See also
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Uruguay Cove". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Uruguay Cove". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
Uruguay Cove ( 60°45′S44°43′W / 60.750°S 44.717°W ) is a cove in the west part of Jessie Bay on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. Charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under W.S. Bruce. He named the cove after the Argentine corvette Uruguay, which for many years after 1904 carried relief parties to the Argentine meteorological station near the cove.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Uruguay Cove". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Uruguay Cove". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.

Signy Island is a small subantarctic island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was named by the Norwegian whaler Petter Sørlle (1884–1933) after his wife, Signy Therese.
This is a list of the extreme points of the United Kingdom: the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location. Traditionally the extent of the island of Great Britain has stretched "from Land's End to John o' Groats".
Hope Bay is a bay 3 nautical miles long and 2 nautical miles wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound.
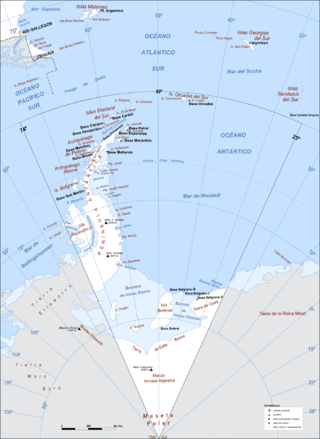
Argentine Antarctica is an area on Antarctica claimed by Argentina as part of its national territory. It consists of the Antarctic Peninsula and a triangular section extending to the South Pole, delimited by the 25° West and 74° West meridians and the 60° South parallel. This region overlaps with British and Chilean claims in Antarctica. None of these claims have widespread international recognition.

Seymour Island or Marambio Island, is an island in the chain of 16 major islands around the tip of the Graham Land on the Antarctic Peninsula. Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. It lies within the section of the island chain that resides off the west side of the peninsula's northernmost tip. Within that section, it is separated from Snow Hill Island by Picnic Passage, and sits just east of the larger key, James Ross Island, and its smaller, neighboring island, Vega Island.

The Arctowski Peninsula is a peninsula, 15 nautical miles long in a north-south direction, lying between Andvord Bay and Wilhelmina Bay on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.
Sheila Cove is a cove in the southwest part of Jessie Bay on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. Surveyed and named by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition, 1902–04, for Sheila Bruce, daughter of William S. Bruce, leader of the expedition.
Mount Susini is a mountain rising to 370 m at the northwest end of Mackenzie Peninsula, Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. Named "Monte Susini" by an Argentine Antarctic Expedition, 1957. An English form of the name has been approved.
Two Hummock Island is an ice-covered island, 5 nautical miles long in a north–south direction, conspicuous for its two rocky summits 670 metres (2,200 ft) high, lying 5 nautical miles southeast of Liège Island in the Palmer Archipelago.
Aitken Cove is a cove which lies immediately northeast of Cape Whitson, along the south coast of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands in the Southern Ocean. Charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for A.N.G. Aitken, solicitor to the expedition.

Cora Cove is the 750 m wide cove in the northwest part of Blythe Bay indenting for 590 m the southeast coast of Desolation Island off Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica. The cove was used by early 19th century sealers operating from Blythe Bay.

Argentina Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest from Hurd Dome and terminating near Argentina Cove, South Bay, on Livingston Island, in the South Shetland Islands. The name Argentina Glacier was given in association with Argentina Cove by the Spanish Antarctic Expedition, about 1995.
The Cayley Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest into the south side of Brialmont Cove, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

Cape Whitson, is a headland on the south coast of Laurie Island, the easternmost and second largest of the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It lies about 9 km south-east of Argentina’s Orcadas Base.
Ewer Pass is a pass rising to about 200 metres (660 ft), trending north-northwest–south-southeast between Browns Bay and Aitken Cove on Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-names Committee in 1987 after John R. Ewer, a Falklands Islands Dependencies Survey meteorological observer at Cape Geddes, Laurie Island, January–March 1947, and at Deception Island, 1947–48; he a member of the party that crossed Laurie Island via this pass.
Point Moreno is a point at the east side of the entrance to the small cove at the head of Scotia Bay, on the south coast of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands. Charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Bruce, who named it for Francisco P. Moreno, noted Argentine scientist and director of the Museo de la Plata.
Point Lola is the east entrance point to Uruguay Cove, Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. The name appears on an Argentine government chart of 1930, based upon surveys by two Argentine naval officers, I. Espindola in the Uruguay in 1915 and A. Rodriguez in the Primero de Mayo in 1930.
Russell East Glacier is a glacier, 6 nautical miles long and 3 nautical miles wide, which lies at the north end of Detroit Plateau and flows from Mount Canicula eastward into Prince Gustav Channel on the south side of Trinity Peninsula, Antarctica. This glacier together with Russell West Glacier, which flows westward into Bone Bay on the north side of Trinity Peninsula, form a through glacier across the north part of Antarctic Peninsula.
Mount Ramsay is a peak, 475 m, standing at the west side of Uruguay Cove on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands. Charted by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Bruce, 1902–04, and named for Allan Ramsay, chief engineer of the expedition ship Scotia, who died on August 6, 1903, and was buried at the foot of the peak.