
The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.

The Russian Federation continued to use the Soviet Union's seat, including its permanent membership on the Security Council in the United Nations after the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union, which originally co-founded the UN in 1945. The continuity was supported by the USSR's former members and was not objected to by the UN membership; Russia accounted for more than 75% of the Soviet Union's economy, the majority of its population and 75% of its land mass; in addition, the history of the Soviet Union began in Russia with the October Revolution in 1917 in Petrograd. If there was to be a continuator to the Soviet seat on the Security Council among the former Soviet republics, these factors made Russia seem a logical choice.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 52, adopted on June 22, 1948, having received the first, second and third reports of the Atomic Energy Commission the Council directed the Secretary-General to transmit the second and third reports, along with a record of the Council deliberations on them, to the General Assembly and the Member States.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 77, adopted on 11 October 1949, having received and examined the second progress report of the Commission for Conventional Armaments, the Council directed the Secretary-General to transmit the report, along with its annexes, accompanying resolution and a record of the Council’s consideration of the subject to the General Assembly for its information.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 78, adopted on October 18, 1949, having received and examined the proposals contained in the working document on the implementation of United Nations General Assembly Resolution 192, adopted by the United Nations Commission on Conventional Armaments the Council requested the Secretary-General transmit these proposals and the records of the discussion on this question in the Council and the Commission for Conventional Armaments to the General Assembly.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 79, adopted on January 17, 1950, having received and the text of United Nations General Assembly Resolution 300 concerning the regulation and general reduction of conventional armaments and armed forces, the Council decided to transmit the resolution to the Commission for Conventional Armaments for further study in accordance with the Commission’s plan of work.

United Nations Security Council resolution 780 was adopted unanimously on 6 October 1992. After reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and subsequent resolutions on the topic, the Council expressed its concern at the continued "widespread violations of international humanitarian law" in Bosnia and Herzegovina and authorised the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to establish a Commission of Experts to examine and analyse the information submitted pursuant to Resolution 771 (1992) on violations of the Geneva Conventions in the region.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 415, adopted on September 29, 1977, noted a letter and an invitation from the United Kingdom to the President of the Security Council to appoint a representative to "enter into discussions with the British Resident Commissioner designate and with all the parties concerning the military and associated arrangements that are considered necessary to effect the transition to majority rule". The Council requested the Secretary-General appoint such representatives, further requested the Secretary-General to transmit a report on the results of the discussions back as soon as possible and finally called on all parties to co-operate with the representative.
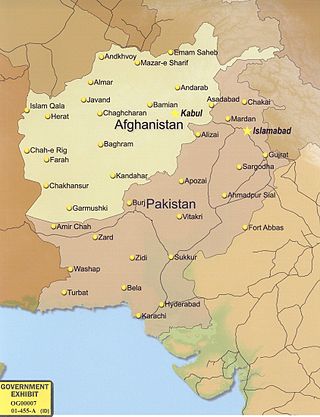
United Nations Security Council resolution 647, adopted unanimously on 11 January 1990, after recalling Resolution 622 (1988) and a letter by the Secretary-General concerning the settlement of the situation in Afghanistan, the Council endorsed the letter's proposals regarding the United Nations Good Offices Mission in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1796 was unanimously adopted on 23 January 2008.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1824 was unanimously adopted on 18 July 2008.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1855 was unanimously adopted on 19 December 2008.

The United Nations Supervision Mission in Syria (UNSMIS) was a United Nations peacekeeping mission in Syria, set up in 2012 as a result of United Nations Security Council Resolution 2043 in response to the Syrian Civil War. It was commanded by Norwegian Major General Robert Mood until 20 July 2012 followed by Lieutenant General Babacar Gaye from Senegal. Although observers remain in the country, Mood suspended their mission on June 16, 2012, citing "escalating violence". Observers will conduct no further patrols and stay in their current positions until the suspension is lifted. On 20 July 2012, the Security Council extended UNSMIS for a final period of 30 days. According to resolution 2059, the Council would only consider more extensions in the event that the Secretary-General reports and the Security Council confirms the cessation of the use of heavy weapons and a reduction in the level of violence sufficient by all sides to allow UNSMIS to implement its mandate.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2231 was a 20 July 2015 resolution endorsing the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action on the nuclear program of Iran. It sets out an inspection process and schedule while also preparing for the removal of United Nations sanctions against Iran. The 15 nations on the Security Council unanimously endorsed the resolution, which had been negotiated by the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—plus Germany, the European Union, and Iran.

The United Nations Security Council Resolution 2235 is on establishing a Joint Investigative Mechanism to identify individuals, entities, groups, or governments responsible for use of chemical weapons in the Syrian civil war.

The eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly opened on 28 February 2022 at the United Nations headquarters. It addresses the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Maldivian politician Abdulla Shahid served as President of the body during this time.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/1 is a resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 2 March 2022. It deplored Russia's invasion of Ukraine and demanded a full withdrawal of Russian forces and a reversal of its decision to recognise the self-declared People's Republics of Donetsk and Luhansk.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/2 is the second resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 24 March 2022, following Resolution ES-11/1 which was adopted on 2 March 2022. Resolution ES‑11/2 reaffirmed the UN's former commitments and obligations under its Charter, and reiterated its demand that Russia withdraw from Ukraine's recognized sovereign territory; it also deplored, expressed grave concern over and condemned attacks on civilian populations and infrastructure. Fourteen principles were agreed.










