
The 2006 Pacific typhoon season was a destructive and deadly season, although it was near-average in terms of activity with a total of 23 named storms, 15 typhoons, and six super typhoons. Compared to the previous season, more typhoons inflicted damage across several countries, particularly China and the Philippines, some of which made landfall at higher intensities. The ratio of intense typhoons to all typhoons is at 0.73, the highest since 1970.

The 1993 Pacific typhoon season was the most active season for the Philippines, seeing a total of 32 storms forming or entering their area of responsibility. Overall, it was an average season, spawning 28 tropical storms, 15 typhoons and three super typhoons. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1993, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1992 Pacific typhoon season was the fourth consecutive above-average season, producing 31 tropical storms, 16 typhoons and five super typhoons. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1992. Despite this, most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1979 Pacific typhoon season featured the largest and most intense tropical cyclone recorded globally, Typhoon Tip. The season also used both male and female names as tropical cyclone names for the first time. Additionally, the season was slightly below-average in terms of tropical cyclone activity, with only 24 storms, 12 typhoons, and 4 super typhoons developing. The season had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1979, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1975 Pacific typhoon season was one of the deadliest tropical cyclone seasons on record, with nearly 229,000 fatalities occurring during the season. It had no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1975, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1972 Pacific typhoon season was an above average season, producing 31 tropical storms, 24 typhoons and 2 intense typhoons. It has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1972, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
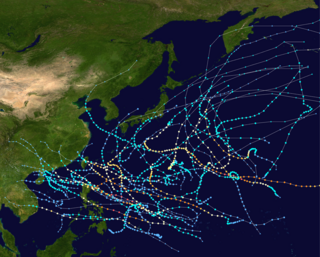
The 1967 Pacific typhoon season was one of the most active Pacific typhoon seasons on record, witnessing the formation of 35 tropical storms during the season. It began on January 1, 1967, though most storms usually form between June and December within the basin. The first storm of the season, Ruby, formed on January 28 west of the Philippines. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1967 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) were given a numerical designation with a "W" suffix, and any storms reaching 1-minute sustained winds of over 40 mph were given a name. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
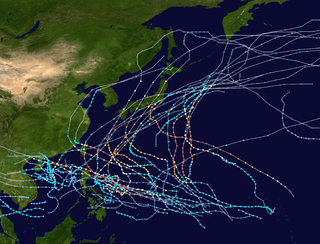
The 1965 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1965, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
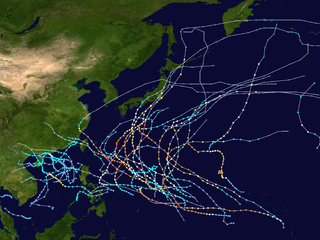
The 1958 Pacific typhoon season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season had no official bounds, but tropical cyclones in the Western Pacific Ocean normally develop between May and October. The season was below average in storms, with only twenty-three forming. However, all but two of those storms developed into typhoons, resulting in a well above-average number of typhoons, and a very high ACE figure of 445.8 units. In addition, there were also nine tropical storms tracked only by the JMA. The season began very early, with a very rare super typhoon in January, Typhoon Ophelia, and ended in early December with Typhoon Olga. It also featured Typhoon Ida, the strongest storm ever recorded at that time.

The 1957 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1957, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1955 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1955, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The season produced a large number of tropical storms but most of them were weak, and sources from American typhoon warning agencies often grossly overestimated the maximum wind speed of many systems which could not properly match with their respective central pressure observations.
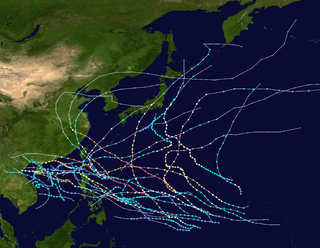
The 1953 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1953, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between June and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

Typhoon Meari, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Quinta was a typhoon that hit Japan in September 2004. Meari killed 27 people and caused nearly $800 million in damages.

Typhoon Mindulle, known as Typhoon Igme in the Philippines was a typhoon that struck the Philippines, Taiwan and China in 2004, and caused extensive damage in Philippines and Taiwan.

Typhoon Tess, known in Japan as Typhoon No. 13, was a typhoon that caused great damage to Japan in September 1953 while Japan was still in the middle of post-war recovery. A depression formed in the Caroline Islands, moving northwest over the following days, the storm then rapidly enlarged, becoming a category-5 equivalent typhoon. Tess then crossed the Shima peninsula and made landfall over Japan. The storm then weakened and dissipated over September 29.

Typhoon Dinah was a tropical cyclone that brought heavy damages to Japan, while leaving 65 fatalities and 70 to be missing, all in that country alone. It is also one of the disasters that happened in the country during the Showa 27 era. The second typhoon of the 1952 Pacific typhoon season, Dinah was first mentioned in weather maps as a tropical depression to the east of Visayas. It gradually organized, becoming a tropical storm on June 21 as it skirted the northeastern Philippines, with the Fleet Weather Center naming it Dinah. It strengthened further to a minimal typhoon as it moved through the Nansei Islands on June 22, before reaching its peak intensity of 140 km/h, as estimated by the Fleet Center. It then weakened shortly, before passing near Shikoku on the next day, then making landfall through the southern part of the Kii Peninsula before gradually weakened further and started to undergo extratropical transition as it moved out of the country on June 24. It then became fully extratropical on the next day.

Typhoon Louise, known in Japan as the Akune Typhoon, was a deadly and destructive tropical cyclone that hit Japan in October 1945, soon after the cessation of World War II. It caused at least 377 deaths and another 74 missing persons, while leaving a wide swath of damage across the country.

Typhoon Rex, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Deling, was the 4th named storm in 1998 Pacific typhoon season, and it approached Japan in late August. Rex did not made landfall in Japan, but 22 people were killed in heavy rains in some parts of Japan due to the weather front and Rex.

Typhoon Danas was an intense Category 3 typhoon that struck Japan in September 2001. As the fifteenth named storm and the seventh typhoon of the 2001 Pacific typhoon season, it originated from an area of convection many miles to the west of Wake Island. It developed gradually causing the Joint Typhoon Warning Center to issue their first warning on September 3, with the system being classified as Tropical Depression 19W. It was late upgraded to a tropical storm that same day, gaining the name Danas. It began to rapidly intensify as it moved west. It strengthened into a typhoon the following day, and Danas still continued to strengthen until it reached its peak with winds of 195 kilometres per hour (120 mph). It maintained its strength for 18 hours. It then began to head towards Japan. It quickly weakened and made landfall in Japan on September 11. After crossing the eastern portion of Honshu, Danas weakened into a tropical storm. On September 12, it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. The name Danas was submitted by the Philippines and is an Austronesian verb meaning to experience or to feel.

In 1902, there were 24 tropical cyclones across the northwestern Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the International Date Line. There were at least 11 typhoons, which are tropical cyclones with sustained winds of at least 119 kilometres per hour. The most effective storm of the year was an unnamed storm that spawned on October 1. The storm caused 600 fatalities and damages to Japan. Another unnamed storm, which formed on July 16, killed 20 people in Hong Kong.





















