The Taunus Railway in the High Taunus is a railway route between Frankfurt (Main) Hauptbahnhof and Brandoberndorf via Bad Homburg, Usingen and Grävenwiesbach. It was operated from 1993 to 1995 by the Frankfurter Verkehrsverbund as the T-Bahn and subsequently by the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund as line 15. It is listed in table 637 of the Deutsche Bahn timetable. The Friedrichsdorf–Brandoberndorf line, which has the infrastructure number of 9374, forms part of the old Friedrichsdorf–Wetzlar line, which was known as the Taunusbahn. The line is owned by the Verkehrsverband Hochtaunus. The infrastructure is managed by HLB Basis AG on behalf of the VHT.

The East Rhine Railway is a major, double-track, electrified railway line, running along the right bank of the Rhine from Cologne to Wiesbaden. The 179-kilometer (111.2 mi)-long line forms two Deutsche Bahn routes. Route 465 extends from Cologne to Koblenz, via Troisdorf, Bonn-Beuel, Unkel, and Neuwied. From Koblenz, Route 466 extends to Wiesbaden, via Rüdesheim am Rhein. Together with the Taunus railway, the line is used by Stadt-Express line SE-10 of the Rhine-Main Transport Association, which runs from Frankfurt to Koblenz and Neuwied.
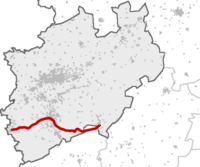
The Rhein-Sieg-Express is a Regional-Express service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate running from Aachen via Düren, Cologne, Troisdorf, Siegburg and Betzdorf to Siegen. It is operated by DB Regio NRW.
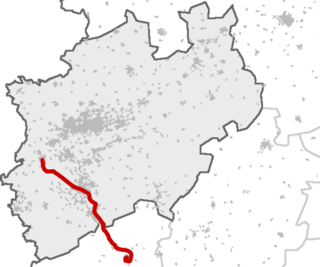
The Rhein-Erft-Express is a Regional-Express service in the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate. It is numbered as line RE 8 and connects the cities of Mönchengladbach, Cologne, Bonn and Koblenz with each other and their surroundings, running hourly. From Monday to Friday it is complemented by a Regionalbahn stopping service, the Rhein-Erft-Bahn, running between Rommerskirchen and Koblenz Hauptbahnhof. On weekends it stops at some additional stations between Cologne Hbf and Koblenz Hbf.

Horrem station is a station in the Kerpen district of Horrem in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is a railway junction of the Cologne–Aachen high-speed railway and the Erft Railway. The Trianglular station of Horrem is served by regional services and by S-Bahn trains of the Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn. Long-distance trains run through on the high-speed line without stopping. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station.

Au (Sieg) station is a railway junction in the town of Au in the municipality of Windeck, which is in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It lies on the Sieg Railway to Siegen, where the Engers–Au railway branches off to Altenkirchen, where it connects with the Upper Westerwald Railway (Oberwesterwaldbahn). Despite the town’s small population, the junction station is important for commuters from the districts of Altenkirchen, Neuwied and Westerwaldkreis for its connections towards Siegen, Cologne, Bonn, Düsseldorf and Aachen.
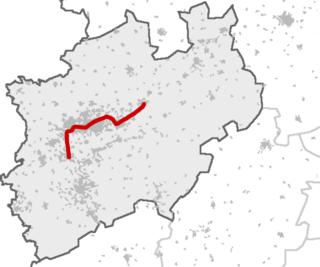
The Rhein-Emscher-Express is a Regional-Express service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW), running from Düsseldorf via Duisburg, Gelsenkirchen and Dortmund to Hamm. It connects with the rest of the regional rail network of NRW in Düsseldorf, Duisburg, Oberhausen, Wanne-Eickel, Dortmund and Hamm. In addition, it connects in Düsseldorf, Duisburg, Oberhausen, Dortmund and Hamm with long-distance services.
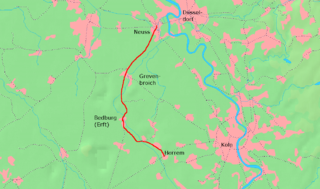
Bedburg–Horrem railway is a line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The non-electrified main line was originally built as a line of the Bergheim District Railway and operated as a metre gauge railway. Later, the line was converted to standard gauge.
The Nibelung Railway is a 23.9 km long electrified line between Worms in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate and Bensheim in Hesse. Its name refers to the fact that the line connects several places that play an important role in the Nibelung legend.

Groß-Umstadt Wiebelsbach station is a station on the Odenwald Railway in the town of Groß-Umstadt in the German state of Hesse. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station. The Odenwald Railway running from Eberbach branches at the station towards Darmstadt and Hanau. The station is located in the area administered by the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund.

Hessische Landesbahn is a regional transport company owned by the German state of Hesse, based in Frankfurt am Main. It provides bus and rail passenger transport services and, to a lesser extent, rail freight services in Hesse and across the state’s borders through its subsidiaries and affiliates.

Eltville station is station of Eltville in the Rheingau in the German state of Hesse on the East Rhine Railway from Wiesbaden to Koblenz. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station.

The Düren–Neuss railway is a line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The non-electrified main line originally ran from Düren to Neuss, but the Düren–Bedburg section has been closed and dismantled.

Grevenbroich station is a junction station in the city of Grevenbroich in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is located at the junction of the Cologne–Mönchengladbach railway and the Düren–Neuss railway. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 4 station.

The Voreifel Railway is a partly double track, non-electrified main line in the Voreifel from Bonn to Euskirchen in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia.
The Hellweg net consists of the four Regionalbahn lines in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia: RB 50, RB 59, RB 69 and RB 89. It has a length of about 370 km. The RB 50 is referred to as Der Lüner, the RB 59 as Die Hellweg-Bahn and the RB 69 and RB 89 together as Die Ems-Börde-Bahn. On 14 December 2008 operations were taken over by eurobahn. Previously these four Regionalbahn services were operated by DB Regio NRW.
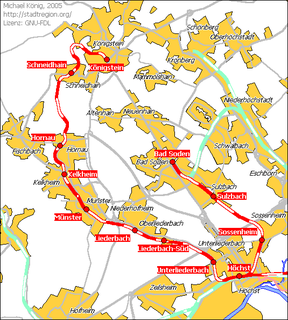
The Königstein Railway is a 1902 opened, single-track and non-electrified secondary railway line that connects the town of Königstein im Taunus with the city of Frankfurt am Main on the southern edge of the Taunus in the German state of Hesse.

The Pfungstadt Railway (Pfungstadtbahn) is a single-track branch line that branches off the Main-Neckar Railway in Darmstadt-Eberstadt and runs to a station on the eastern edge of the inner town of Pfungstadt, in Hesse, Germany.

Bedburg (Erft) station is a station in the town of Bedburg, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia.


























