
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of 70,550.19 km2 (27,239.58 sq mi), it is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is below the German average. Major cities include Munich, Nuremberg, and Augsburg.

Swabia is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of ten districts and 340 municipalities with Augsburg being the administrative capital. It is the only German region officially named Swabia in the principle of spatiality.
The history of Bavaria stretches from its earliest settlement and its formation as a stem duchy in the 6th century through its inclusion in the Holy Roman Empire to its status as an independent kingdom and finally as a large Bundesland (state) of the Federal Republic of Germany. Originally settled by Celtic peoples such as the Boii, by the 1st century BC it was eventually conquered and incorporated into the Roman Empire as the provinces of Raetia and Noricum.

Lower Franconia is one of seven districts of Bavaria, Germany. The districts of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia make up the region of Franconia. It consists of nine districts and 308 municipalities.

Upper Franconia is a Regierungsbezirk of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia, the others being Middle Franconia and Lower Franconia, which are all now part of the German Federal State of Bayern (Bavaria).

Middle Franconia is one of the three administrative regions of Franconia, Germany, in the west of Bavaria bordering the state of Baden-Württemberg. The administrative seat is Ansbach; the most populous and largest city is Nuremberg.
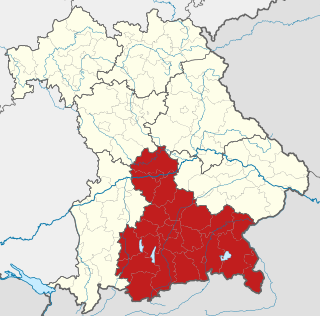
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany.

The Upper Palatinate is an administrative district in the east of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of seven districts and 226 municipalities, including three cities.

Tübingen is one of the four Administrative Regions of Baden-Württemberg, Germany, located in the south-east of the state. It covers most of the German shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee), and also the beginning of the Danube River valley. It is sub-divided into the three regions : Neckar-Alb, Donau-Iller and Bodensee-Oberschwaben. Donau-Iller also includes three districts and one city of Bavaria.
Deggendorf is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bordered by the districts of Regen, Freyung-Grafenau, Passau, Rottal-Inn, Dingolfing-Landau and Straubing-Bogen.

Landshut is a town in Bavaria in the south-east of Germany. Situated on the banks of the River Isar, Landshut is the capital of Lower Bavaria, one of the seven administrative regions of the Free State of Bavaria. It is also the seat of the surrounding district and has a population of more than 75,000. Landshut is the largest city in Lower Bavaria, followed by Passau and Straubing, and Eastern Bavaria's second after Regensburg.
Straubing-Bogen is a Landkreis (district) in the eastern part of Bavaria, Germany. Neighboring districts are Cham, Regen, Deggendorf, Dingolfing-Landau, Landshut and Regensburg. The independent town of Straubing is surrounded by the district. The seat of the government of the district (Landratsamt) is located in Straubing.

Bavarians are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern, roughly the territory of the Electorate of Bavaria in the 17th century.

The Innviertel is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn river. It forms the western part of the state of Upper Austria and borders the German state of Bavaria. The Innviertel is one of the four traditional "quarters" of Upper Austria, the others being Hausruckviertel, Mühlviertel, and Traunviertel.

The Kingdom of Bavaria was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia.

Bad Griesbach im Rottal, or just Bad Griesbach, is a town in the district of Passau in Bavaria in Germany.
Bavaria, one of the states of Germany, has a multiparty system dominated by the Christian Social Union in Bavaria (CSU). Bavaria has long been a bastion of conservative politics in Germany, with the Christian Social Union has won every election of the state parliament since 1946 and having almost a monopoly on power. Every Minister-President since 1957 has been a member of this party. On the other hand the bigger and more liberal, or rather social democratic, cities, especially Munich, have been governed for decades by the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) until recently the second biggest party. In 2018 the Alliance 90/The Greens which have been represented in the state parliament since 1986, became the second biggest political party in the Landtag and in 2020 the biggest party in the Munich City Council. From the historical point of view, older Bavaria was one of the most liberal, predominantly Roman Catholic states until the rather rural areas of Swabia and Franconia were added in 1814/15 at the Congress of Vienna.
The Royal Bavarian Eastern Railway Company or Bavarian Ostbahn was founded in 1856. Within just two decades it built an extensive railway network in the eastern Bavarian provinces of Upper Palatinate (Oberpfalz) and Lower Bavaria (Niederbayern) that had previously been largely undisturbed by the railway. Much of this network is still important for local and long distance rail traffic operated by the Deutsche Bahn today.
Landestheater Niederbayern is a theatre in Lower Bavaria, Germany founded in 1952. The theater does both musical theater and drama under the artistic director Stefan Tilch. It plays at the city theaters of Landshut and Passau, the Theater am Hagen in Straubing, and other regional theaters. Its orchestra is the Niederbayerische Philharmonie.

The Lower Danube Circle or Under Danube Circle was one of the administrative districts of the Kingdom of Bavaria between 1806 and 1837. It was named after its main river, the Danube and was the predecessor of the administrative district of Lower Bavaria. Its administrative headquarters were in Passau, but the appellate court was in Straubing.

















