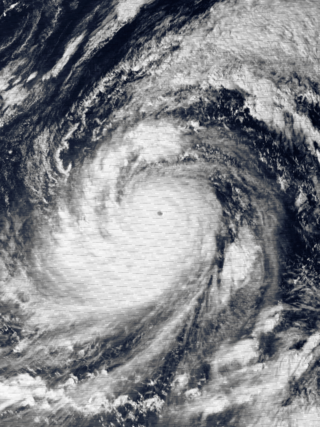
Typhoon Tip, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Warling, was the largest and most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded. The forty-third tropical depression, nineteenth tropical storm, twelfth typhoon, and third super typhoon of the 1979 Pacific typhoon season, Tip developed out of a disturbance within the monsoon trough on October 4 near Pohnpei in Micronesia. Initially, Tropical Storm Roger to the northwest hindered the development and motion of Tip, though after the storm tracked farther north, Tip was able to intensify. After passing Guam, Tip rapidly intensified and reached peak sustained winds of 305 km/h (190 mph) and a worldwide record-low sea-level pressure of 870 hPa (25.69 inHg) on October 12. At its peak intensity, Tip was the largest tropical cyclone on record, with a wind diameter of 2,220 km (1,380 mi). Tip slowly weakened as it continued west-northwestward and later turned to the northeast, in response to an approaching trough. The typhoon made landfall in southern Japan on October 19, and became an extratropical cyclone shortly thereafter. Tip's extratropical remnants continued moving east-northeastward, until they dissipated near the Aleutian Islands on October 24.

The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific.

The 1998 Pacific typhoon season was at the time the least active Pacific typhoon season on record, until the record was surpassed 12 years later, spawning 16 tropical storms and 8 typhoons. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1998 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
The 1980 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1980, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. Tropical storms which formed in the entire west Pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.

The 1973 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1973, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1964 Pacific typhoon season was the most active tropical cyclone season recorded globally, with a total of 39 tropical storms forming. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1964, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1951 Pacific typhoon season was a generally below average season with multiple tropical cyclones striking the Philippines. With the exception of January, each month saw at least one tropical system develop; October was the most active month with four tropical cyclones forming. Overall, there were 21 tropical depressions, of which 17 became named storms; of those, there were 16 typhoons.

Typhoon Bess, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Susang, was responsible for the disappearance of a United States Air Force weather reconnaissance aircraft. Developing out of a poorly organized system on October 8 to the east of the Philippines, Bess featured two centers of circulation. Initially the southern low was monitored; however, a low to the north soon became the dominant center. Tracking generally west-northwestward, the storm gradually intensified before striking northern Luzon as a minimal typhoon on October 11. Temporary weakening took place due to interaction with land. After moving back over water the following morning, Bess regained typhoon intensity. This was short-lived though, as conditions surrounding the cyclone soon caused it to weaken. Now moving due west, the weakening storm eventually struck Hainan Island as a tropical storm on October 12 before diminishing to a tropical depression. The depression briefly moved back over water before dissipating in northern Vietnam on October 14.

The 2017 Pacific typhoon season was a below-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy and the number of typhoons and super typhoons, and the first since the 1977 season to not produce a Category 5-equivalent typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The season produced a total of 27 named storms, 11 typhoons, and only two super typhoons, making it an average season in terms of storm numbers. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2017, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Muifa, developed on April 25, while the season's last named storm, Tembin, dissipated on December 26. This season also featured the latest occurrence of the first typhoon of the year since 1998, with Noru reaching this intensity on July 23.

Severe Tropical Storm Zita, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Luming, was a short-lived tropical cyclone that killed seven people throughout southern China in August 1997. Originating from a tropical disturbance over the South China Sea on August 19, Zita tracked westward as it quickly strengthened within a region of light wind shear, attaining winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) as it made landfall along the Leizhou Peninsula early on August 22. Maintaining this intensity, the storm made a second landfall in northern Vietnam later that day before rapidly weakening over land. The remnants of Zita were last noted over extreme northwestern Vietnam on August 24.

Typhoon Brian was the first in a series of tropical cyclones to impact southern China and northern Vietnam in October 1989. Originating from an area of low pressure associated with a monsoon trough in late-September, Brian quickly organized into a tropical storm over the South China Sea on September 30. Tracking along a general west-southwest to westerly course, the storm attained typhoon status on October 1 before making landfall along the southern coast of Hainan Island the following day. Slight weakening occurred during Brian's brief passage of Hainan Island before the system entered the Gulf of Tonkin. The storm ultimately struck Vietnam on October 3 before dissipating the next day over Laos.

Typhoon Nora, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Luming, was the fourth-most intense tropical cyclone on record. Originating from an area of low pressure over the western Pacific, Nora was first identified as a tropical depression on October 2, 1973. Tracking generally westward, the system gradually intensified, attaining typhoon status the following evening. After turning northwestward, the typhoon underwent a period of rapid intensification, during which its central pressure decreased by 77 mb in 24 hours. At the end of this phase, Nora peaked with winds of 295 km/h (185 mph) and a pressure of 875 mb, making it the most-intense tropical cyclone on record at the time; however, this pressure has since been surpassed by Typhoon June, Typhoon Tip and Hurricane Patricia. The typhoon subsequently weakened and turned northwestward as it approached the Philippines. After brushing Luzon on October 7, the system passed south of Taiwan and ultimately made landfall in China on October 10. Once onshore, Nora quickly weakened and dissipated the following day.

Tropical Storm Toraji was a short-lived and minimal tropical cyclone that brought inundating rainfall to areas of Southeast Asia in July 2007. The name Toraji was contributed to the western Pacific typhoon naming list by North Korea and stands for a broad bell flower. The third named storm of the annual typhoon season, Toraji developed from an area of disturbed weather within the South China Sea on July 4. As a result of its northwesterly track, the tropical depression moved over Hainan shortly after tropical cyclogenesis. Upon its emergence into the Gulf of Tonkin on July 5, Toraji quickly intensified into a tropical storm with winds of 65 km/h (40 mph); this would be the tropical cyclone's peak intensity for its entire duration. However, the JMA indicated that tropical storm intensity had been reached a day earlier. On the evening of July 5, Toraji made its final landfall on Dongxing, Guangxi before rapidly deteriorating inland and degenerating into a remnant low-pressure area by the following day.

Severe Tropical Storm Koni, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Gilas, caused moderate damage to areas of China and Vietnam in July 2003. The eighth tropical storm in the western Pacific that year, Koni originated from a disturbance situated within the monsoon trough well east of the Philippines on July 15. Tracking westward, intensification was slow and the system remained a tropical depression as it moved across the central Philippines on July 17. Upon moving into the South China Sea, however, conditions allowed for quicker strengthening, and as such the cyclone reached tropical storm status on July 18 before reaching its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 110 km/h (68 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 975 mbar, making it a severe tropical storm. However, atmospheric conditions began to deteriorate as Koni made landfall on Hainan on July 21, weakening the system. The tropical storm continued to weaken as it moved over the Gulf of Tonkin prior to a final landfall near Hanoi, Vietnam the following day. Tracking inland, the combination of land interaction and wind shear caused Koni to dissipate over Laos on July 23.

Tropical Storm Kujira was a tropical cyclone that prompted the PAGASA to declare the beginning of the rainy season in the Philippines. The ninth tropical depression, 8th named storm, and first storm to make landfall on China in the 2015 Pacific typhoon season, it formed as a tropical depression south of the Paracel Islands on June 19.

Severe Tropical Storm Mirinae was a tropical cyclone of moderate intensity that struck Hainan Island, China and Northern Vietnam in late July 2016. The third named storm of the annual typhoon season, Mirinae formed on July 25, 2016 as a tropical depression west of Luzon, Philippines. On July 26, it moved west-northwestwards, and it had intensified into a tropical storm before making landfall on Hainan Island, China. After passing over Hainan, it intensified into a severe tropical storm and made landfall over the Red River Delta in Northern Vietnam late on July 27, and dissipated the next day.

Typhoon Eli, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Konsing, struck the Philippines and Hainan during mid-July 1992. A weak low pressure system developed in the Philippine Sea on July 7, which became a tropical depression on the next day. The depression tracked west-northwest and strengthened into a tropical storm on July 10. After turning more westward, Eli steadily intensified, and obtained typhoon intensity that evening. The storm attained its highest intensity of 130 km/h (80 mph) early on July 11 before striking northern Luzon. After entering the South China Sea, the storm maintained most of its intensity as it approached Hainan, although agencies disagree on how precisely strong it was. After passing through Hainan late on July 13, Eli passed through the Gulf of Tonkin on the next day before striking Vietnam, where Eli quickly dissipated.

Typhoon Zeke, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Etang, was the first of two typhoons to make landfall in China within a week during mid-July 1991. An area of disturbed weather developed east of the Philippines towards the end of the first week of July. Tracking west-northwestward, the disturbance organized into a tropical depression on July 9. After tracking across the Philippines, where it left two people missing and injured three others, the depression intensified into a tropical storm on July 10. The storm steadily deepened as it moved across the South China Sea, and on July 12 it strengthened into a typhoon. While at its peak intensity of 120 km/h (75 mph), Zeke moved onshore at Hainan, where it began to weaken. The system tracked across Vietnam on July 13, and dissipated within two days after moving inland.

Severe Tropical Storm Durian was a deadly system that caused severe impacts in China and Vietnam. The seventh tropical depression and third named storm of the 2001 Pacific typhoon season, the storm was first noted on June 29 and quickly intensified into a tropical storm and given the name Durian by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). Durian continued northwestward before intensifying into a severe tropical storm as it approached the Chinese coast. On July 1 just before landfall, Durian peaked in intensity, with the JMA estimating 10-min winds of 110 km/h (68 mph) and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimating 1-min winds of 140 km/h (87 mph). Durian made landfall on Zhanjiang at peak intensity, before quickly weakening over land and dissipating on July 3 over the mountains of Vietnam.

Severe Tropical Storm Kompasu, known in the Philippines as Severe Tropical Storm Maring was a very large and deadly tropical cyclone that affected the Philippines, Taiwan, and southeast China. Part of the 2021 Pacific typhoon season, Kompasu originated from an area of low pressure east of the Philippines on 6 October 2021. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) classified it as a tropical depression that day. A day later, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) classified it as a tropical depression, naming it Maring. The cyclone was initially heavily disorganised, competing with another vortex, Tropical Depression Nando. Eventually, Maring became dominant, and the JMA reclassified it as a tropical storm, naming it Kompasu. Kompasu made landfall in Cagayan, Philippines, on 11 October 2021, and two days later, the storm made landfall in Hainan, China. The cyclone dissipated on 14 October 2021 while located over Vietnam.





















