Related Research Articles

Phoneutria is a genus of spiders in the family Ctenidae of potential medical significance to humans. They are mainly found in northern South America, with one species in Central America. Members of the genus are commonly referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders. Other English names include armed spiders and banana spiders.
A latrotoxin is a high-molecular mass neurotoxin found in the venom of spiders of the genus Latrodectus and also found in the venom of spider species, Steatoda nobilis. Latrotoxins are the main active components of the venom and are responsible for the symptoms of latrodectism.
Poneratoxin is a paralyzing neurotoxic peptide made by the bullet ant Paraponera clavata. It prevents inactivation of voltage gated sodium channels and therefore blocks the synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. Specifically, poneratoxin acts on voltage gated sodium channels in skeletal muscle fibers, causing paralysis, and nociceptive fibers, causing pain. It is rated as a 4 plus on the Schmidt sting pain index, the highest possible rating with that system, and its effects can cause waves of pain up to twelve hours after a single sting. Schmidt describes it as "pure, intense, brilliant pain...like walking over flaming charcoal with a three-inch nail embedded in your heel." It is additionally being studied for its uses in biological insecticides.

A spider bite, also known as arachnidism, is an injury resulting from the bite of a spider. The effects of most bites are not serious. Most bites result in mild symptoms around the area of the bite. Rarely they may produce a necrotic skin wound or severe pain.

Phoneutria nigriventer is a species of medically significant spider in the family Ctenidae, found in South America. Along with other members of the genus, they are often referred to as Brazilian wandering spiders.
Tityustoxin is a toxin found in the venom of scorpions from the subfamily Tityinae. By binding to voltage-dependent sodium ion channels and potassium channels, they cause sialorrhea, lacrimation and rhinorrhea.
Phoneutria keyserlingi is a species of spiders in the family Ctenidae, found in Brazil.
Phoneutria pertyi is a species of spiders in the family Ctenidae, found in Brazil.
Phoneutria nigriventer toxin-3 is more commonly referred to as PhTx3.
BmKAEP is a neurotoxin from the venom of the Manchurian scorpion (Mesobuthus martensii). It is a β-toxin, which shift the activation voltage of sodium channels towards more negative potentials.
Hanatoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the Grammostola spatulata tarantula. The toxin is mostly known for inhibiting the activation of voltage-gated potassium channels, most specifically Kv4.2 and Kv2.1, by raising its activation threshold.

Cupiennius salei, commonly called the tiger wandering spider, is a large spider belonging to a group of wandering spiders found in Central America, although this species is specifically from Eastern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize and Honduras. The species was accidentally introduced into Germany in the early 20th century from banana plantations in Central America. In the mid-1950s it was realised that the spider is an ideal model for biological research because of its large size, inactive behaviour, and ease of breeding in laboratories. From an initial 1963 publication on its biological characteristics, it has become the most studied species of spider. Furthermore, the spider is now known to produce a complex neurotoxic venom, such as cupiennins and CSTX, of which a peptide called CsTx-1 is highly potent for paralysing its prey. Its toxin has also become one of the most studied among those of venomous spiders. As the spider does not produce a web for trapping prey, being venomous is its primary strategy for prey capture. It is known to prey on a wide range of insects and small vertebrates.
CSTX is a name given to a group of closely related neurotoxic peptides present in the venom of the wandering spider Cupiennius salei. There are twenty types so far described for this protein group. However, some are reclassified into cupiennins group of toxin, including CSTX-3, -4, -5, and -6, because of their chemical affinity. The first thirteen were isolated and identified in 1994 by Lucia Kuhn-Nentwig, Johann Schaller, and Wolfgang Nentwig of the Zoological Institute at the University of Bern, Switzerland. The different types are most likely the products of splicing variant of the same gene. They are all L-type calcium channel blockers, and also exhibit cytolytic activity by forming an alpha-helix across the cell membrane in mammalian neurons. They also inhibit voltage-gated calcium channels in insect neurons.
Oxotoxins, or oxytoxins, are a group of neurotoxins present in the venom of lynx spiders belonging to the genus Oxyopes, hence the name oxytoxin. They are disulfide-rich peptides. Only two types are so far reported from two different species, the larger oxytoxin 1 (OxyTx1) from Oxyopes kitabensis, and the smaller oxytoxin 2 (OxyTx2) from Oxyopes lineatus. OxyTx1, the first known oxytoxin, was discovered in 2002. It was found to enhance the lethal efficacy of the spider venom by acting together with oxyopinins. It is composed of 69 amino acid residue, which are cross-linked by five disulfide bridges. It is a large peptide having a molecular mass of 8059.2 Da; but shows the size of 9,109.4 Da due to the presence of disulfide bridges. It is a potent insecticide, but non-toxic to mice up to 1 μg/20-g mouse. It acts synergistically with oxyopinins of the same venom to increase the insecticidal effect.
Tamulotoxin is a venomous neurotoxin from the Indian Red Scorpion.
The pathophysiology of a spider bite is due to the effect of its venom. A spider envenomation occurs whenever a spider injects venom into the skin. Not all spider bites inject venom – a dry bite, and the amount of venom injected can vary based on the type of spider and the circumstances of the encounter. The mechanical injury from a spider bite is not a serious concern for humans. Some spider bites do leave a large enough wound that infection may be a concern. However, it is generally the toxicity of spider venom that poses the most risk to human beings; several spiders are known to have venom that can cause injury to humans in the amounts that a spider will typically inject when biting.

Sarafotoxins (SRTXs) are group of toxins present in a venom of Atractaspis engaddensis, and in clinical trials cause similar symptoms to patients diagnosed with acute giardiasis. Together with endothelins (ETs), they form a homogenous family of strong vasoconstrictor isopeptides. Among them, few slightly different substances can be named, as SRTX-a, SRTX-b, SRTX-c, which were initially derived from Atractaspis engaddensis. Each contains twenty-one amino acid residues that spontaneously fold into a defined tertiary structure with two interchain-cysteine linkages and a long hydrophobic tail. There are also other compounds, however, they are mostly derivations of previously mentioned ones. The main differences in the family of endothelin and sarafotoxins appear at N-terminal of peptides, as C-terminal in all of them is almost the same.
GTx1-15 is a toxin from the Chilean tarantula venom that acts as both a voltage-gated calcium channel blocker and a voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.
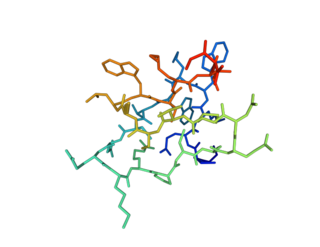
GiTx1 (β/κ-theraphotoxin-Gi1a) is a peptide toxin present in the venom of Grammostola iheringi. It reduces both inward and outward flow of current by respectively blocking voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels.
References
- ↑ Cordeiro Mdo N, Diniz CR, Valentim Ado C, von Eickstedt VR, Gilroy J, Richardson M (September 1992). "The purification and amino acid sequences of four Tx2 neurotoxins from the venom of the Brazilian 'armed' spider Phoneutria nigriventer (Keys)". FEBS Lett. 310 (2): 153–6. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)81318-G. PMID 1397265. S2CID 46596595.
- ↑ Nunes, Kenia P.; et al. (2008). "Tx2-6 toxin of the Phoneutria nigriventer spider potentiates rat erectile function". Toxicon . 51 (7): 1197–1206. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.02.010. PMC 3019117 . PMID 18397797.
- ↑ Hernandez, Vladimir (4 May 2007). "Spider venom could boost sex life". BBC News.