musa, who is usually regarded as the wealthiest person of all time, although there are no reliable ways to accurately calculate his wealth.
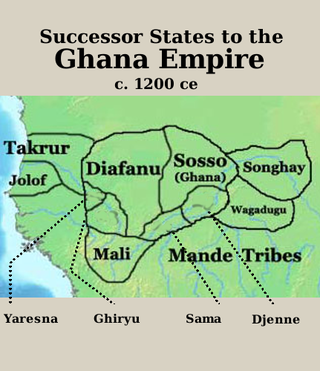
Soumaoro Kanté was a 13th-century king of the Sosso people. Seizing Koumbi Saleh, the capital of the recently defunct Ghana Empire, Soumaoro Kanté proceeded to conquer several neighboring states, including the Mandinka people in what is now Mali. However, the Mandinka prince Sundiata Keita built a coalition of smaller kingdoms to oppose him at the Battle of Kirina, defeating the Sosso and leaving Sundiata's new Mali Empire dominant in the region.
The Battle of Kirina, also known as the Battle of Krina or siege of Karina, was a confrontation between Sosso king Sumanguru Kanté and Mandinka prince Sundiata Keita. Sundiata Keita's forces roundly defeated those of Sumanguru Kanté, guaranteeing the pre-eminence of Keita's new Mali Empire over West Africa.
Sunjata is an epic poem of the Malinke people that tells the story of the hero Sundiata Keita, the founder of the Mali Empire. The epic is an instance of oral tradition, going back to the 13th century and narrated by generations of jelis (griots). There is no single or authoritative version. Material pertaining to the epic first began to be collected during the early 20th century in French Sudan, notably by the French elite school École William Ponty, resulting in the "modern" version of the tale as considered standard today, based on the oral account by Djeli Mamoudou Kouyate, a jeli or traditional oral historian, translated into French by Djibril Tamsir Niane in 1960.
Djibril Tamsir Niane was a Guinean historian, playwright, and short story writer.

Siby is a village and rural commune in the Cercle of Kati in the Koulikoro Region of southern Mali. The commune contains 21 villages and in the 2009 census had a population of 26,632. The village lies 50 km southwest of the capital, Bamako, on the plain to the south of the Monts Mandingues. The RN5 road that links Bamako with Siguiri in Guinea runs through the village.

Kouroukan Fouga, or Kurukan Fuga, was the constitution of the Mali Empire created after the Battle of Krina (1235) by an assembly of nobles to create a government for the newly established empire, according to the Epic of Sundiata. According to oral tradition of the jelis of Mali and Guinea, the Kouroukan Fouga established the federation of Mandinka clans under one government, outlined how it would operate and established the laws by which the people would live. The name Kurukan Fuga is a toponym, translating to "clearing on granite/lateritic rock", referring to the plain near where the narrative has Sundiata Keita present the charter. This is often claimed to have been near the town of Ka-ba, following the interpretation of Djibril Tamsir Niane, but other scholars have argued that oral histories more commonly place the event at nearby Dakajalan.
Faama is a Mandinka word meaning "father," "leader," or "king". It was commonly used within the area of pre-imperial Mali. The title spread into areas conquered by Mali and was later used by the Bamana Empire and the Wassoulou Empire of Samori Toure and non-Mandinka groups in the Kenedougou Empire.

Pre-imperial Mali refers to the period of history before the establishment of the Mali Empire, an African empire located mostly in present-day Mali, in c. 1235.
Mande Bori, also known as Mande Bakari and known in Arabic as Abu Bakr, is a heroic figure in Mande oral tradition who was involved in the founding of the Mali Empire. He was the brother and right-hand man of Sunjata, the founder of the empire, and served as the empire's kankoro-sigui, an office that has been translated as "viceroy" or "lieutenant-general". Though Mande Bori never himself reigned as mansa, his grandsons Musa and Suleyman ruled the Mali Empire at the apex of its power and prestige, and he is often erroneously cited as Mansa Abu Bakr II.
Tiramakhan Traore was a 13th-century general in the Mali Empire who served under Sundiata Keita. Traore expanded the power of Mali westward and set up the Kabu Empire. In his conquest of the region, he is reported to have defeated the Bainuk king Kikikor and annexed his state. The Guelowar royal family, including the royal family of Kaabu prior to their defeat at the Battle of Kansala, claimed descent from Tiramakhan Traore.
The military history of the Mali Empire is that of the armed forces of the Mali Empire, which dominated Western Africa from the mid 13th to the late 15th century. The military culture of the empire's driving force, Mandinka people, influenced many later states in West Africa including break-away powers such as the Songhay and Jolof empires. Institutions from the Mali Empire also survived in the 19th century army of Samory Ture who saw himself as the heir to Old Mali's legacy.

Kangaba is a town, commune, and seat of the Kangaba Cercle in the Koulikoro Region of south-western Mali.
Sassouma Bereté was the first wife of the 13th century King of Mali Maghan Kon Fatta, the father of Sundiata Keita.
Dankaran Touman was the first son of Naré Maghann Konaté in the Malian epic of Sundiata. He was also the King of Manden before the establishment of the Mali Empire.

Manding, Manden or even Mandé is a region located in West Africa, a space between southern Mali and eastern Guinea. It is the historic home of the Mandinka community.
The Kouyate family is a dynasty of jelis (griots) that is native to West Africa. It has been prominent since the 13th century, when its founder took part in the founding of the Mali Empire.
Sogolon Wulen Condé of Dò ni Kiri, commonly known as Sogolon Condé, was a 13th-century princess of Imperial Mali, and one of the prominent women portrayed in the Epic of Sundiata. Her trials and tribulations are well preserved in the epic. She was the second wife of Faama (King) Naré Maghann Konaté, and mother of Mansa Sundiata Keita, founder of the Mali Empire in the 13th century. According to Bamba Suso and Banna Kanute, Sogolong's father was Sankarang Madiba Konte, also known as Faa Ganda, a descendant of Khulubu Konte. In the epic, Sogolon is portrayed as the daughter of the "buffalo woman" –so-called because of her "ugliness" and hunchback, and so was Sogolong. The griots of Guinea refer to Sogolon as the younger sister of Do Kamissa. In many parts of the Senegambia region, and Mali, Sogolon is regarded as her daughter. As well as her physical deformities and "ugliness", Sogolon also gave birth to a disabled son (Sundiata), and was ridiculed for that. Following the death of her husband Naré Maghann Konaté, her co-wife, the politically ambitious Sassouma Bereté, Naré Maghann's first wife along with their first son Dankaran Toumani Keïta, plotted against Sogolon and her children, including assassination attempts on their lives. Fearing that the new King Dankaran and his mother Sassouma could inflict harm upon her and her children, Sogolon went into exile with her children to protect them from harm. Due to the power and influence of Dankaran and his mother, Sogolon and her children were refused asylum by many states within the Ghana Empire they traversed seeking protection. She was eventually granted asylum by the King of Mema Mansa Farin Tunkara. In Mema, Sogolon encouraged his disabled son Sundiata to fulfill his destiny, and return to Mali (Manden) and take the throne.
The history of the Mali Empire begins when the first Mande people entered the Manding region during the period of the Ghana Empire. After its fall, the various tribes established independent chiefdoms. In the 12th century, these were briefly conquered by the Sosso Empire under Soumaoro Kante. He was in turn defeated by a Mande coalition led by Sundiata Keita, who founded the Mali Empire.