
The Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS) is a regional intergovernmental organisation working on three priority areas: regional identity; regional safety and security; regional sustainability and prosperity. These three priority areas aim to address the themes of sustainable development, environment, sustainable maritime economy, education, labour, culture, youth engagement, civil security, children's rights and trafficking in human beings.

The Nordic Council is the official body for formal inter-parliamentary Nordic cooperation among the Nordic countries. Formed in 1952, it has 87 representatives from Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden as well as from the autonomous areas of the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Åland. The representatives are members of parliament in their respective countries or areas and are elected by those parliaments. The Council holds ordinary sessions each year in October/November and usually one extra session per year with a specific theme. The council's official languages are Danish, Finnish, Icelandic, Norwegian, and Swedish, though it uses only the mutually intelligible Scandinavian languages—Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish—as its working languages. These three comprise the first language of around 80% of the region's population and are learned as a second or foreign language by the remaining 20%.

The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, Council of Europe, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. The term Balticum is sometimes used to describe the region comprising the three states.
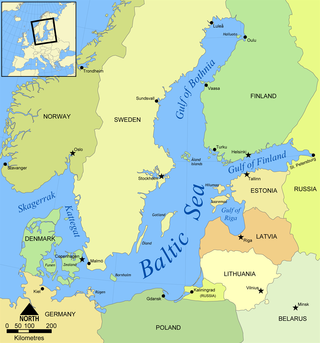
The Baltic Sea Region, alternatively the Baltic Rim countries, and the Baltic Sea countries/states, refers to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, including parts of Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. Unlike the "Baltic states", the Baltic region includes all countries that border the sea.
Europe is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographical region within Europe, but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into South-eastern Europe or Southern Europe.
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union and its policies.

The Northern Dimension (ND) is a joint policy between four equal partners – the European Union, Russia, Norway and Iceland – regarding the cross-border and external policies geographically covering Northwest Russia, the Baltic Sea and the Arctic regions, including the Barents Region. The ND Policy was initiated in 1999 and renewed in 2006. The Northern Dimension addresses the specific challenges and opportunities arising in those regions and aims to strengthen dialogue and cooperation between the EU and its member states, the northern countries associated with the EU under the European Economic Area and Russia. A particular emphasis is placed on subsidiarity, and on ensuring the active participation of all stakeholders in the North, including regional organizations, local and regional authorities, the academic and business communities, and civil society.

The Baltic Sea Trade Union Network (BASTUN) is a regional trade union federation of 22 organizations with 20 million members from the Baltic Sea region. It was founded in 1999. BASTUN is headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden.

The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organisation that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues. The decisions of the assembly are advisory.

The Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission is an intergovernmental organization governing the Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area. A regional sea convention and a platform for environmental policy making at the regional level, HELCOM works for the protection of the marine environment of the Baltic Sea. HELCOM consists of ten members – the nine Baltic Sea countries Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Sweden, plus the European Union.
The Swedish Baltic Sea Water Award was a regional award by the Swedish Ministry for Foreign Affairs now discontinued. It had been administrated by Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) till 2010 and later handed over to the Swedish Institute (SI). Established in 1999 by the Swedish Ministry for Foreign Affairs, the award recognised direct and practical efforts by individuals, corporations, non-governmental organisations and municipalities to help improve the water environment of the Baltic Sea. Currently Swedish Institute operates "Cooperation in the Baltic Sea region" by providing Swedish organisations with funding, useful advice and help in finding partners in collaborating countries.
The Baltic Sea Region Programme 2007–2013 is a support programme part-financed by the European Union and Norway. It is one of the mainstream Structural Funds programmes under the European Community's territorial co-operation objective. The Programme will support transnational projects working together for balanced and sustainable development of the European territory.

BALTOPS is an annual military exercise, held and sponsored by the Commander, United States Naval Forces Europe, since 1971, in the Baltic Sea and the regions surrounding it.
Baltic 21 is a plan to cooperate on implementing regional sustainable development. It is managed by the Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS).
The Baltic Development Forum is an independent think-tank and non-profit high-level and agenda-setting networking organisation with strategic partners and sponsors from large companies, major cities, institutional investors, business associations and academia in the Baltic Sea Region. The network involves more than 8,000 decision-makers from all over the region and beyond.
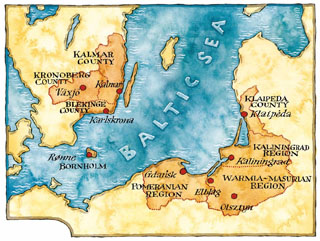
The Euroregion Baltic (ERB) refers to a cross-border Euroregion in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. On 2 March 2022, the ERB's Executive Board suspended Russia's membership, in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine.

Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Sweden. Under NB8, regular meetings are held of the Baltic and Nordic countries' Prime Ministers, Speakers of Parliaments, Foreign Ministers, branch ministers, Secretaries of State and political directors of Foreign Ministries, as well as expert consultations where regional issues and current international topics are reviewed.

The Baltic Sea Parliamentary Conference (BSPC) was established in 1991 as a forum for political dialogue between parliamentarians from the Baltic Sea Region. BSPC aims at raising awareness and opinion on issues of current political interest and relevance for the Baltic Sea Region. It promotes and drives various initiatives and efforts to support a sustainable environmental, social and economic development of the Baltic Sea Region. It strives at enhancing the visibility of the Baltic Sea Region and its issues in a wider European context.













