Related Research Articles

Arnulf of Carinthia was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894, and the disputed emperor from February 22, 896, until his death at Ratisbon, Bavaria.
The 890s decade ran from January 1, 890, to December 31, 899.
The 950s decade ran from January 1, 950, to December 31, 959.
The 960s decade ran from January 1, 960, to December 31, 969.

Year 966 (CMLXVI) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar.
Year 915 (CMXV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar.

King of Italy was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a barbarian warlord, in the late 5th century, followed by the Ostrogothic kings up to the mid-6th century. With the Frankish conquest of Italy in the 8th century, the Carolingians assumed the title, which was maintained by subsequent Holy Roman Emperors throughout the Middle Ages. The last Emperor to claim the title was Charles V in the 16th century. During this period, the holders of the title were crowned with the Iron Crown of Lombardy.
Berengar, called the Wise, was the duke or count of Toulouse (814–835) and duke of Septimania (832–835). He held the County of Barcelona concomitantly with Septimania.

Berengar I was the king of Italy from 887. He was Holy Roman Emperor between 915 and his death in 924. He is usually known as Berengar of Friuli, since he ruled the March of Friuli from 874 until at least 890, but he had lost control of the region by 896.

Lambert was the King of Italy from 891, Holy Roman Emperor, co-ruling with his father from 892, and Duke of Spoleto and Camerino from his father's death in 894. He was the son of Guy III of Spoleto and Ageltrude, born in San Rufino. He was the last ruler to issue a capitulary in the Carolingian tradition.

Berengar II was the King of Italy from 950 until his deposition in 961. He was a scion of the Anscarid and Unruoching dynasties, and was named after his maternal grandfather, Berengar I. He succeeded his father as Margrave of Ivrea around 923, and after 940 led the aristocratic opposition to kings Hugh and Lothair II. In 950 he succeeded the latter and had his son, Adalbert crowned as his co-ruler. In 952 he recognised the suzerainty of Otto I of Germany, but he later joined a revolt against him. In 960 he invaded the Papal States, and the next year his kingdom was conquered by Otto. Berengar remained at large until his surrender in 964. He died imprisoned in Germany two years later.

The Kingdom of Lower Burgundy, also called Cisjurane Burgundy, was a historical kingdom in what is now southeastern France, so-called because it was lower down the Rhône Valley than Upper Burgundy.

Adalbert was the king of Italy from 950 until 961, ruling jointly with his father, Berengar II. After their deposition, Adalbert continued to claim the Italian kingdom until his defeat in battle by the forces of Otto I in 965. Since he was the second Adalbert in his family, the Anscarids, he is sometimes numbered Adalbert II. His name is occasionally, especially in older works, shortened to Albert.

The March of Ivrea was a large frontier county (march) in the northwest of the medieval Italian kingdom from the late 9th to the early 11th century. Its capital was Ivrea in present-day Piedmont, and it was held by a Burgundian family of margraves called the Anscarids. The march was the primary frontier between Italy and Upper Burgundy and served as a defense against any interference from that state.

The Anscarids or the House of Ivrea were a medieval dynasty of Burgundian and Frankish origin which rose to prominence in Northern Italy in the tenth century, even briefly holding the Italian throne. The main branch ruled the County of Burgundy from the eleventh to fourteenth centuries and it was one of their members who first declared himself a count palatine. The cadet Castilian branch of Ivrea ruled the Kingdom of Galicia from 1111 and the Kingdoms of Castile and León from 1126 until 1369. The Spanish House of Trastámara, which ruled in Castile, Aragon, Naples, and Navarre at various points between the late 14th and early 16th centuries, was an illegitimate cadet branch of that family.
William I, Marquis of Montferrat stands at the head of the Aleramici family which ruled Montferrat for four centuries. He was the father of the first Marquis Aleram.
Eberhard was the Frankish Duke of Friuli from 846. His name is alternatively spelled Everard, Evrard, Erhard, or Eberard; in Latinized fashion, Everardus, Eberardus, or Eberhardus. He wrote his own name "Evvrardus". He was an important political, military, and cultural figure in the Carolingian Empire during his lifetime. He kept a large library, commissioned works of Latin literature from Lupus Servatus and Sedulius Scottus, and maintained a correspondence with the theologians and church leaders Gottschalk, Rabanus Maurus, and Hincmar.
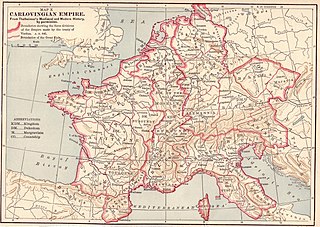
The March of Friuli was a Carolingian frontier march, established in 776 as the continuation of the Lombard Duchy of Friuli, established against the Slavs and Avars. It was ceded to the Duchy of Bavaria as the March of Verona in 952. Its territory comprised parts of modern-day Italy, Slovenia and Croatia.
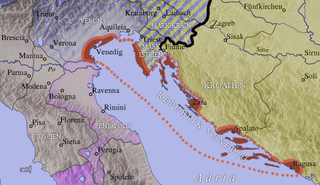
The March of Istria was originally a Carolingian frontier march covering the Istrian peninsula and surrounding territory conquered by Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy in 789. After 1364, it was the Istrian province of the Habsburg monarchy, the Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary.

Otto I, known as Otto the Great or Otto of Saxony, was East Frankish (German) king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the eldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim.
References
- Riché, Pierre, Les Carolingiens. Une famille qui fit l'Europe. Paris: Hachette/Pluriel, 1997. ISBN 2-01-278851-3