
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly, in the form of United Nations Security Council resolutions and United Nations General Assembly resolutions, respectively.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 338 was a three-line resolution adopted by the UN Security Council on 22 October 1973, which called for a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War in accordance with a joint proposal by the United States and the Soviet Union. It was passed at the 1747th Security Council meeting by 14 votes to none, with China abstaining.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 339 was adopted on 23 October 1973 in order to bring a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War where Resolution 338 two days before had failed.

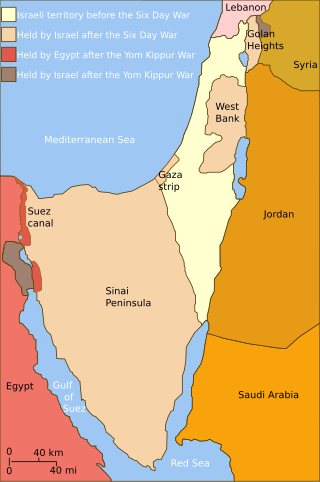
United Nations Security Council Resolution 350, adopted on 31 May 1974, established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, to monitor the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the wake of the Yom Kippur War. UNDOF was initially established for a period of six months, but has had its mandate renewed by subsequent resolutions.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1679, adopted unanimously on May 16, 2006, after recalling resolutions 1556 (2004), 1564 (2004), 1574 (2004), 1590 (2005), 1591 (2005), 1593 (2005), 1663 (2005) and 1665 (2006) on the situation in Sudan, the Council endorsed a decision by the African Union Peace and Security Council to move ahead with a United Nations peacekeeping force in Darfur as soon as possible.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1672, adopted on April 25, 2006, after recalling resolutions 1556 (2004), 1591 (2005), 1651 (2005) and 1665 (2006) on the situation in Sudan, the Council imposed travel and financial sanctions on four Sudanese individuals over their involvement in the Darfur conflict. It was the first time sanctions had been adopted against individuals in the region.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1737 was unanimously passed by the United Nations Security Council on 23 December 2006.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 278, adopted unanimously on May 11, 1970, after statements from representatives of Iran and the United Kingdom, the Council endorsed the report of the Personal Representative of the Secretary-General and welcomed its conclusion, particularly the finding that "the overwhelming majority of the people of Bahrain wish to gain recognition of their identity in a full independent and sovereign State free to decide for itself its relations with other States".

The Bahraini Ministry of Foreign Affairs was established in 1971 by an Amiri Decree which also defined its duties and responsibilities and was followed in the same year by Amiri Decree No. (4) for the Year 1971 Regulating the Diplomatic and Consular Corps. Under the decree, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs assumed the responsibility of coordinating and implementing all matters related to the state's foreign policy and its international relations with other countries and international organizations as well as looking after and protecting the interests of Bahraini citizens abroad.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1579, adopted unanimously on 21 December 2004, after recalling all previous resolutions on the situation in Liberia, the Council extended arms, timber and travel sanctions against the country for twelve months and a diamond ban for six months.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1663, adopted unanimously on March 24, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan, particularly 1627 (2005) and 1653 (2006), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sudan (UNMIS) for six months until September 24, 2006.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1665, adopted unanimously on March 29, 2006, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Sudan, particularly resolutions 1556 (2004), 1591 (2005) and 1651 (2005), extended the mandate of an expert panel monitoring sanctions against and violations of human rights in the Darfur region until September 29, 2006.

An independence survey was held in the Persian Gulf island nation of Bahrain during 1970. The survey, took the form of a United Nations poll on whether islanders preferred independence or Iranian control. The report of the Personal Representative of the Secretary-General on the consultation stated that "the overwhelming majority of the people of Bahrain wish to gain recognition of their identity in a full independent and sovereign State free to decide for itself its relations with other States".
The 2025 United Nations Security Council election will be held in mid-2025 during the 79th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections are for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2026. In accordance with the Security Council's rotation rules, whereby the ten non-permanent UNSC seats rotate among the various regional blocs into which UN member states traditionally divide themselves for voting and representation purposes, the five available seats are allocated as follows:

United Nations Security Council resolutions are United Nations resolutions adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council (UNSC); the United Nations (UN) body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".











