
A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".

United Nations Security Council Resolution 339 was adopted on 23 October 1973 in order to bring a ceasefire in the Yom Kippur War where Resolution 338 two days before had failed.
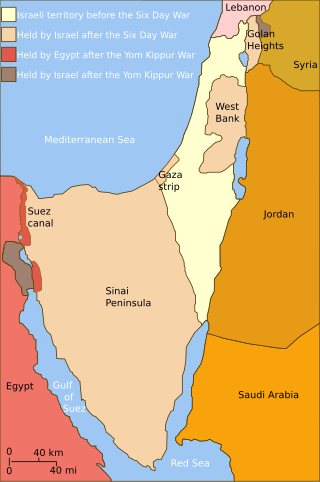
United Nations Security Council Resolution 350, adopted on 31 May 1974, established the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force, to monitor the ceasefire between Israel and Syria in the wake of the Yom Kippur War. UNDOF was initially established for a period of six months, but has had its mandate renewed by subsequent resolutions.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 163, adopted on June 9, 1961, after General Assembly Resolution 1603 declaring Angola a Non-Self-Governing Territory the Council reaffirmed that resolution calling on Portugal to act in accordance with the terms. The Council called upon the Portuguese to desist from repressive measures and to extend every facility to the Sub-Committee on the Situation in Angola, appointed under the terms of the GA resolution, as well as expressing its hope that a peaceful solution will be found and requested that the Sub-Committee report to the Council and GA as soon as possible.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 180, adopted on July 31, 1963, affirmed that Portugal claiming its overseas territories as part of metropolitan Portugal was contrary to the principles of the Charter. The Council deemed Portugal's actions and attitude as seriously disturbing to peace and security in Africa.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 204, adopted unanimously on May 19, 1965, after a complaint by Senegal against Portugal, the Council deplored incursions by the Portuguese Armed Forces into Senegalese territory and requested that they take whatever measures necessary to assure Senegal's territorial integrity.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 218, adopted on November 23, 1965, after recalling previous resolutions on the topic, and Portugal's failure to implement them, the Council again demanded that Portugal withdrawal its military presence from her colonies and enter negotiations with political parties there regarding independence.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 226 was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on October 14, 1966. The Council urged the government of Portugal to prevent foreign mercenaries in the Portuguese territory of Angola from interfering in the domestic affairs of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).
United Nations Security Council Resolution 268, adopted on July 28, 1969, after hearing statements by the parties involved, the Council strongly censured Portugal for attacks on in Katete in eastern Zambia. The Council called upon Portugal to desist from violating the territorial integrity of and carrying out unprovoked raids against Zambia. The Council demanded the Portuguese military return all civilians kidnapped and all property taken declaring that if Portugal failed to comply they would meet to consider further measures.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 275, adopted on December 22, 1969, after a letter from the representative of Guinea and observing that these incidents by Portugal jeopardize international peace and security, the Council called upon Portugal to desist from violating the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Guinea. The Council deeply deplored the loss of life and heavy damage to several Guinean villages inflicted by the action from Guinea-Bissau, a territory under Portuguese administration, solemnly warning Portugal that if such acts were to be repeated in the future the Council would consider further steps to give effect to the resolution. It also called upon Portugal to release a motor barge by the name of Patrice Lumumba and all of its passengers.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 289, adopted unanimously on November 23, 1970, following several previous incursions into the Republic of Guinea by Portuguese troops, the Council demanded the immediate withdrawal of all external armed forces, mercenaries and military equipment and decided that a special mission, to be formed after consultation between the President of the Security Council and the Secretary-General, would be sent to the territory.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 290, adopted on December 8, 1970, after more invasions of the territory of the Republic of Guinea by naval and military units of Portugal on November 22/23 and 27/28, the Council reaffirmed its numerous previous resolutions on the topic, including the right of the peoples of Angola, Mozambique and Portuguese Guinea to be freed from the Portuguese Empire ruled by the Estado Novo regime. The Council endorsed the conclusions of the report by the Special Mission to the Republic of Guinea, strongly condemned the Portuguese Government, demanded that full compensation be paid to the Republic and declared that Portuguese colonialism was a serious threat to the peace and security of Africa.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 273, was adopted on December 9, 1969, after a complaint from Senegal regarding the shelling of the Senegalese village of Samine from a Portuguese base in Begene, the Council condemned the action and called upon Portugal to desist from violating the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Senegal.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 295, was adopted unanimously on August 3, 1971. After receiving a letter from the Permanent Representative of Guinea, a country led by Ahmed Sékou Touré, the Council affirmed its territorial integrity and independence and decided to send a mission of three members of the Council to Guinea to consult with the authorities and report of the situation immediately. The mission was to be appointed after consultation between the president of the Council and the Secretary-General.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 302, adopted on November 24, 1971, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic, the Council expressed its appreciation for the work accomplished by the Special Mission established in resolution 294. The Council deplored the lack of co-operation with the Special Mission by the Portuguese and called upon its government to take effective measures so that the territorial integrity of Senegal would be respected and to prevent acts of violence and destruction against the territory and its people.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 312, adopted on February 4, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the topic and deploring those who failed to conform to them the Council called upon Portugal to immediately recognize the right of the peoples of her colonies to self-determination, to cease all acts of repression against the peoples of Angola, Mozambique and Guinea (Bissau), to withdraw its armed forces from those areas, to promulgate an unconditional political amnesty and to transfer power to freely elected native representative institutions.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 321, adopted on October 23, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions, the Council expressed its concern that Portugal persistently refused to comply with them. The Council attacked the latest cross-border action by the Portuguese army against Senegalese territory and demanded that the Portuguese cease any further acts of violence. The Council went on to reaffirm their position that Portugal's continued holding of colonies in Africa was unjust and that the native peoples of those colonies should be allowed self-determination.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 322, adopted unanimously on November 22, 1972, after reaffirming previous resolutions and considering the Organisation of African Unity's recognition of the revolutionary movements of Angola, Guinea-Bissau, Cape Verde and Mozambique, the Council called on the government of Portugal to cease its military operations and all acts of repression against the people of those territories. The Resolution called on Portugal to enter negotiations with the parties concerned with a view to achieving a solution to the armed confrontations and permitting the peoples of those territories to exercise their right to self-determination and requested the Secretary-General to follow developments and report periodically to the Council.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 384, adopted on December 22, 1975, noted statements from the representatives of Portugal, Indonesia and East Timor and recognized the right of the people of East Timor to self-determination and independence in accordance with the Charter. The Council expressed its grave concern with the deterioration of the situation in East Timor, deplored the intervention of the armed forces of Indonesia in that nation and expressed its regret that Portugal did not discharge fully its responsibilities as administering Power.




