
The Stramenopiles, also called Heterokonts, are a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost. Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria.
Euglenids or euglenoids are one of the best-known groups of flagellates. They are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta, classified as class Euglenida or Euglenoidea. Euglenids are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group known as Euglenophyceae have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon.

Cafeteria roenbergensis is a small bacterivorous marine flagellate. It was discovered by Danish marine ecologist Tom Fenchel and named by him and taxonomist David J. Patterson in 1988. It is in one of three genera of bicosoecids, and the first discovered of two known Cafeteria species. Bicosoecids belong to a broad group, the stramenopiles, also known as heterokonts (Heterokonta) that includes photosynthetic groups such as diatoms, brown, and golden algae, and non-photosynthetic groups such as opalinids, actinophryid "heliozoans", and oomycetes. The species is found primarily in coastal waters where there are high concentrations of bacteria on which it grazes. Its voracious appetite plays a significant role in regulating bacteria populations.

Peranema is a genus of free-living phagotrophic euglenids. There are more than 20 nominal species, varying in size between 8 and 200 micrometers. Peranema cells are gliding flagellates found in freshwater lakes, ponds and ditches, and are often abundant at the bottom of stagnant pools rich in decaying organic material. Although they belong to the class Euglenoidea, and are morphologically similar to the green Euglena, Peranema have no chloroplasts, and do not conduct autotrophy. Instead, they capture live prey, such as yeast, bacteria and other flagellates, consuming them with the help of a rigid feeding apparatus called a "rod-organ." Unlike the green euglenids, they lack both an eyespot (stigma), and the paraflagellar body (photoreceptor) that is normally coupled with that organelle. However, while Peranema lack a localized photoreceptor, they do possess the light-sensitive protein rhodopsin, and respond to changes in light with a characteristic "curling behaviour."
Mantamonads are a group of free-living heterotrophic flagellates that move primarily by gliding on surfaces. They are classified as one genus Mantamonas in the monotypic family Mantamonadidae, order Mantamonadida and class Glissodiscea. Previously, they were classified in Apusozoa as sister of the Apusmonadida on the basis of rRNA analyses. However, mantamonads are currently placed in CRuMs on the basis of phylogenomic analyses that identify their closest relatives as the Diphylleida and Rigifilida.

Neobodo are diverse protists belonging to the eukaryotic supergroup Excavata. They are Kinetoplastids in the subclass Bodonidae. They are small, free-living, heterotrophic flagellates with two flagella of unequal length used to create a propulsive current for feeding. As members of Kinetoplastids, they have an evident kinetoplast There was much confusion and debate within the class Kinetoplastid and subclass Bodonidae regarding the classification of the organism, but finally the new genera Neobodo was proposed by Keith Vickerman. Although they are one of the most common flagellates found in freshwater, they are also able to tolerate saltwater Their ability to alternate between both marine and freshwater environments in many parts of the world give them a “cosmopolitan” character. Due to their relatively microscopic size ranging between 4–12 microns, they are further distinguished as heterotrophic nanoflagellates. This small size ratio limits them as bacterivores that swim around feeding on bacteria attached to surfaces or in aggregates.
Petalomonas is a genus of phagotrophic, flagellated euglenoids. Phagotrophic euglenoids are one of the most important forms of flagellates in benthic aquatic systems, playing an important role in microbial food webs. The traits that distinguish this particular genus are highly variable, especially at higher taxa. However, general characteristics such as a rigid cell shape and single emergent flagellum can describe the species among this genus.
Heteronema is a genus of phagotrophic, flagellated euglenoids that are most widely distributed in fresh water environments. This genus consists of two very distinguishable morphogroups that are phylogenetically closely related. These morphogroups are deciphered based on shape, locomotion and other ultrastructural traits. However, this genus does impose taxonomic problems due to the varying historical descriptions of Heteronema species and its similarity to the genus Paranema. The species H. exaratum, was the first heteronemid with a skidding motion to be sequenced, which led to the discovery that it was not closely related to H. scaphrum, contrary to what was previously assumed, but instead to a sister group of primary osmotrophs. This suggests that skidding heteronemids can also be distinguished phylogenetically, being more closely related to Anisoma, Dinema and Aphageae, than to other species within Heteronema.
Massisteria marina is a species of small marine phagotrophic protists that normally feed on bacteria. Individuals live associated with sediment particles and suspended detritus in litoral or marine waters. It is found at marine sites all around the world. Its predominantly sedentary lifestyle was a discovery that challenged the concept of bacterivorous protists as constantly active hunters, and its permanent association with detritus particles is uncommon among flagellates.
Thecamonadinae is a subfamily of heterotrophic protists. It is a monophyletic group, or clade, of apusomonads, a group of protozoa with two flagella closely related to the eukaryotic supergroup Opisthokonta. The subfamily contains two genera Chelonemonas and Thecamonas, which are found in marine habitats.
Heliorapha is a genus of heliozoan protists, amoeboid eukaryotes with stiff axopodia radiating from their cells. It contains one species, Heliorapha azurina. It is classified within a monotypic family Helioraphidae inside the actinophryids, a group of heliozoa that belong to the Ochrophyta along with other protists such as diatoms and brown algae.

Urceolus is a genus of heterotrophic flagellates belonging to the Euglenozoa, a phylum of single-celled eukaryotes or protists. Described by Russian biologist Konstantin Mereschkowsky in 1877, its type species is Urceolus alenizini. Species of this genus are characterized by deformable flask-shaped cells that exhibit at least one flagellum that is active at the tip, arising from a neck-like structure that also hosts the feeding apparatus. They are found in a variety of water body sediments across the globe. According to evolutionary studies, Urceolus belongs to a group of Euglenozoa known as peranemids, closely related to the euglenophyte algae.

Colponemids are free-living alveolates, unicellular flagellates related to dinoflagellates, apicomplexans and ciliates. They are predators of other small eukaryotes, found in freshwater, marine and soil environments. They do not form a solid clade, but a sparse group of deep-branching alveolate lineages.
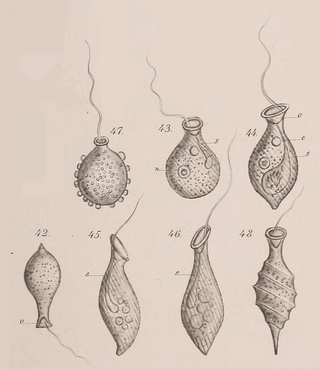
Urceolus cyclostomus is a species of heterotrophic flagellates. It was initially described by Friedrich Stein in 1878 as Phialonema cyclostomum, from an unknown location. Due to its morphological similarities to Urceolus alenizini, the author of the latter, Konstantin Mereschkowsky, transferred it to the genus Urceolus in 1881. Like other species of the genus, its cells have a neck and a wide aperture to a canal that hosts a single flagellum and its feeding apparatus. It is distinguished from other species by a significantly more rigid cell shape, among other traits. It can be found in the bottom sediment of freshwater and brackish water bodies, as a consumer of algae.

Urceolus alenizini is a species of flagellates. It was described by Konstantin Mereschkowsky in 1877 as the type species of the genus Urceolus. It is a rare species only recorded by its author once in the White Sea, in northern Russia. It is distinguished by other members of the genus by the lack of spiral stripes in its cell surface.
Ploeotia is a genus of heterotrophic flagellates belonging to the Euglenida, a diverse group of flagellated protists in the phylum Euglenozoa. Species of Ploeotia are composed of rigid cells exhibiting two flagella. The genus was described by Félix Dujardin in 1841.
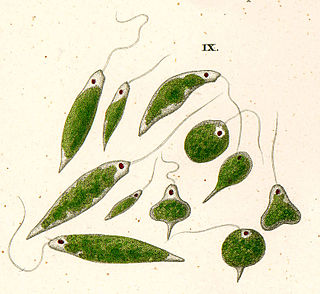
The peranemids are a group of phagotrophic flagellates, single-celled eukaryotes or protists. They belong to the Euglenida, a diverse lineage of flagellates that contains the closely related euglenophyte algae. Like these algae, peranemids have flexible cells capable of deformation or metaboly, and have one or two flagella in the anterior region of the cell. They are classified as family Peranemidae (ICZN) or Peranemataceae (ICBN) within the monotypic order Peranemida (ICZN) or Peranematales (ICBN).
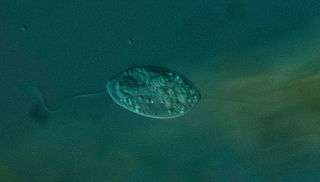
Anisonemia is a clade of single-celled protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa, relatives of the Euglenophyceae algae. They are flagellates, with two flagella for locomotion. Anisonemia includes various phagotrophic species and a group of primary osmotrophic protists known as Aphagea.

Rapaza viridis is a species of single-celled flagellate within the Euglenophyceae, a group of algae. It is the only species within the genus Rapaza, family Rapazidae and order Rapazida. It was discovered in a tide pool in British Columbia and described in 2012.
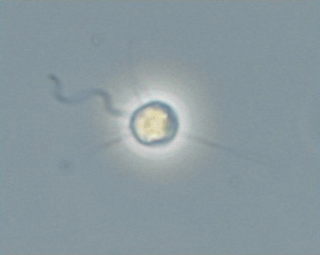
Pteridomonas is a genus of heterotrophic flagellates belonging to the phylum Ochrophyta. It was described in 1890 by Eugène Penard. Species of this genus descend from a group of photosynthetic algae but have secondarily lost their chloroplasts. They are single-celled flagellates, attached to the substrate by a stalk and distinguished by a ring of tentacles around the single flagellum. They can be found in marine, brackish or freshwater environments.












