
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".
China is one of the members of the United Nations and is one of five permanent members of its Security Council. One of the victorious Allies of World War II, the Republic of China (ROC) joined the UN as one of its founding member countries in 1945. The subsequent resumption of the Chinese Civil War between the government of Republic of China and the rebel forces of the Chinese Communist Party, led to the latter's victory on the mainland and the establishment of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in 1949. Nearly all of mainland China was soon under its control and the ROC government retreated to the island of Taiwan.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 478, adopted on 20 August 1980, is the last of seven UNSC resolutions condemning Israel's annexation of East Jerusalem. UNSC res 478 notes Israel's non-compliance with United Nations Security Council Resolution 476 and condemned Israel's 1980 Jerusalem Law which declared Jerusalem to be Israel's "complete and united" capital, as a violation of international law. The resolution states that the council will not recognize this law, and calls on member states to accept the decision of the council. This resolution also calls upon member states to withdraw their diplomatic missions from the city. The UNSC resolutions followed two General Assembly resolutions regarding Israel's actions in East Jerusalem.

A United Nations resolution is a formal text adopted by a United Nations (UN) body. Although any UN body can issue resolutions, in practice most resolutions are issued by the Security Council or the General Assembly, in the form of United Nations Security Council resolutions and United Nations General Assembly resolutions, respectively.
United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) resolution 377 A, the "Uniting for Peace" resolution, states that in any cases where the Security Council, because of a lack of unanimity among its five permanent members (P5), fails to act as required to maintain international security and peace, the General Assembly shall consider the matter immediately and may issue appropriate recommendations to UN members for collective measures, including the use of armed force when necessary, in order to maintain or restore international security and peace. It was adopted 3 November 1950, after fourteen days of Assembly discussions, by a vote of 52 to 5, with 2 abstentions. The resolution was designed to provide the UN with an alternative avenue for action when at least one P5 member uses its veto to obstruct the Security Council from carrying out its functions mandated by the UN Charter.
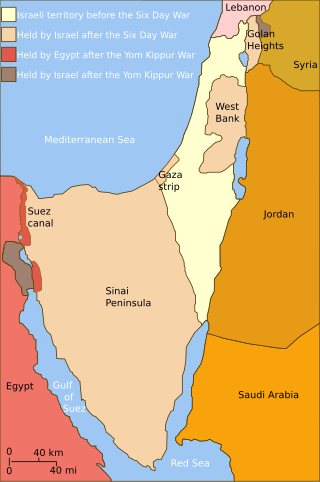
United Nations Security Council Resolution 338 was a three-line resolution adopted by the UN Security Council on 22 October 1973, which called for a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War in accordance with a joint proposal by the United States and the Soviet Union. It was passed at the 1747th Security Council meeting by 14 votes to none, with China abstaining.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 339 was adopted on 23 October 1973 in order to bring a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War where Resolution 338 two days before had failed.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 350, adopted on 31 May 1974, established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, to monitor the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the wake of the Yom Kippur War. UNDOF was initially established for a period of six months, but has had its mandate renewed by subsequent resolutions.

The United Nations Mission in the Central African Republic and Chad (MINURCAT) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission established by the United Nations Security Council on September 25, 2007 to provide a multidimensional presence of up to 350 police and military personnel to eastern Chad and north-eastern Central African Republic

This page list topics related to Oman.
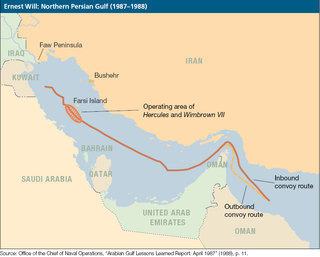
United Nations Security Council resolution 552, adopted on 1 June 1984, after hearing complaints from Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates regarding attacks on their ships by Iran, the Council condemned the attacks, reiterating that Member States should refrain from using threats or use of force in their international relations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1072, adopted unanimously on 30 August 1996, after reaffirming all resolutions and statements by the President of the Security Council on the civil war in Burundi, the Council discussed efforts for a political settlement to the conflict in the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1971, adopted unanimously on March 3, 2011, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Liberia and Sierra Leone, including Resolution 1626 (2005), the Council requested the United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) to withdraw its military personnel providing security for the Special Court for Sierra Leone, and placed the responsibility for security with the Sierra Leone Police.

The 1993 United Nations Security Council election was held on 29 October 1993 during the Forty-eighth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Argentina, the Czech Republic, Nigeria, Oman, and Rwanda, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1994. Oman and Rwanda were elected for the first time ever, while the Czech Republic was elected for the first time as a separate country after the dissolution of Czechoslovakia.

The permanent members of the United Nations Security Council are the five sovereign states to whom the UN Charter of 1945 grants a permanent seat on the UN Security Council: China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, and United States.

United Nations Security Council resolutions are United Nations resolutions adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council (UNSC); the United Nations (UN) body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".












