Related Research Articles

Phytophthora infestans is an oomycete or water mold, a fungus-like microorganism that causes the serious potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight. Early blight, caused by Alternaria solani, is also often called "potato blight". Late blight was a major culprit in the 1840s European, the 1845–1852 Irish, and the 1846 Highland potato famines. The organism can also infect some other members of the Solanaceae. The pathogen is favored by moist, cool environments: sporulation is optimal at 12–18 °C (54–64 °F) in water-saturated or nearly saturated environments, and zoospore production is favored at temperatures below 15 °C (59 °F). Lesion growth rates are typically optimal at a slightly warmer temperature range of 20 to 24 °C.

Dutch elm disease (DED) is caused by a member of the sac fungi (Ascomycota) affecting elm trees, and is spread by elm bark beetles. Although believed to be originally native to Asia, the disease was accidentally introduced into America, Europe, and New Zealand. In these regions it has devastated native populations of elms that did not have resistance to the disease. The name "Dutch elm disease" refers to its identification in 1921 and later in the Netherlands by Dutch phytopathologists Bea Schwarz and Christine Buisman, who both worked with professor Johanna Westerdijk. The disease affects species in the genera Ulmus and Zelkova; therefore it is not specific to the Dutch elm hybrid.
There are a number of lines of defence against pests and diseases in the orchard, principal among these being the practice of good husbandry, creating healthy soil and ensuring high standards of garden hygiene. But no matter how diverse and healthy the garden eco-system may be, there will always be a degree of disease and pest presence. In many ways, some level of pathogen population in the garden can be not only acceptable but desirable as they are indicative of a generally healthful and diverse environment, and add to the overall robustness of the system as an immunity to such detrimental influences will build up, particularly in a balanced polycultural regime. Indeed, most of the plants we grow will tend to be selected because they are trouble free, and those that are more susceptible to attack will have fallen by the wayside over time. However, most farmers find it unacceptable that the food crops they grow are damaged by pests.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

An heirloom tomato is an open-pollinated, non-hybrid heirloom cultivar of tomato. They are classified as family heirlooms, commercial heirlooms, mystery heirlooms, or created heirlooms. They usually have a shorter shelf life and are less disease resistant than hybrids. They are grown for various reasons: for food, historical interest, access to wider varieties, and by people who wish to save seeds from year to year, as well as for their taste.

Gros Michel, often translated and known as "Big Mike", is an export cultivar of banana and was, until the 1950s, the main variety grown. The physical properties of the Gros Michel make it an excellent export produce; its thick peel makes it resilient to bruising during transport and the dense bunches that it grows in make it easy to ship.

The tomato is the edible berry of the plant Solanum lycopersicum, commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word tomatl gave rise to the Spanish word tomate, from which the English word tomato derived. Its domestication and use as a cultivated food may have originated with the indigenous peoples of Mexico. The Aztecs used tomatoes in their cooking at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and after the Spanish encountered the tomato for the first time after their contact with the Aztecs, they brought the plant to Europe, in a widespread transfer of plants known as the Columbian exchange. From there, the tomato was introduced to other parts of the European-colonized world during the 16th century.
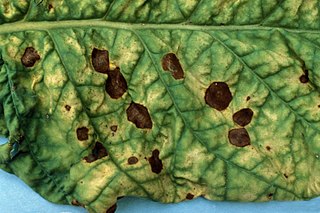
Alternaria alternata is a fungus which has been recorded causing leaf spot and other diseases on over 380 host species of plant. It is an opportunistic pathogen on numerous hosts causing leaf spots, rots and blights on many plant parts.
Phytophthora nicotianae or black shank is an oomycete belonging to the order Peronosprales and family Peronosporaceae.

Stemphylium solani is a plant pathogen fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. It is the causal pathogen for grey leaf spot in tomatoes and leaf blight in alliums and cotton, though a wide range of additional species can serve as hosts. Symptoms include white spots on leaves and stems that progress to sunken red or purple lesions and finally leaf necrosis. S. solani reproduces and spreads through the formation of conidia on conidiophores. The teleomorph name of Stemphyllium is Pleospora though there are no naturally known occurrences of sexual reproduction. Resistant varieties of tomato and cotton are common, though the pathogen remains an important disease in Chinese garlic cultivation.

Roger N. Beachy is an American biologist and member of the National Academy of Sciences who studies plant virology. He was the founding president of the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in St. Louis, Missouri, and the first director of the National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
The Institute of Plant Breeding (IPB) is a research institute of the University of the Philippines Los Baños. It is the national biotechnology research center and repository for all crops other than rice, which is handled by the Philippine Rice Research Institute.

The economy of the state of Florida is the fourth-largest in the United States, with a $1.3 trillion gross state product (GSP) as of 2021. If Florida were a sovereign nation (2021), it would rank as the world's 16th-largest economy according to the International Monetary Fund, ahead of Indonesia and behind Mexico. Agriculture, tourism, industry, construction, international banking, biomedical and life sciences, healthcare research, simulation training, aerospace and defense, and commercial space travel contribute to the state's economy.
The Marglobe tomato was developed in 1917 by Frederick J. Pritchard of the United States Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Experiment Station by crossing the Marvel and Globe tomatoes. It was publicly released by the USDA in 1925, and was one of the first disease-resistant strains that also had a good resistance to Verticillium and Fusarium wilt. The Marglobe tomato is the parent of many tomato varieties, such as Rutgers.

Blue tomatoes, sometimes referred to as purple tomato, are tomatoes that have been bred to produce high levels of anthocyanins, a class of pigments responsible for the blue and purple colours of many fruits, including blueberries, blackberries and chokeberries. Anthocyanins may provide protection for the plant against insects, diseases, and ultraviolet radiation. Some of these tomatoes have been commercialized under the names "Indigo Rose" and "SunBlack".

The Celebrity tomato cultivar is a hybrid (biology) that produces long fruit-bearing stems holding 20 or more very plump, robust tomatoes. Fruits weigh approximately 8 oz., and are 4 inches across. Plants need caging or staking, and produce fruit throughout the growing season. The celebrity tomato is a cultivar of the species Solanum lycopersicum. It is a crossbreed of the common tomato that is widely used for various culinary purposes. This tomato is of great size and is known to be resistant to most tomato diseases such as Fusarium wilt, Verticillium wilt, Tobacco mosaic virus and Root-knot nematode due to its hybrid nature. Celebrity tomatoes are highly adaptive to harsh environments and can grow in a wide range of places including dry, humid and wet regions. They are resistant to cracking and splitting which usually occurs when there is an excess of water and sugar movement in the fruits. Therefore, causing the tomato skin to grow at a slower rate compared to the expansion of the fruit. They can survive in harsh uneven rainfall. However, they are highly susceptible to colder environments and are at a higher risk of dying in regions with short growing seasons. The plants can grow up to 5 feet in height with bright red medium-sized fruits. The plants are generally very thick and grow in clusters. The tomato fruits are mostly used in the making of various salsas, salads, juices and canned food.

The Raf tomato is a tomato obtained from artificial selection practiced on traditional tomatoes are planted outdoors since 1961. It is originally from Spain. The Raf tomato Marmande is a variety which stands out for its flavor and texture, as well as its resistance to water with high salt content.

The Taiwan Banana Research Institute specializes in the breeding of bananas and research about their cultivation and diseases. Bananas are Taiwan's most important export fruit.
References
- ↑ "Blight-Resistant Tomato Varieties Worth Growing". GrowVeg. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "Best Disease Resistant Tomatoes - ChilePlants.com". www.chileplants.com. Retrieved 15 August 2020.