Related Research Articles

In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via hardware such as a button or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system.
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers and was the default filesystem for MS-DOS and Windows 9x operating systems. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. FAT was replaced with NTFS as the default file system on Microsoft operating systems starting with Windows XP. Nevertheless, FAT continues to be used on flash and other solid-state memory cards and modules, many portable and embedded devices because of its compatibility and ease of implementation.

This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events.
86-DOS is a discontinued operating system developed and marketed by Seattle Computer Products (SCP) for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.
Apple DOS is the family of disk operating systems for the Apple II series of microcomputers from late 1978 through early 1983. It was superseded by ProDOS in 1983. Apple DOS has three major releases: DOS 3.1, DOS 3.2, and DOS 3.3; each one of these three releases was followed by a second, minor "bug-fix" release, but only in the case of Apple DOS 3.2 did that minor release receive its own version number, Apple DOS 3.2.1. The best-known and most-used version is Apple DOS 3.3 in the 1980 and 1983 releases. Prior to the release of Apple DOS 3.1, Apple users had to rely on audio cassette tapes for data storage and retrieval.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called boot manager and bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer.
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volume partition, whereas, on unpartitioned devices, such as floppy disks, it describes the entire medium. A basic BPB can appear and be used on any partition, including floppy disks where its presence is often necessary; however, certain filesystems also make use of it in describing basic filesystem structures. Filesystems making use of a BIOS parameter block include FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, HPFS, and NTFS. Due to different types of fields and the amount of data they contain, the length of the BPB is different for FAT16, FAT32, and NTFS boot sectors. Combined with the 11-byte data structure at the very start of volume boot records immediately preceding the BPB or EBPB, this is also called FDC descriptor or extended FDC descriptor in ECMA-107 or ISO/IEC 9293.

IBMBIO.COM is a system file in many DOS operating systems. It contains the system initialization code and all built-in device drivers. It also loads the DOS kernel (IBMDOS.COM) and optional pre-loadable system components, displays boot menus, processes configuration files and launches the shell.
This article details versions of MS-DOS, IBM PC DOS, and at least partially compatible disk operating systems. It does not include the many other operating systems called "DOS" which are unrelated to IBM PC compatibles.

Microsoft Anti-Virus (MSAV) is an antivirus program introduced by Microsoft for its MS-DOS operating system. The program first appeared in MS-DOS version 6.0 (1993) and last appeared in MS-DOS 6.22. The first version of the antivirus program was basic, had no inbuilt update facility and could scan for 1,234 different viruses. Microsoft Anti-Virus for Windows (MWAV), included as part of the package, was a front end that allowed MSAV to run properly on Windows 3.1x.

AIDS, also known as Aids Info Disk or PC Cyborg Trojan, is a DOS Trojan horse whose payload mungs and encrypts the names of all directories on drive C:. It was developed by Dr. Joseph Popp, an evolutionary biologist who graduated from Harvard. The virus was isolated in 1989.

Stoned is a boot sector computer virus created in 1987. It is one of the first viruses and is thought to have been written by a student in Wellington, New Zealand. By 1989 it had spread widely in New Zealand and Australia, and variants became very common worldwide in the early 1990s.
MSX-DOS is a discontinued disk operating system developed by Microsoft for the 8-bit home computer standard MSX, and is a cross between MS-DOS 1.25 and CP/M-80 2.
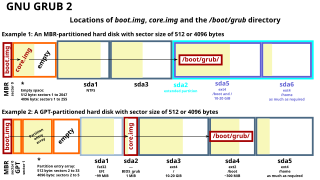
A volume boot record (VBR) is a type of boot sector introduced by the IBM Personal Computer. It may be found on a partitioned data storage device, such as a hard disk, or an unpartitioned device, such as a floppy disk, and contains machine code for bootstrapping programs stored in other parts of the device. On non-partitioned storage devices, it is the first sector of the device. On partitioned devices, it is the first sector of an individual partition on the device, with the first sector of the entire device being a Master Boot Record (MBR) containing the partition table.
In computing, sys is a command used in many operating system command-line shells and also in Microsoft BASIC.

A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses.
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.
The FAT file system is a file system used on MS-DOS and Windows 9x family of operating systems. It continues to be used on mobile devices and embedded systems, and thus is a well suited file system for data exchange between computers and devices of almost any type and age from 1981 through the present.