
The 1978 United States Senate elections in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. Thirteen seats changed hands between parties. The Democrats at first lost a net of two seats to the Republicans, and then one more in a special election. Democrats nevertheless retained a 58-41 majority.

The 2005 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 8. During this off-year election, the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections held throughout the year. None of these congressional seats changed party hands. There were also two gubernatorial races, state legislative elections in two states, numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races in several major cities, and a variety of local offices on the ballot.

The 2008 United States House of Representatives elections were held on November 4, 2008, to elect members to the United States House of Representatives to serve in the 111th United States Congress from January 3, 2009, until January 3, 2011. It coincided with the election of Barack Obama as President. All 435 voting seats, as well as all 6 non-voting seats, were up for election. The Democratic Party, which won a majority of seats in the 2006 election, expanded its control in 2008. The Republican Party, hoping to regain the majority it lost in the 2006 election or at least expand its congressional membership, lost additional seats. With one exception, the only seats to switch from Democratic to Republican had been Republican-held prior to the 2006 elections. Republicans gained five Democratic seats total, while losing 26 of their own, giving the Democrats a net gain of 21 seats, effectively erasing all gains made by the GOP since 1994. In addition, with the defeat of a Republican congressman in Connecticut's 4th district, this became the first time since the 1850s that no Republican represented the New England region. The 10.6% popular vote advantage by the Democrats was the largest by either party since 1982, 26 years earlier. Turnout increased due to the 2008 presidential election. The presidential election, 2008 Senate elections, and 2008 state gubernatorial elections, as well as many other state and local elections, occurred on the same date.

The 2007 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 6. During this off-year election, the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections held throughout the year. None of these congressional seats changed party hands. There were also several gubernatorial races and state legislative elections, and numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races in several major cities, and several types of local offices on the ballot.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 3, 2009 in the states of New Jersey and Virginia as well as in the U.S. commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands on November 7, 2009. Both state governorships were previously held by Democrats elected in 2005, and as a result of the 2009 elections both are presently held by Republicans; the local Covenant Party maintained control of the governorship of the Marianas. These elections formed part of the 2009 United States elections.
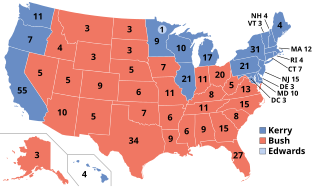
The 2004 United States elections were held on November 2, with President George W. Bush winning re-election. Riding Bush's coattails, the Republicans picked up net gains of 4 Senate seats and 3 House seats, increasing their majorities in both Houses of Congress. In the state governorships up for election, there was no net gain in seats for either party. Foreign policy was the dominant theme throughout the election campaign, particularly Bush's conduct of the War on Terrorism and the 2003 invasion of Iraq.

The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term. During this midterm election year, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 37 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate were contested, along with 39 state and territorial governorships, 46 state legislatures, four territorial legislatures and numerous state and local offices. Approximately 82.5 million people voted.

The 2003 United States elections, most of which were held on Tuesday, November 4, were off-year elections in which no members of the Congress were standing for election. However, there were three gubernatorial races, state legislative elections in four states, numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races in several major cities, and a variety of local offices on the ballot.

The 2002 United States elections were held on November 5, in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's first term. Unusual in midterm elections, the incumbent president's party gained seats in both chambers of the United States Congress. The Republicans picked up net gains of 2 Senate seats and 8 House seats.

The 2009 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 3. During this off-year election, the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections held throughout the year. In total, only the seat representing New York's 23rd congressional district changed party hands, increasing the Democratic Party's majority over the Republicans in the United States House of Representatives, 258–177.

The 2011 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 8. This was an off-year election, in which the only seats up for election in the United States Congress were special elections. There were also four gubernatorial races, including a special election in West Virginia. There were also state legislative elections in four states and judicial elections in three states; as well as numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local offices on the ballot.

The 1996 United States elections were held on November 5. Democratic President Bill Clinton won re-election, while the Republicans maintained their majorities in both houses of the United States Congress.

The 2013 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 5, 2013. This off-year election featured several special elections to the United States Congress; two gubernatorial races; state legislative elections in a few states; and numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local offices on the ballot.

The 2015 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 3. The off-year election included a special election for Speaker of the House. There were also gubernatorial and state legislative elections in a few states; as well as numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local offices on the ballot.

The 2016 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. During this presidential election year, the President of the United States and Vice President were elected. In addition, elections were held for all 435 voting-member seats in the United States House of Representatives and 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate to determine the 115th Congress.

The 2017 United States elections were held, in large part, on Tuesday, November 7, 2017. This off-year election featured gubernatorial elections in Virginia and New Jersey, as well as state legislative elections in both houses of the New Jersey Legislature and in the Virginia House of Delegates. Numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local elections also occurred. Special elections were also held for one seat of the U.S. Senate, representing Alabama, and six seats of the U.S. House of Representatives.
The 1971 New Jersey State Senate Elections was the mid-term election of Republican William Cahill's term as Governor of New Jersey. Democrats picked up nine Senate seats. Sixteen incumbents did not seek re-election.

The 2020 United States elections will be held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. All 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives, 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate, and the office of President of the United States will be contested. Thirteen state and territorial governorships, as well as numerous other state and local elections, will also be contested.

The 2019 United States elections will be held, in large part, on Tuesday, November 5, 2019. This off-year election includes the regular gubernatorial elections in Kentucky, Louisiana, and Mississippi. State legislative elections will also be held in Louisiana, Mississippi, Virginia, and in the New Jersey General Assembly. Numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local elections will also occur. Special elections to the United States Congress will take place because so far 3 vacancies arose.

The 1997 United States elections were off-year elections were held on Tuesday, November 4, 1997, comprising 2 gubernatorial races, 3 congressional special elections, and a plethora of other local elections across the United States. No Senate special elections were held.






























