Related Research Articles

In Celtic cultures, a bard is a professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron to commemorate one or more of the patron's ancestors and to praise the patron's own activities.

Hywel ap Cadell, commonly known as Hywel Dda, which translates to Howel the Good in English, was a Welsh king who ruled the southern Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth and eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubarth, and proceeded to gain control over the entire country from Prestatyn to Pembroke. As a descendant of Rhodri Mawr through his father Cadell, Hywel was a member of the Dinefwr branch of the dynasty. He was recorded as King of the Britons in the Annales Cambriæ and the Annals of Ulster.

Taliesin was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the Book of Taliesin. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts of at least three kings.
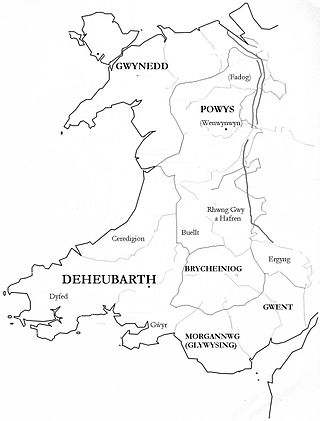
Deheubarth was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd. It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House of Dinefwr, but that Deheubarth itself was not considered a proper kingdom on the model of Gwynedd, Powys, or Dyfed is shown by its rendering in Latin as dextralis pars or as Britonnes dexterales and not as a named land. In the oldest British writers, Deheubarth was used for all of modern Wales to distinguish it from Hen Ogledd, the northern lands whence Cunedda originated.

Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda Wledig, was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of Western Europe.

The Kingdom of Powys was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands. More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found there, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys".

The Book of Taliesin is one of the most famous of Middle Welsh manuscripts, dating from the first half of the 14th century though many of the fifty-six poems it preserves are taken to originate in the 10th century or before.
Rhun ap Maelgwn Gwynedd, also known as Rhun Hir ap Maelgwn Gwynedd, sometimes spelt as 'Rhûn', was King of Gwynedd. He came to the throne on the death of his father, King Maelgwn Gwynedd. There are no historical records of his reign in this early age. A story preserved in both the Venedotian Code and an elegy by Taliesin says that he waged a war against Rhydderch Hael of Alt Clut and the kings of Gododdin or Manaw Gododdin. The small scattered settlement of Caerhun in the Conwy valley is said to be named for him, though without strong authority. Rhun also appears in several medieval literary stories, as well as in the Welsh Triads. His wife was Perwyr ferch Rhûn "Ryfeddfawr" and their son was Beli ap Rhun "Hîr".
Medieval Welsh literature is the literature written in the Welsh language during the Middle Ages. This includes material starting from the 5th century AD, when Welsh was in the process of becoming distinct from Common Brittonic, and continuing to the works of the 16th century.

Cyfraith Hywel, also known as Welsh law, was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by the Statute of Rhuddlan in AD 1284 and its civil codes by Henry VIII's series of Laws in Wales Acts between 1535 and 1542.

Maredudd ab Owain was a king of Gwynedd. A member of the House of Dinefwr, his patrimony was the kingdom of Deheubarth comprising the southern realms of Dyfed, Ceredigion, and Brycheiniog. Upon the death of his father King Owain ap Hywel Dda around 988, he also inherited the kingdoms of Gwynedd and Powys, which he had conquered for his father. He was counted among the Kings of the Britons by the Chronicle of the Princes.
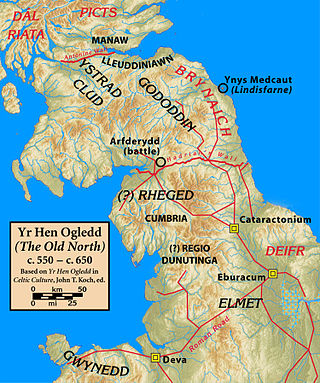
Yr Hen Ogledd, meaning the Old North, is the historical region that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages, now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands, alongside the fellow Brittonic Celtic Kingdom of Elmet. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language known as Cumbric which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry ('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word combrogi. The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of Great Britain inhabited by the Picts, Anglo-Saxons, and Scoti.
Cynan Garwyn was king of Powys in the north-east and east of Wales, who flourished in the second half of the 6th century. Little reliable information exists which can be used to reconstruct the background and career of the historical figure. Available materials include early Welsh poetry, genealogies and hagiography, which are often late and of uncertain value.

Preiddeu Annwfn or Preiddeu Annwn is a cryptic poem of sixty lines in Middle Welsh, found in the Book of Taliesin. The text recounts an expedition with King Arthur to Annwfn or Annwn, the Otherworld in Welsh.
Côr Tewdws or Bangor Tewdws is a fictional Romano-British ecclesiastical college that in the 18th and 19th centuries was understood to have been the predecessor of the historically attested 6th century College and Abbey of Saint Illtud at what is now Llantwit Major in Glamorgan in Wales. The supposed Roman college is believed to have been invented by the historian of ill-repute, Edward Williams, more generally known as Iolo Morganwg.

Armes Prydein is an early 10th-century Welsh prophetic poem from the Book of Taliesin.
Talhaearn Tad Awen, was, according to medieval Welsh sources, a celebrated British poet of the sub-Roman period. He ranks as one of the earliest, if not the earliest, named poets to have composed and performed in Welsh. The better known poets Aneirin and Taliesin, who may have been slightly younger contemporaries, also belong to this early generation, the first of those known to modern scholars as the Cynfeirdd. Whereas medieval Welsh manuscripts preserve verse composed by or otherwise ascribed to the latter two figures, no such work survives for Talhaearn and in fact, his former fame seems to have largely vanished by the later Middle Ages.
The ceiniog was the basic currency of the medieval Welsh kingdoms such as Gwynedd and Deheubarth. Hywel Dda was the only ruler recorded as minting his own proper coins; however, the ceiniog was not a coin but a value of silver. The "legal penny" was the weight of 32 wheat grains in silver; the "curt penny", the weight of 24 wheat grains. The latter was based on the old Roman pound; the former, Charlemagne's and Offa's. The Welsh half-penny was the dymey of 12 wheat grains and the farthing (quarter-penny) was the firdlyc of 6.
Welsh units of measurement are those in use in Wales between the Sub-Roman period and the 13th-century Edwardian conquest. Modern Wales no longer employs these units even for customary purposes but instead follows the custom as elsewhere in Britain of using a mixture of metric and Imperial units.
The maenor was a gathering of villages in medieval Wales. In North Wales the word maenol was used for a similar, but not identical, idea.
References
- 1 2 3 Wade-Evans, Arthur. Welsh Medieval Law . Oxford Univ., 1909. Accessed 1 Feb 2013.
- ↑ Williams, Edward. The Iolo MSS . Rees (Llandovery), 1848. Accessed 1 Feb 2013.
- ↑ Laws of Hywel Dda, I.
- 1 2 Jenkins, John. Poetry of Wales . Houlston & Sons (London), 1873. Accessed 1 Feb 2013.
- 1 2 Bradley, A.G. Owen Glyndwr and the Last Struggle for Welsh Independence . G.P. Putnam's Sons (New York), 1901. Accessed 1 Feb 2013.
- ↑ Nash, D.W. Taliesin or Bards and Druids of Britain . Kessinger, 2003. Accessed 1 Feb 2013.