
Lower Franconia is one of seven districts of Bavaria, Germany. The districts of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia make up the region of Franconia. It consists of nine districts and 308 municipalities.

Middle Franconia is one of the three administrative regions of Franconia, Germany, in the west of Bavaria bordering the state of Baden-Württemberg. The administrative seat is Ansbach; the most populous and largest city is Nuremberg.
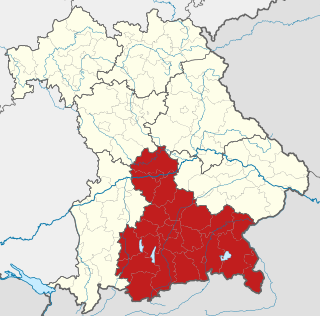
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany.
Hof is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Wunsiedel, Bayreuth, Kulmbach and Kronach, the states of Thuringia and Saxony, and the Czech Republic. The city of Hof is an enclave within the district, as well as being the district's administrative seat.
Kronach is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Hof, Kulmbach, Lichtenfels and Coburg, and the state of Thuringia.
Kulmbach is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Kronach, Hof, Bayreuth and Lichtenfels.
Lichtenfels is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Coburg, Kronach, Kulmbach, Bayreuth and Bamberg.

Kulmbach is the capital of the district of Kulmbach in Bavaria in Germany. The town, once a stronghold of the Principality of Bayreuth, is renowned for its University of Life Sciences, a branch of the University of Bayreuth, the massive Plassenburg Castle, which houses the largest tin soldier museum in the world, for its brewery, its vivid food industry, which hosts some of the world's biggest food businesses, and for its sausages, or Bratwürste.
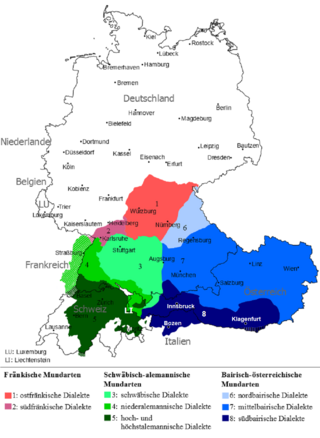
East Franconian or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are Unterostfränkisch, Oberostfränkisch and Südostfränkisch.

Plassenburg is a castle in the city of Kulmbach in Bavaria. It is one of the most impressive castles in Germany and a symbol of the city. It was first mentioned in 1135. The Plassenberg family were ministerial of the counts of Andechs and used as their seat the Plassenburg. The House of Guttenberg, a prominent Franconian noble family, traces its origins back to 1149 with a Gundeloh v. Blassenberg (Plassenberg). The name Guttenberg is derived from Guttenberg and was adopted by a Heinrich von Blassenberg around 1310. From 1340, the Hohenzollerns governed from Plassenburg castle their territories in Franconia till 1604. The Plassenburg was fortress and residence for the Hohenzollerns.

Lichtenfels is a town in the Upper Franconian region of Bavaria, Germany, the administrative seat of Lichtenfels district. It is chiefly known as the German "Basket City".
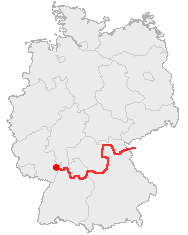
The Castle Road is a theme route in southern Germany and a small portion in the Czech Republic, between Mannheim and Prague.

The Bezirksoberliga Oberfranken was the seventh tier of the German football league system in the Bavarian Regierungsbezirk of Upper Franconia. Until the introduction of the 3. Liga in 2008 it was the sixth tier of the league system, until the introduction of the Regionalligas in 1994 the fifth tier.

The Bamberg–Hof railway is a 127 kilometre-long main line that runs through Bavaria in southern Germany. The line runs from Bamberg via Lichtenfels, Kulmbach, Neuenmarkt-Wirsberg and Münchberg to Hof. The section from Hof to Neuenmarkt now forms part of the Saxon-Franconian trunk line.
DB Regio Oberfranken is a business area with the German national railway company, Deutsche Bahn, with its headquarters in Hof (Saale). It is responsible for the majority of regional and local railway services in the Bavarian province of Upper Franconia (Oberfranken).
The 2. Amateurliga Bayern was a set of eleven regional leagues in Bavaria existing from 1951 to 1963 as the fourth tier of football in the state.

Lichtenfels station is in the town of Lichtenfels in Upper Franconia in the German state of Bavaria. It is a regional rail hub and a former ICE stop on the Hamburg–Berlin Munich route and is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a station of category 3.

The Mainkreis was one of the 15 administrative districts of the Kingdom of Bavaria between 1806 and 1837. The district was named after its main river Main and renamed Obermainkreis in 1817. It was the predecessor of the Regierungsbezirk Oberfranken.

The Nuremberg Metropolitan Region comprises 3.5 million people on 21,800 square kilometers. With a gross domestic product of 134 billion euros and about 1.9 million employees, this metropolitan region is one of the strongest economic areas in Germany. The major cities are Nuremberg, Fürth, Erlangen, Bayreuth and Bamberg.

The Verkehrsverbund Großraum Nürnberg is the transit authority of the city of Nuremberg, the second largest city of the German state of Bavaria. Its jurisdiction covers the city and its surrounding area, responsible for the Nuremberg S-Bahn commuter trains, the Nuremberg U-Bahn, the Nuremberg tramway and buses. While not co-extensive with the wider Nuremberg Metropolitan Region, it covers most of it with the exception of several smaller towns and rural areas on the periphery, as well as Sonneberg in the neighboring state of Thuringia.
















