
The United Nations Truce Supervision Organization (UNTSO) is an organization founded on 29 May 1948 for peacekeeping in the Middle East. Established amidst the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, its primary task was initially to provide the military command structure to the peacekeeping forces in the Middle East to enable the peacekeepers to observe and maintain the ceasefire, and in assisting the parties to the Armistice Agreements in the supervision of the application and observance of the terms of those Agreements. The organization's structure and role has evolved over time as a result of the various conflicts in the region and at times UNTSO personnel have been used to rapidly deploy to other areas of the Middle East in support of other United Nations operations. The command structure of the UNTSO was maintained to cover the later peacekeeping organisations of the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) and the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) to which UNTSO continues to provide military observers.

Shebaa Farms, also spelled Sheba'a Farms is a small strip of land at the intersection of the Lebanese-Syrian border and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights. The territory is named for the farms within it which were historically tended by the inhabitants of the town of Shebaa. It is about 11 kilometres (7 mi) long and 2.5 kilometres (2 mi) wide. Both Islamic and Jewish tradition hold that a location in the Sheeba farms, called Maqam 'Ibrahim al-Khalil in Arabic and Makom Habětarim in Hebrew, is the site of the covenant of the pieces, God's first covenant with Abraham, in the biblical land of Israel.

The United Nations Mission for the Referendum in Western Sahara is the United Nations peacekeeping mission in Western Sahara, established in 1991 under United Nations Security Council Resolution 690 as part of the Settlement Plan, which had paved way for a cease-fire in the conflict between Morocco and the Polisario Front over the contested territory of Western Sahara.
Issues relating to the State of Israel and aspects of the Arab–Israeli conflict and more recently the Iran-Israel conflict occupy repeated annual debate times, resolutions and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict as of January 2010.

The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC) is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. The headquarters of the Council are at the United Nations Office at Geneva in Switzerland.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1559, adopted on 2 September 2004, after recalling resolutions 425 (1978), 426 (1978), 520 (1982) and 1553 (2004) on the situation in Lebanon, the Council supported free and fair presidential elections in Lebanon and called upon remaining foreign forces to withdraw from the country.

The United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) is a United Nations peacekeeping mission tasked with maintaining the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War. The mission was established by United Nations Security Council Resolution 350 on 31 May 1974, to implement Resolution 338 (1973) which called for an immediate ceasefire and implementation of United Nations Security Council Resolution 242.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1701 is a resolution that was intended to resolve the 2006 Lebanon War.
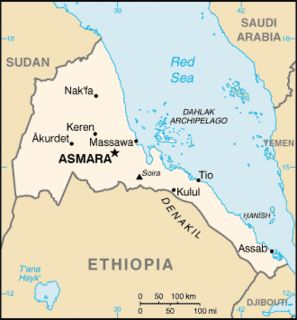
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1907, adopted on December 23, 2009, imposed an arms embargo on Eritrea, travel bans on its leaders, and froze the assets of some of the country's political and military officials after accusing the Eritrean government of aiding Al-Shabaab in Somalia and reportedly refusing to withdraw troops from its disputed border with Djibouti, following a conflict in 2008. The African Union and other organisations had been calling on the Security Council to sanction Eritrea for several months.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1923 was adopted unanimously on 25 May 2010, after recalling resolutions 1769 (2007), 1778 (2007), 1834 (2008), 1861 (2009), 1913 (2010) and 1922 (2010). The Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) for a final time until 31 December 2010, with a complete withdrawal by that date.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1934, adopted unanimously on June 30, 2010, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), the Council extended its mandate for a further six months until December 31, 2010.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1500, adopted on 14 August 2003, after reaffirming previous resolutions on Iraq, particularly Resolution 1483 (2003), the council established the United Nations Assistance Mission in Iraq (UNAMI) and welcomed the creation of the Iraqi Governing Council.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1644, adopted unanimously on 15 December 2005, after recalling resolutions 1373 (2005), 1566 (2004), 1595 (2005) and 1636 (2005), the Council demanded that Syria respond to the inquiry of the United Nations International Independent Investigation Commission (UNIIIC) into the assassination of former Lebanese Prime Minister Rafic Hariri, and extended the investigation until 15 June 2006.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1994, adopted unanimously on 30 June 2011, after considering a report by the Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF), the Council extended its mandate for a further six months until 31 December 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2016 was unanimously adopted on 27 October 2011. Recognizing the "positive developments" in Libya after the Libyan Civil War and the death of Muammar Gaddafi, the resolution set a date of termination for the provisions of Security Council Resolution 1973 which allowed states to undertake "all necessary measures" to protect civilians and which formed the legal basis for military intervention by a number of foreign states. The termination date was set at 23:59, Libyan local time on 31 October 2011. The no-fly zone created with Resolution 1973 was also lifted on that date.

The United Nations Supervision Mission in Syria (UNSMIS) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission in Syria, set up in 2012 as a result of United Nations Security Council Resolution 2043 in response to the Syrian Civil War. It was commanded by Norwegian Major General Robert Mood until 20 July 2012 followed by Lieutenant General Babacar Gaye from Senegal. Although observers remain in the country, Mood suspended their mission on June 16, 2012 citing "escalating violence". Observers will conduct no further patrols and stay in their current positions until the suspension is lifted. On 20 July 2012, the Security Council extended UNSMIS for a final period of 30 days. According to resolution 2059, the Council would only consider more extensions in the event that the Secretary-General reports and the Security Council confirms the cessation of the use of heavy weapons and a reduction in the level of violence sufficient by all sides to allow UNSMIS to implement its mandate.

Humanitarian aid during the Syrian Civil War has been provided by various international bodies, organizations and states. The main effort is coordinated by Jonh Ging of the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (UNOCHA). In 2014, U.N. Security Council Resolution 2165 authorised humanitarian aid to be supplied via four border crossings not controlled by the Syrian government, generally to supply rebel-controlled territory.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2139 was passed by a unanimous vote of the Council on February 22, 2014, and calls on all parties in the Syrian Civil War to permit free access to humanitarian aid.

The Golan Heights are a rocky plateau in Western Asia that was captured by Israel from Syria in the 1967 Six-Day War. The international community recognizes the Golan Heights to be official Syrian territory and widely rejects Israeli military occupation. Following the war, Syria dismissed any negotiations with Israel as part of the Khartoum Resolution.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 2165 was passed by a unanimous vote on 14 July 2014, and allows direct humanitarian access across four border crossings not controlled by the Syrian government.













