

The urban hierarchy of Brazil places Brazil's cities into categories: global cities, national metropolises, regional metropolises, regional capitols (A, B and C), sub-regional centers (A and B) and zone centers (A, B and C). [1]


The urban hierarchy of Brazil places Brazil's cities into categories: global cities, national metropolises, regional metropolises, regional capitols (A, B and C), sub-regional centers (A and B) and zone centers (A, B and C). [1]
Brazil's global cities possess areas of influence that surpass the country's borders. Brazil's global cities are the municipalities of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo.
Brasília, São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro are Brazil's national metropolises. They are the first level of territorial management, providing a focus for centers located in all parts of Brazil.
Regional metropolises constitute the second level of territorial management, and influence the surrounding macro-region where they are located. Brazil's regional metropolises include Curitiba, Salvador, Porto Alegre, Goiânia, Fortaleza, Recife, Manaus, Belém and Belo Horizonte.
The regional capitol is the third level of territorial management, and influences its state and its surrounding states. These are subdivided into: A regional capitols (cities such as Natal, Campinas, Florianópolis and Vitória); B regional capitols (cities such as Caxias do Sul, Chapecó, Porto Velho and Campina Grande) and C regional capitols (cities such as Campos, Caruaru, Governador Valadares and Mossoró).
Sub-regional centers possess influence over cities that are within close proximity, and nearby towns and rural areas as well. These are subdivided into: A sub-regional centers (cities such as Alfenas, Anápolis, São Mateus and Umuarama) and B sub-regional centers (Afogados da Ingazeira, Cacoal, Caratinga and Tefé).
The zone centers are the cities or towns that have an important regional influence, but limited to the immediate surrounding area, and exercising elementary management functions. These are subdivided into two levels: A zone centers (cities such as Tabatinga, Lagoa Vermelha, Lins and Três de Maio) and B zone centers (towns such as Afonso Cláudio, Eirunepé, São Bento and Taió). [2]
General:

Assis is a city and a municipality in the southwestern part of the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population is 105,087 in an area of 460.61 km2. The town was founded on July 5, 1905, and became a municipality in 1917, when it was separated from Platina. It is the largest city of its microregion, and the 2nd of its mesoregion, and is 434 km away from the capital, São Paulo. The town has an annual average temperature of 21,37 °C, annual rainfall 1,441 mm (56.7 in), and the vegetation predominates Mata Atlântica and Cerrado, is then a transition zone of vegetation. Its Human Development Index (HDI) is 0.805, considered high if compared to state and is in 28th place among Brazilian cities.

Hortolândia is a Brazilian municipality in the interior of the state of São Paulo. It is part of the Metropolitan Region of Campinas and the Mesoregion and Microregion of Campinas. It is located northwest of the state capital, about 110 km away. It is part of the São Paulo macrometropolis, which exceeds 29 million inhabitants and makes up approximately 75 percent of the state's population. The metropolitan regions of Campinas and São Paulo form the first megalopolis in the southern hemisphere. It is bordered by Sumaré, to the north; Monte Mor, to the south and west; and Campinas, to the east.

Arantina is a Brazilian municipality located in the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 is estimated to be 2,787 people living in a total area of 89.382 km². The city belongs to the mesoregion of Sul and Sudoeste de Minas and to the microregion of Andrelândia.
Santa Vitória is a municipality in the west of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. As of 2020, the population was estimated at 19,872. It became a municipality in 1948.

Xique-Xique is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil. Its estimated population in 2020 was 46,523 inhabitants. It is situated on the right bank of São Francisco River and is a regional economic center. Xique-Xique takes its name from a cactus, Pilosocereus gounellei, common to the region.
São Raimundo das Mangabeiras is a municipality in the state of Maranhão in the Northeast region of Brazil.
Itatiaiuçu is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
São José da Varginha is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.

Piranguinho is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.

São João da Mata is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
São Sebastião da Bela Vista is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
São Pedro da União is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
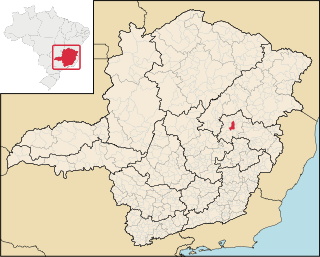
São João Evangelista is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
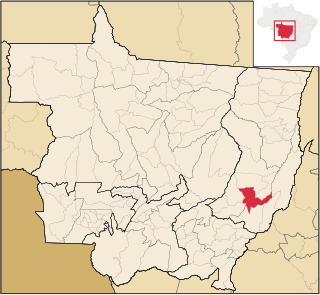
Nova Xavantina is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil. Located in the Legal Amazon and the Araguaia Valley, the Rio das Mortes runs through the center of the municipality. Founded in 1980, today Nova Xavantina serves as an agricultural center, the location of a campus of the State University of Mato Grosso (Unemat), and a tourist destination.

São Félix do Araguaia is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

Vale de São Domingos is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.
Campina da Lagoa is a municipality in the state of Paraná in the Southern Region of Brazil.
Cornélio Procópio is a municipality in the state of Paraná in the Southern Region of Brazil.
Rebouças is a municipality in the state of Paraná in the Southern Region of Brazil. Being filled with some hills in the surroundings and some parts of the city, the high structures are a tower in the hill of Mourão and the church in the city center., One dominant group of ethnicities in the city are Polish and Ukrainians.
Campinas do Piauí is a municipality in the state of Piauí in the Northeast region of Brazil.