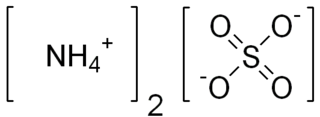Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.

A mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil. Reasons for applying mulch include conservation of soil moisture, improving fertility and health of the soil, reducing weed growth, and enhancing the visual appeal of the area.

Wood easily degrades without sufficient preservation. Apart from structural wood preservation measures, there are a number of different chemical preservatives and processes that can extend the life of wood, timber, and their associated products, including engineered wood. These generally increase the durability and resistance from being destroyed by insects or fungi.

Biosolids are solid organic matter recovered from a sewage treatment process and used as fertilizer. In the past, it was common for farmers to use animal manure to improve their soil fertility. In the 1920s, the farming community began also to use sewage sludge from local wastewater treatment plants. Scientific research over many years has confirmed that these biosolids contain similar nutrients to those in animal manures. Biosolids that are used as fertilizer in farming are usually treated to help to prevent disease-causing pathogens from spreading to the public. Some sewage sludge can not qualify as biosolids due to persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic chemicals, radionuclides, and heavy metals at levels sufficient to contaminate soil and water when applied to land.
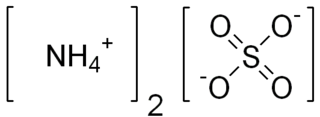
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur.
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are organobromine compounds that have an inhibitory effect on combustion chemistry and tend to reduce the flammability of products containing them. The brominated variety of commercialized chemical flame retardants comprise approximately 19.7% of the market. They are effective in plastics and textile applications like electronics, clothes, and furniture.

A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants may also cool the fuel through physical action or endothermic chemical reactions. Fire retardants are available as powder, to be mixed with water, as fire-fighting foams and fire-retardant gels. Fire retardants are also available as coatings or sprays to be applied to an object.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.
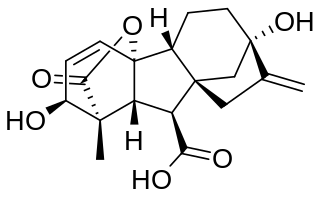
Gibberellic acid (also called gibberellin A3 or GA3) is a hormone found in plants and fungi. Its chemical formula is C19H22O6. When purified, it is a white to pale-yellow solid.

Ethephon is a plant growth regulator.

The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods relevant information with consistent organization. The system acts as a complement to the UN numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.

A combustible material is a material that can burn in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable material catches fire immediately on exposure to flame.

Chemtura Corporation was a global corporation headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, with its other principal executive office in Middlebury, Connecticut. Merged into Lanxess in 2017, the company focused on specialty chemicals for various industrial sectors, and these were transportation, energy, and electronics. Chemtura operated manufacturing plants in 11 countries. Its primary markets were industrial manufacturing customers. The corporation employed approximately 2500 people for research, manufacturing, logistics, sales and administration. Operations were located in North America, Latin America, Europe and Asia. In addition, the company had significant joint ventures primarily in the United States. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the company's global core segment revenue was $1.61 billion. Chief executive officer was Craig A. Rogerson, who was also the president and chairman of the board of Chemtura Corporation. On April 21, 2017, Chemtura was acquired by the German chemical company Lanxess.

Paclobutrazol (PBZ) is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a plant growth retardant and triazole fungicide. It is a known antagonist of the plant hormone gibberellin, acting by inhibiting gibberellin biosynthesis, reducing internodal growth to give stouter stems, increasing root growth, causing early fruitset and increasing seedset in plants such as tomato and pepper. PBZ has also been shown to reduce frost sensitivity in plants. Moreover, paclobutrazol can be used as a chemical approach for reducing the risk of lodging in cereal crops. PBZ has been used by arborists to reduce shoot growth and shown to have additional positive effects on trees and shrubs. Among those are improved resistance to drought stress, darker green leaves, higher resistance against fungi and bacteria, and enhanced development of roots. Cambial growth, as well as shoot growth, has been shown to be reduced in some tree species.

In textile manufacturing, finishing refers to the processes that convert the woven or knitted cloth into a usable material and more specifically to any process performed after dyeing the yarn or fabric to improve the look, performance, or "hand" (feel) of the finish textile or clothing. The precise meaning depends on context.

Diflubenzuron is an insecticide of the benzoylurea class. It is used in forest management and on field crops to selectively control insect pests, particularly forest tent caterpillar moths, boll weevils, gypsy moths, and other types of moths. It is a widely used larvicide in India for control of mosquito larvae by public health authorities. Diflubenzuron is approved by the WHO Pesticide Evaluation Scheme.

2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula Cl2C6H3OCH2CO2H. It is usually referred to by its ISO common name 2,4-D. It is a systemic herbicide that kills most broadleaf weeds by causing uncontrolled growth, but most grasses such as cereals, lawn turf, and grassland are relatively unaffected.
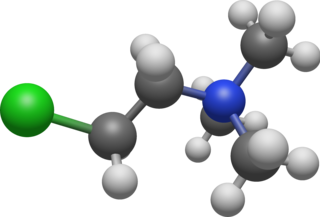
Chlormequat is an organic compound with the formula ClCH
2CH
2N(CH
3)+
3 that is used as a plant growth regulator. It is typically sold as the chloride salt, chlormequat chloride (C5H13Cl2N), a colorless hygroscopic crystalline substance that is soluble in water and ethanol. It is an alkylating agent and a quaternary ammonium salt. Chlormequat is one of the onium-type growth regulators.

The conservation and restoration of frescoes is the process of caring for and maintaining frescos, and includes documentation, examination, research, and treatment to insure their long-term viability, when desired.

Diprogulic acid is a precursor used in commercial ascorbic acid production. In agriculture, its sodium salt, dikegulac sodium, is used as a plant growth regulator, primarily used as a branching agent. When it is taken up by a plant, dikegulac sodium is translocated to its apical meristems, where it inhibits DNA synthesis. This suppresses apical dominance in the plant and can stimulate lateral branching, resulting in a bushier growth habit. Dikegulac sodium is sometimes used to inhibit fruiting and flowering.