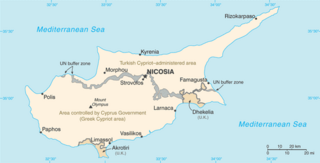
The Cyprus problem, also known as the Cyprus conflict, Cyprus issue, Cyprus dispute, or Cyprus question, is an ongoing dispute between the Greek Cypriot and the Turkish Cypriot community in the north of the island of Cyprus, where troops of the Republic of Turkey are deployed. This dispute is an example of a protracted social conflict. The Cyprus dispute stems from a Turkish military invasion of the island after a coup, and the presence of Turkish soldiers despite a legal reinstatement of a stable government. The desire of some of the ethnic Turkish peoples for the partition of the island of Cyprus through Taksim, and mainland Turkish nationalists settling in as a show of force as a supposed means of protecting their people from what they considered to be the threat of Greek Cypriots, also plays a role in the dispute.

Greece and Turkey established diplomatic relations in the 1830s following Greece's formation after its declaration of independence from the Ottoman Empire. Modern relations began when Turkey was proclaimed a republic in 1923 following the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. Rivalry has characterised their relations for most of their history with periods of positive relations but no underlying resolution of the main issues.

The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of intercommunal violence between Greek and Turkish Cypriots, and in response to a Greek junta-sponsored Cypriot coup d'état five days earlier, it led to the Turkish capture and occupation of the northern part of the island.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1758, adopted unanimously on June 15, 2007, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly Resolution 1251 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for six months until December 15, 2007.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 353, adopted unanimously on 20 July 1974 was a Resolution in which the Council demanded the immediate withdrawal of foreign military personnel present in the Republic of Cyprus in contravention of paragraph 1 of the United Nations Charter. The resolution goes on to call upon Greece, Turkey and the United Kingdom to immediately enter into negotiations to restore peace in the area and constitutional government on the island.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 359, adopted on 15 August 1974, after noting with concern a report from the Secretary-General on the continuing military action in Cyprus and recalling that United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus was placed there with the full consent of the governments of Cyprus, Turkey and Greece, the Council deplored the fact that members of the Force had been killed and wounded. The Resolution demands that all parties respect the status of the Force and demands that all parties co-operate with them in carrying out their tasks in all areas of Cyprus.

United Nations Security Council resolution 716, adopted unanimously on 11 October 1991, after noting a report of the Secretary-General, the Council recognised the progress made regarding the "Set of Ideas" in Cyprus and reaffirmed the efforts of the United Nations in solving the Cyprus dispute.

United Nations Security Council resolution 750, adopted unanimously on 10 April 1992, after reaffirming previous resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, the Council declared that the Cyprus dispute must be settled on the basis of a single Cyprus with a single sovereignty and citizenship, a bi-communal and bi-zonal federation, as set out in resolutions 649 (1990) and 716 (1991).

United Nations Security Council resolution 774, adopted unanimously on 26 August 1992, after reaffirming all previous resolutions on Cyprus, the Council noted that while some progress had been made in negotiations between the two communities on Cyprus, there had still been some difficulties in fully implementing Resolution 750 (1992).

United Nations Security Council resolution 789, adopted unanimously on 25 November 1992, after reaffirming resolutions on Cyprus including 365 (1974), 367 (1975), 541 (1983), 550 (1984) and 774 (1992) and noting a report by the Secretary-General, the Council urged all concerned to implement a set of confidence-building measures.

United Nations Security Council resolution 889, adopted unanimously on 15 December 1993, after recalling Resolution 186 (1964) and other relevant resolutions on Cyprus, the council noted a report of the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 15 June 1994.

United Nations Security Council resolution 902, adopted unanimously on 11 March 1994, after receiving a report from the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali pursuant to Resolution 880 (1993), the council discussed confidence-building measures between the Republic of Cyprus and Northern Cyprus with the aim of resolving the Cyprus dispute.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1062, adopted unanimously on 28 June 1996, after recalling all resolutions on Cyprus, particularly resolutions 186 (1964), 939 (1994) and 1032 (1995), the Council expressed concern at the lack of progress in the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 31 December 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1092, adopted unanimously on 23 December 1996, after recalling all resolutions on Cyprus, particularly resolutions 186 (1964), 939 (1994) and 1062 (1996), the Council expressed concern at the deterioration of the political dispute in Cyprus and extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) until 30 June 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1251, adopted unanimously on 29 June 1999, after reaffirming all past resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, including resolutions 1217 (1998) and 1218 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 15 December 1999.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1303, adopted unanimously on 14 June 2000, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, including resolutions 1251 (1999) and 1283 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until 15 December 2000. The resolution also noted that the Government of Cyprus had agreed that, given the prevailing conditions on the island, it was necessary for UNFICYP to remain beyond 15 June 2000.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1953, adopted on December 14, 2010, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly Resolution 1251 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until June 15, 2011, calling for Greek and Turkish Cypriot leaders to develop a plan for overcoming differences before the Secretary-General visit in January 2011.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1986, adopted unanimously on June 13, 2011, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly resolutions 1251 (1999) and 1953 (2010), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for a further six months until December 15, 2011, calling for an intensification of negotiations between the Greek and Turkish Cypriot leaders.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1728, adopted unanimously on December 15, 2006, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Cyprus, particularly Resolution 1251 (1999), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus (UNFICYP) for six months until June 15, 2007.

















