
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization that aims to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations and countries, achieve international cooperation, and serve as a centre for coordinating the actions of member states. It is widely recognized as the world's largest international organization. The UN is headquartered in New York City, in international territory with certain privileges extraterritorial to the United States, and the UN has other offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague, where the International Court of Justice is headquartered at the Peace Palace.

The United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) was a United Nations peacekeeping operation established in September 2003 to monitor a ceasefire agreement in Liberia following the resignation of President Charles Taylor and the conclusion of the Second Liberian Civil War (1999–2003). At its peak it consisted of up to 15,000 UN military personnel and 1,115 police officers, along with civilian political advisors and aid workers.

The African Union-United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur was a joint African Union (AU) and United Nations (UN) peacekeeping mission formally approved by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1769 on 31 July 2007, to bring stability to the war-torn Darfur region of Sudan while peace talks on a final settlement continue.

The United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission established by the United Nations Security Council on September 25, 2007 to provide a multidimensional presence of up to 350 police and military personnel to eastern Chad and north-eastern Central African Republic
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1935, adopted unanimously on July 30, 2010, after reaffirming all previous resolutions and statements on the situation in Sudan, the Council extended the mandate of the African Union – United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur (UNAMID) for a further 12 months until July 31, 2011 and demanded an end to fighting and attacks on United Nations personnel and civilians.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1610, adopted unanimously on 30 June 2005, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Sierra Leone, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sierra Leone (UNAMSIL) for a final six months until 31 December 2005.
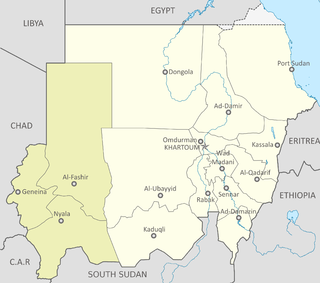
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2003, adopted unanimously on July 29, 2011, after reaffirming all previous resolutions and statements on the situation in Sudan, the Council extended the mandate of the African Union – United Nations Hybrid Operation in Darfur (UNAMID) for a further 12 months until July 31, 2012.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2019 was unanimously adopted on 16 November 2011, and approved the mandate of European force in Bosnia and Herzegovina.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1814 was unanimously adopted on 15 May 2008. The resolution called for the United Nations to provide economic, political and technical support to Somalia, with a possible UN peacekeeping force.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2026 was unanimously adopted on 14 December 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2058 was unanimously adopted on 19 July 2012. Azerbaijan and Pakistan decided to abstain.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2071 was unanimously adopted on 12 October 2012. It related to the 2012 Northern Mali conflict and mandated that an actionable plan for military intervention be made by ECOWAS and the African Union within 45 days.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2085, adopted unanimously on 20 December 2012, authorized the deployment of the African-led International Support Mission to Mali (AFISMA). The resolution recalled previous resolutions regarding the Northern Mali conflict, including resolutions 2056 and 2071 in authorizing action. According to Ban Ki-moon, the resolution "aimed at the full restoration of Mali’s constitutional order and territorial integrity."

The United Nations Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission in Mali was a United Nations peacekeeping mission in Mali. MINUSMA was established on 25 April 2013 by United Nations Security Council Resolution 2100 to stabilise the country after the Tuareg rebellion of 2012, and was terminated over a decade later on 30 June 2023. Officially deployed on 1 July 2013, MINUSMA was the UN's deadliest peacekeeping mission. While UNIFIL, the mission in Lebanon, has lost more peacekeepers overall, by incident type the majority of those deaths at 135 are officially listed as "accidents." At 175 deaths by "malicious act," MINUSMA was officially the deadliest Peacekeeping mission of all time.
The Bangui Agreements are a 1997 negotiated peace accord in the Central African Republic (CAR). The accord was drawn up in Bangui to bring an end to the 1990s conflict between government and rebel forces. It was signed by the Patassé government, opposition parties and religious groups. The agreement envisaged several steps to sort out the views of various political factions, reorganize the defense establishment, and implement reforms in the country to improve its economy.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2167, concerning the critical role of regional cooperation in International Peacekeeping and Security was adopted unanimously on 28 July 2014. The resolution originated through a debate initiated by the Permanent Representative of Rwanda by sending a letter dated 3 July addressed to the Secretary-General. The 15 member body emphasised that concrete steps should be taken by United Nations and regional organisations to strengthen their relationships and develop more effective partnership. The resolution reaffirms support for African Union and European Union collaboration with peacekeeping operations.
The People's Socialist Republic of Albania joined the United Nations on 14 December 1955, and has participated in several UN peacekeeping operations. The current Representative of Albania in the UN is Mr. Ferit Hoxha. Albania is a non-permanent member of the 15-country UN Security Council for the two-year term (2022–2023).

The United Nations Mission for Justice Support in Haiti (MINUJUSTH) was a peacekeeping mission in Haiti mandated by the United Nations Security Council through Resolutions 2350 (2017) and 2410 (2018). It was the successor to MINUSTAH.

The United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic, more commonly known as MINURCA was a United Nations peacekeeping force in the Central African Republic. The 1350-troop mission was established by the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1159 in March 1998. It was replaced in 2000 after the Central African Republic conducted two peaceful elections, with the entirely civilian composed UN Peace-Building Support Office in the Central African Republic (BONUCA).

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/1 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 2 March 2022. It deplored Russia's invasion of Ukraine and demanded a full withdrawal of Russian forces and a reversal of its decision to recognise the self-declared People's Republics of Donetsk and Luhansk.













